Preening is a bird's behavior of grooming and maintaining its feathers by using its beak to clean, arrange, and apply oil from the uropygial gland for waterproofing and flexibility. Molting is the natural process of shedding old feathers and growing new ones, ensuring optimal feather condition for flight, insulation, and camouflage. Understanding the differences between preening and molting highlights essential stages of feather care crucial for a bird's health and survival.
Table of Comparison
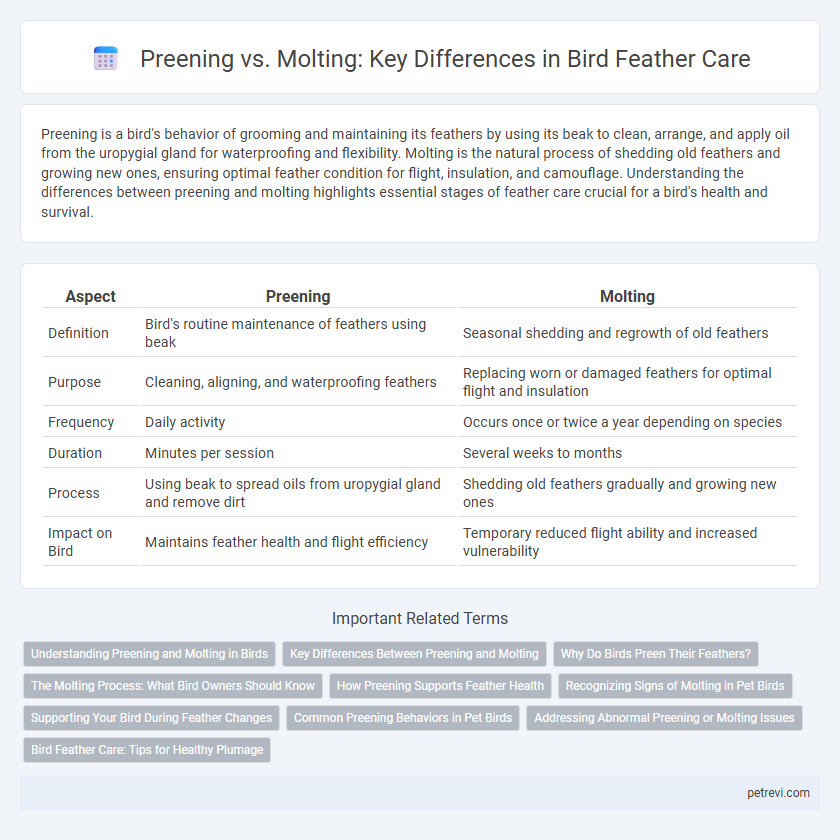
| Aspect | Preening | Molting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bird's routine maintenance of feathers using beak | Seasonal shedding and regrowth of old feathers |
| Purpose | Cleaning, aligning, and waterproofing feathers | Replacing worn or damaged feathers for optimal flight and insulation |
| Frequency | Daily activity | Occurs once or twice a year depending on species |
| Duration | Minutes per session | Several weeks to months |
| Process | Using beak to spread oils from uropygial gland and remove dirt | Shedding old feathers gradually and growing new ones |
| Impact on Bird | Maintains feather health and flight efficiency | Temporary reduced flight ability and increased vulnerability |
Understanding Preening and Molting in Birds
Preening is an essential behavior where birds use their beaks to clean, align, and oil their feathers, ensuring waterproofing and insulation. Molting is the natural process of shedding old feathers to make way for new growth, which can temporarily affect a bird's flight and insulation. Understanding these distinct yet complementary processes helps in appreciating how birds maintain feather health and overall survival.
Key Differences Between Preening and Molting
Preening involves birds using their beaks to clean, arrange, and oil feathers, maintaining feather condition and waterproofing. Molting is a natural periodic process where birds shed old feathers and grow new ones, essential for feather renewal and overall health. Preening is a daily maintenance behavior, while molting occurs seasonally and can temporarily affect a bird's flight and insulation.
Why Do Birds Preen Their Feathers?
Birds preen their feathers to maintain optimal feather condition by realigning barbs and removing dirt, debris, and parasites. Preening also distributes oils from the uropygial gland, which waterproofs and adds flexibility to feathers, essential for insulation and flight efficiency. This self-care behavior ensures that feathers remain clean, strong, and functional, directly impacting a bird's health and survival.
The Molting Process: What Bird Owners Should Know
Molting is a natural process where birds shed old feathers to make way for new growth, essential for maintaining optimal flight and insulation. During molting, birds may appear lethargic or less active as energy is diverted to feather regeneration, and feather loss can affect the bird's appearance and behavioral patterns. Bird owners should provide a nutrient-rich diet, ensure minimal stress, and allow a calm environment to support healthy molting and overall feather care.
How Preening Supports Feather Health
Preening is essential for bird feather health as it realigns barbs and barbules, ensuring optimal aerodynamic function and insulation. This behavior also distributes protective oils from the uropygial gland, enhancing waterproofing and reducing feather wear. Regular preening prevents parasites and maintains feather flexibility, directly supporting flight efficiency and overall avian well-being.
Recognizing Signs of Molting in Pet Birds
Molting in pet birds is characterized by the gradual shedding and replacement of feathers, often accompanied by increased feather dust and occasional changes in behavior such as reduced activity or appetite. Recognizable signs include visible pin feathers, irregular feather patches, and temporary bald spots, differing from preening, which is a constant grooming habit to maintain feather health. Understanding these molting indicators helps bird owners provide appropriate care and nutrition to support feather regeneration and overall well-being.
Supporting Your Bird During Feather Changes
Preening helps birds maintain feather health by aligning barbs and distributing natural oils, essential for waterproofing and insulation. Molting is a natural process where birds shed old feathers to grow new ones, often requiring extra nutrition and a stress-free environment for optimal recovery. Providing high-quality protein, vitamins, and a calm habitat supports birds during molting, enhancing their feather regeneration and overall well-being.
Common Preening Behaviors in Pet Birds
Common preening behaviors in pet birds include using their beaks to carefully align feathers, remove dirt, and distribute natural oils from the uropygial gland to maintain feather flexibility and water resistance. Birds often engage in mutual preening, where pairs groom each other's feathers to strengthen social bonds and reach difficult spots. Preening differs from molting, which is the process of shedding old feathers and growing new ones, essential for feather renewal but does not involve the daily maintenance behaviors seen in preening.
Addressing Abnormal Preening or Molting Issues
Abnormal preening or molting in birds often signals underlying health issues such as parasites, nutritional deficiencies, or stress, requiring prompt veterinary evaluation. Regularly monitoring feather condition helps distinguish between natural molting cycles and excessive feather plucking or damage caused by abnormal preening behavior. Implementing proper diet, environmental enrichment, and parasite control can mitigate abnormal feather care practices and promote healthy plumage renewal.
Bird Feather Care: Tips for Healthy Plumage
Preening involves birds using their beaks to clean, align, and apply oil to feathers, crucial for waterproofing and maintaining optimal insulation. Molting is the natural process of shedding old feathers and growing new ones, essential for replacing damaged plumage and supporting flight efficiency. Regular preening combined with a healthy molting cycle ensures birds maintain strong, vibrant feathers vital for protection, temperature regulation, and aerodynamic performance.
Preening vs Molting for Bird Feather Care Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com