Single-species aviaries create an environment tailored to the specific needs and behaviors of one bird species, promoting natural social interactions and reducing stress caused by competition or aggression. Mixed-species aviaries encourage diverse socialization opportunities and stimulate natural behaviors through interspecies interactions, but require careful management to prevent territorial disputes and ensure compatible species. Choosing between single-species and mixed-species aviaries depends on the bird species' social nature, temperament, and the keeper's ability to monitor and manage group dynamics effectively.
Table of Comparison
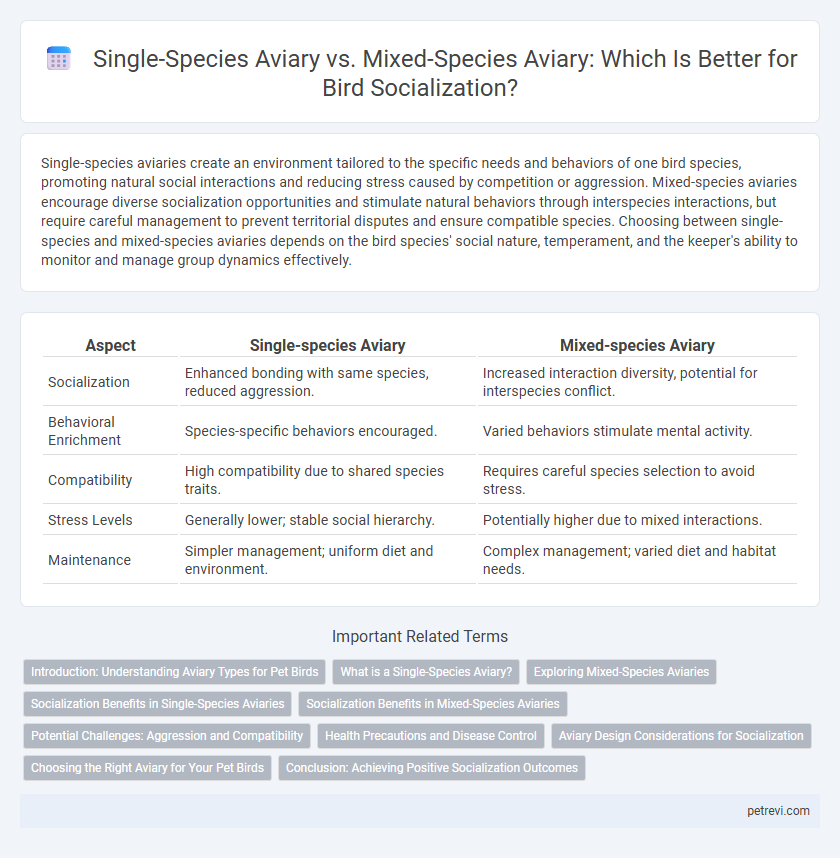
| Aspect | Single-species Aviary | Mixed-species Aviary |
|---|---|---|
| Socialization | Enhanced bonding with same species, reduced aggression. | Increased interaction diversity, potential for interspecies conflict. |
| Behavioral Enrichment | Species-specific behaviors encouraged. | Varied behaviors stimulate mental activity. |
| Compatibility | High compatibility due to shared species traits. | Requires careful species selection to avoid stress. |
| Stress Levels | Generally lower; stable social hierarchy. | Potentially higher due to mixed interactions. |
| Maintenance | Simpler management; uniform diet and environment. | Complex management; varied diet and habitat needs. |
Introduction: Understanding Aviary Types for Pet Birds
Single-species aviaries provide an environment tailored to the specific social, dietary, and habitat needs of one bird species, reducing stress and aggression. Mixed-species aviaries offer diverse social interactions and stimulation, promoting natural behaviors through interspecies communication but require careful monitoring to prevent conflicts. Choosing between aviary types depends on the compatibility of species, space availability, and the owner's ability to manage complex social dynamics.
What is a Single-Species Aviary?
A single-species aviary is a controlled habitat designed to house only one bird species, optimizing conditions specific to its behavior, diet, and social structure. This type of aviary minimizes interspecies competition and stress, promoting natural social interactions and breeding behaviors among conspecifics. By replicating their native environment closely, single-species aviaries support effective socialization and improved health outcomes for the housed species.
Exploring Mixed-Species Aviaries
Mixed-species aviaries promote diverse social interactions by housing compatible bird species that exhibit complementary behaviors and environmental needs, enhancing mental stimulation and reducing stress-related conflicts. Studies show these environments mimic natural habitats, fostering natural foraging, vocalization, and social hierarchy dynamics among species such as finches, canaries, and budgerigars. Properly designed mixed-species aviaries balance species-specific space and resource requirements, optimizing bird welfare and encouraging dynamic interspecies engagement.
Socialization Benefits in Single-Species Aviaries
Single-species aviaries enhance bird socialization by providing an environment where individuals can engage in natural behaviors and form strong social bonds with conspecifics, reducing stress and aggression often seen in mixed-species settings. These aviaries promote cohesive flock dynamics, facilitating communication, mating rituals, and cooperative activities specific to the species. Research indicates that birds in single-species aviaries exhibit improved psychological well-being and increased reproductive success compared to those housed in mixed-species enclosures.
Socialization Benefits in Mixed-Species Aviaries
Mixed-species aviaries enhance bird socialization by promoting natural interactions and diverse communication patterns among different bird species, leading to improved mental stimulation and behavioral enrichment. These environments encourage cooperative behaviors and reduce stress through increased opportunities for social learning and environmental exploration. Birds in mixed-species aviaries often develop stronger social bonds and exhibit more natural flock dynamics compared to single-species aviaries.
Potential Challenges: Aggression and Compatibility
Single-species aviaries reduce risks of aggression by housing birds with similar behaviors and social structures, enhancing compatibility and minimizing territorial disputes. Mixed-species aviaries face challenges in managing interspecies aggression due to different communication styles, mating behaviors, and dietary needs that can create stress and conflict. Proper assessment of species compatibility, environmental enrichment, and monitoring is crucial to prevent injuries and ensure harmonious socialization.
Health Precautions and Disease Control
Single-species aviaries minimize cross-species disease transmission by limiting pathogen exposure to one bird species, enabling targeted health monitoring and specific immunization protocols. Mixed-species aviaries increase the risk of spreading parasites, viruses, and bacterial infections due to varied immune responses and differing hygiene needs among species. Strict quarantine procedures, regular health screenings, and species-specific sanitation practices are essential in both setups to maintain optimal avian health and prevent outbreaks.
Aviary Design Considerations for Socialization
Single-species aviaries promote natural social behaviors by housing birds with similar communication patterns, reducing stress and aggression. Mixed-species aviaries require careful design incorporating varied perching, feeding zones, and visual barriers to accommodate different species' social needs while minimizing territorial conflicts. Effective aviary design integrates ample space, species-specific enrichment, and nesting sites to enhance positive social interactions and overall well-being.
Choosing the Right Aviary for Your Pet Birds
Choosing between a single-species and mixed-species aviary depends on the social behavior and compatibility of the birds involved. Single-species aviaries cater to specific social structures, minimizing aggression and stress, while mixed-species aviaries promote diverse social interaction but require careful selection to prevent territorial conflicts. Prioritizing the natural temperament and environmental needs of your pet birds ensures optimal socialization and well-being within their aviary space.
Conclusion: Achieving Positive Socialization Outcomes
Single-species aviaries foster focused social interactions by minimizing interspecies aggression and stress, promoting natural behaviors within a uniform social structure. Mixed-species aviaries offer enriched environmental stimuli and diverse social dynamics but require careful species compatibility assessment to prevent conflict. Optimal bird socialization outcomes depend on tailored habitat design, continuous monitoring, and species-specific social needs to ensure wellbeing and harmonious group living.
Single-species aviary vs Mixed-species aviary for Bird socialization Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com