Free-range chickens have access to the outdoors but often limited space, allowing for natural behaviors with some confinement. Pasture-raised chickens roam freely on open pasture, feeding primarily on grass, insects, and seeds, which enhances their diet and welfare. This management style typically results in healthier birds and higher-quality meat due to increased exercise and a natural diet.
Table of Comparison
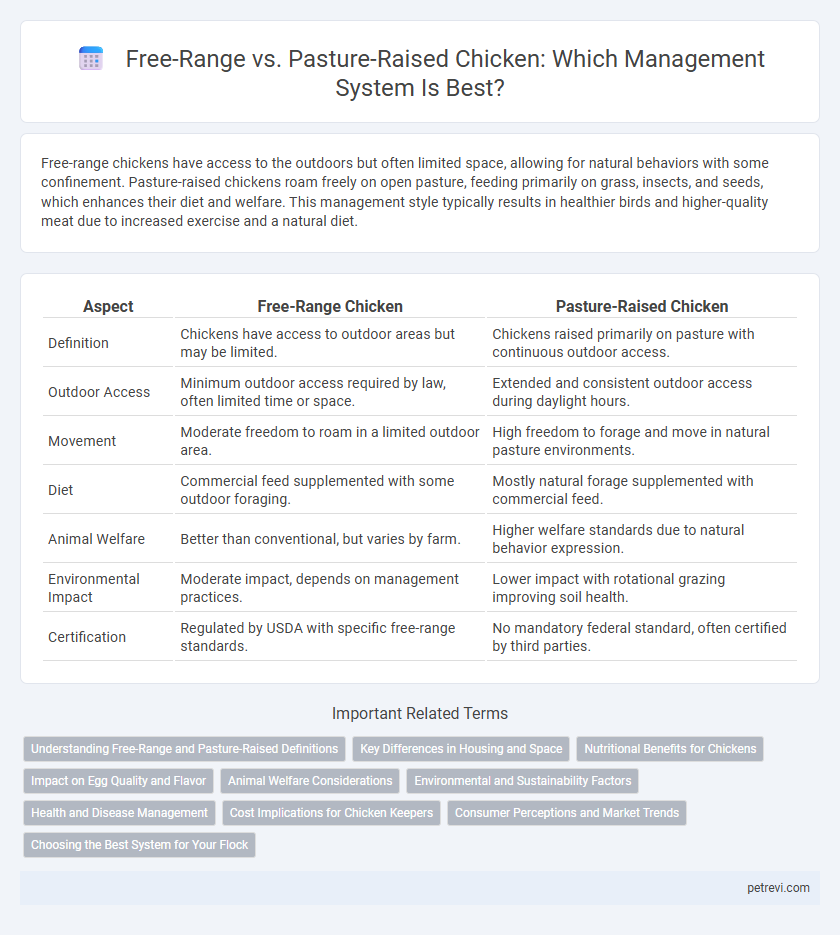
| Aspect | Free-Range Chicken | Pasture-Raised Chicken |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chickens have access to outdoor areas but may be limited. | Chickens raised primarily on pasture with continuous outdoor access. |
| Outdoor Access | Minimum outdoor access required by law, often limited time or space. | Extended and consistent outdoor access during daylight hours. |
| Movement | Moderate freedom to roam in a limited outdoor area. | High freedom to forage and move in natural pasture environments. |
| Diet | Commercial feed supplemented with some outdoor foraging. | Mostly natural forage supplemented with commercial feed. |
| Animal Welfare | Better than conventional, but varies by farm. | Higher welfare standards due to natural behavior expression. |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate impact, depends on management practices. | Lower impact with rotational grazing improving soil health. |
| Certification | Regulated by USDA with specific free-range standards. | No mandatory federal standard, often certified by third parties. |
Understanding Free-Range and Pasture-Raised Definitions
Free-range chickens are allowed outdoor access for a portion of the day but may still have limited space and time outside, whereas pasture-raised chickens spend most of their lives roaming freely on pasture, foraging naturally. The USDA defines free-range as chickens with some outdoor exposure, but pasture-raised standards often include continuous access to outdoor grassy areas, promoting better animal welfare. Understanding these definitions helps consumers make informed choices based on chicken farming practices and animal welfare considerations.
Key Differences in Housing and Space
Free-range chickens have access to the outdoors but may spend significant time confined to indoor housing, often with limited outdoor space. Pasture-raised chickens are provided with ample outdoor pasture area, allowing natural behaviors like foraging and dust bathing, typically resulting in better animal welfare. Housing for pasture-raised chickens is usually portable or mobile coops that follow the flock to fresh grazing areas, unlike fixed housing common in free-range systems.
Nutritional Benefits for Chickens
Free-range chickens have access to the outdoors, which allows them to forage for a varied diet rich in insects and plants, enhancing their intake of natural nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins A and E. Pasture-raised chickens, spending more time on nutrient-dense grasslands, typically have higher levels of beta-carotene and antioxidants in their meat and eggs compared to conventionally raised chickens. These nutritional benefits from diverse diets improve chicken health and can increase the quality and nutritional value of poultry products for human consumption.
Impact on Egg Quality and Flavor
Free-range chickens have access to the outdoors, promoting diverse foraging that enriches their diet and enhances egg flavor with higher omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins A and E. Pasture-raised chickens, typically on nutrient-rich grasses and insects, produce eggs with deeper yolk color and superior nutritional profiles, including increased beta-carotene and antioxidants. Studies show pasture-raised eggs often have a more robust flavor and better shelf life compared to free-range eggs due to the hens' varied natural diet.
Animal Welfare Considerations
Free-range chickens have access to the outdoors but may be confined to a limited outdoor area, while pasture-raised chickens roam freely over larger land areas, allowing natural behaviors such as foraging and dust bathing. Pasture-raised systems generally promote higher animal welfare standards by providing better space, fresh air, and natural habitats that reduce stress and improve overall health. The welfare benefits of pasture-raised chickens include stronger immune systems and lower incidence of diseases compared to most free-range management practices.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Free-range chickens have access to outdoor areas but are typically confined to smaller spaces, leading to moderate soil impact and limited biodiversity benefits. Pasture-raised chickens roam larger, rotationally managed pastures, promoting improved soil health, enhanced nutrient cycling, and greater carbon sequestration. Sustainable pasture-raised systems reduce reliance on synthetic inputs and support long-term environmental resilience compared to conventional free-range practices.
Health and Disease Management
Free-range chickens have access to outdoor areas, promoting natural behaviors that enhance immune function and reduce stress-related illness, while pasture-raised chickens benefit from diverse foraging that improves gut health and nutrient absorption. Disease management in free-range systems requires vigilant monitoring due to increased exposure to wild birds and environmental pathogens, whereas pasture-raised systems often implement rotational grazing to minimize parasite loads and soil-borne diseases. Both methods support healthier flocks compared to conventional confinement, but integrated biosecurity measures are crucial for effective health management in these extensive systems.
Cost Implications for Chicken Keepers
Free-range chicken management typically involves moderate infrastructure costs and allows birds limited outdoor access, resulting in lower feed expenses but variable flock health outcomes. Pasture-raised systems demand higher initial investment in land, fencing, and rotational grazing practices, increasing operational costs but enhancing bird welfare and potentially commanding premium market prices. Chicken keepers must balance these cost implications against production goals, consumer demand, and long-term sustainability when selecting between free-range and pasture-raised methods.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Free-range chicken is often perceived by consumers as healthier and more humane compared to conventional methods, driving increasing demand in retail markets. Pasture-raised chickens, known for their access to natural forage and outdoor environments, are associated with higher welfare standards and superior meat quality, appealing to premium market segments. Market trends indicate a growing preference for pasture-raised products, reflecting consumer willingness to pay more for ethically managed and sustainably produced chicken.
Choosing the Best System for Your Flock
Free-range chicken management allows birds access to outdoor spaces, promoting natural behaviors while often facing variable space and weather conditions. Pasture-raised systems provide more extensive grazing areas and forage opportunities, enhancing animal welfare and producing meat and eggs with higher omega-3 fatty acids. Selecting the best system depends on flock size, land availability, climate, and desired product quality, balancing sustainability and animal health.
Free-Range vs Pasture-Raised for Chicken Management Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com