Organic chicken farming prioritizes animal welfare and avoids synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, and genetically modified feed, resulting in meat often perceived as healthier and environmentally friendly. Conventional chicken farming typically emphasizes higher production efficiency using antibiotics and conventional feed, which may raise concerns about antibiotic resistance and chemical residues. Choosing organic chicken supports sustainable farming practices but generally comes at a higher price compared to conventional options.
Table of Comparison
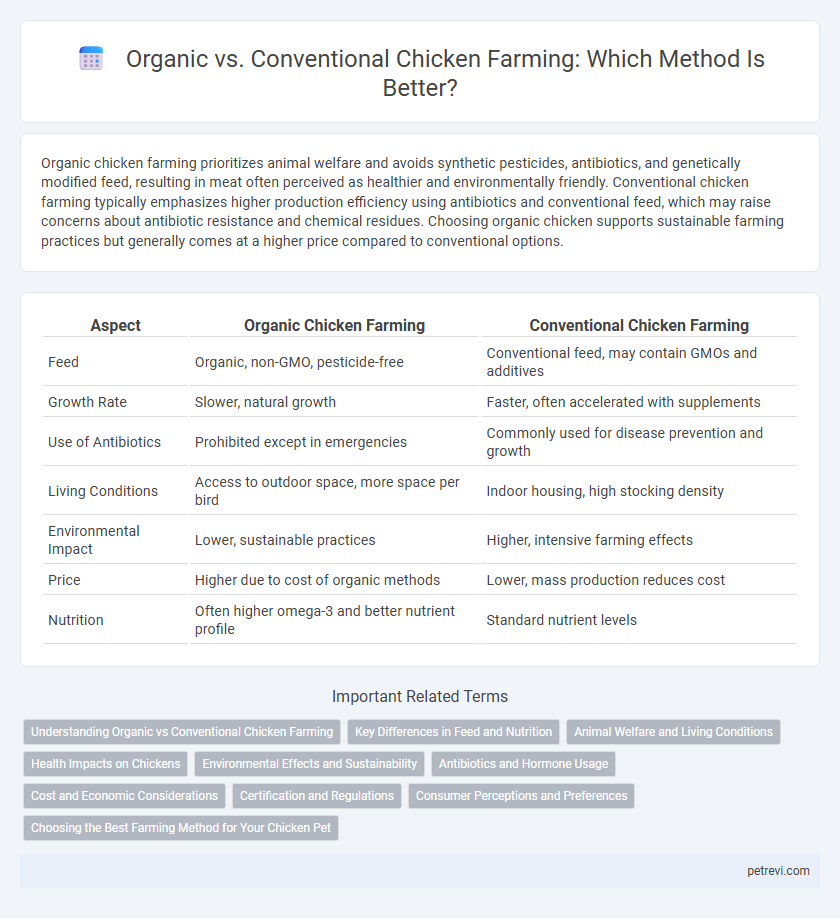
| Aspect | Organic Chicken Farming | Conventional Chicken Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Feed | Organic, non-GMO, pesticide-free | Conventional feed, may contain GMOs and additives |
| Growth Rate | Slower, natural growth | Faster, often accelerated with supplements |
| Use of Antibiotics | Prohibited except in emergencies | Commonly used for disease prevention and growth |
| Living Conditions | Access to outdoor space, more space per bird | Indoor housing, high stocking density |
| Environmental Impact | Lower, sustainable practices | Higher, intensive farming effects |
| Price | Higher due to cost of organic methods | Lower, mass production reduces cost |
| Nutrition | Often higher omega-3 and better nutrient profile | Standard nutrient levels |
Understanding Organic vs Conventional Chicken Farming
Organic chicken farming involves raising birds without synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, or genetically modified feed, promoting animal welfare and environmental sustainability. Conventional chicken farming typically uses controlled environments with antibiotics and chemical inputs to maximize production efficiency and reduce costs. Consumers increasingly prefer organic chicken due to perceived health benefits and eco-friendly practices associated with organic certification standards.
Key Differences in Feed and Nutrition
Organic chicken farming uses feed free from synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs), ensuring the diet consists of certified organic grains and natural supplements. Conventional chicken farming generally relies on feed containing antibiotics, growth promoters, and genetically engineered ingredients to enhance growth rates and reduce disease risks. Nutritionally, organic chicken meat often contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants due to the birds' access to natural forage and absence of synthetic additives in their feed.
Animal Welfare and Living Conditions
Organic chicken farming prioritizes animal welfare by providing chickens with outdoor access, ample space, and natural light, promoting natural behaviors and reducing stress. Conventional chicken farming often involves confined spaces and limited outdoor access, which can lead to higher stress levels and increased susceptibility to disease. Studies indicate that organic methods improve overall welfare metrics, including lower mortality rates and better feather condition compared to conventional systems.
Health Impacts on Chickens
Organic chicken farming promotes better health outcomes for birds by avoiding synthetic antibiotics and hormones, reducing the risk of drug-resistant bacteria and promoting natural immunity. Conventional chicken farming often relies on antibiotics to prevent disease outbreaks, which can lead to compromised gut health and increased susceptibility to infections in chickens. Studies show that organic practices result in lower incidences of respiratory and bacterial infections, contributing to overall improved well-being and reduced mortality rates among organically raised chickens.
Environmental Effects and Sustainability
Organic chicken farming reduces environmental impact by avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which lowers soil and water contamination compared to conventional methods. Conventional chicken farms often contribute to higher greenhouse gas emissions and waste pollution due to intensive feed and antibiotic use. Sustainable practices in organic farming promote biodiversity and improve ecosystem health, making it a more eco-friendly choice for poultry production.
Antibiotics and Hormone Usage
Organic chicken farming strictly prohibits the use of antibiotics and hormones, ensuring meat that is free from synthetic additives and promoting better animal welfare. Conventional chicken farming often employs antibiotics to prevent disease and promote growth, which can contribute to antibiotic resistance and residue concerns in meat products. Consumers seeking healthier and more sustainable options tend to favor organic chickens due to these significant differences in antibiotic and hormone usage.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Organic chicken farming involves higher costs due to expensive feed, certification fees, and slower growth rates compared to conventional methods that prioritize efficiency and lower expenses. Consumer demand for organic chicken drives premium pricing, which can offset higher production costs but limits market size relative to conventional chicken products. Economically, conventional farming yields greater volume and lower prices, benefiting large-scale producers, while organic farming appeals to niche markets emphasizing sustainability and animal welfare.
Certification and Regulations
Organic chicken farming requires strict adherence to certification standards set by organizations like the USDA, mandating no synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, or genetically modified feed, alongside access to outdoor spaces. Conventional chicken farming follows broader regulatory guidelines, often allowing the use of antibiotics, synthetic additives, and confined housing systems, which do not meet organic certification criteria. Certification processes for organic farms include regular inspections and documentation to ensure compliance with animal welfare and environmental sustainability standards.
Consumer Perceptions and Preferences
Consumers increasingly favor organic chicken due to perceptions of higher nutritional value, absence of antibiotics, and more humane farming practices. Studies indicate a willingness to pay premium prices for organic poultry linked to concerns about food safety and environmental sustainability. Conventional chicken remains popular for affordability and consistent availability despite growing organic demand.
Choosing the Best Farming Method for Your Chicken Pet
Choosing between organic and conventional chicken farming depends on factors like feed quality, antibiotic use, and living conditions that impact your pet's health and wellbeing. Organic chicken farming typically avoids synthetic pesticides and antibiotics, promoting a natural diet and free-range environment which can lead to healthier chickens and reduced exposure to harmful chemicals. Conventional farming may offer lower costs and faster growth but often involves antibiotics and confined spaces, which can affect the overall welfare and natural behavior of your chicken pet.
Organic vs Conventional for Chicken Farming Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com