Dewormer rotation involves regularly switching between different classes of deworming medications to prevent parasite resistance in donkeys, while targeted deworming treats only those animals showing signs or testing positive for parasites. Targeted deworming reduces unnecessary medication use, preserving drug effectiveness and minimizing environmental impact. Implementing a strategic combination of both methods enhances long-term parasite control and improves overall donkey health.
Table of Comparison
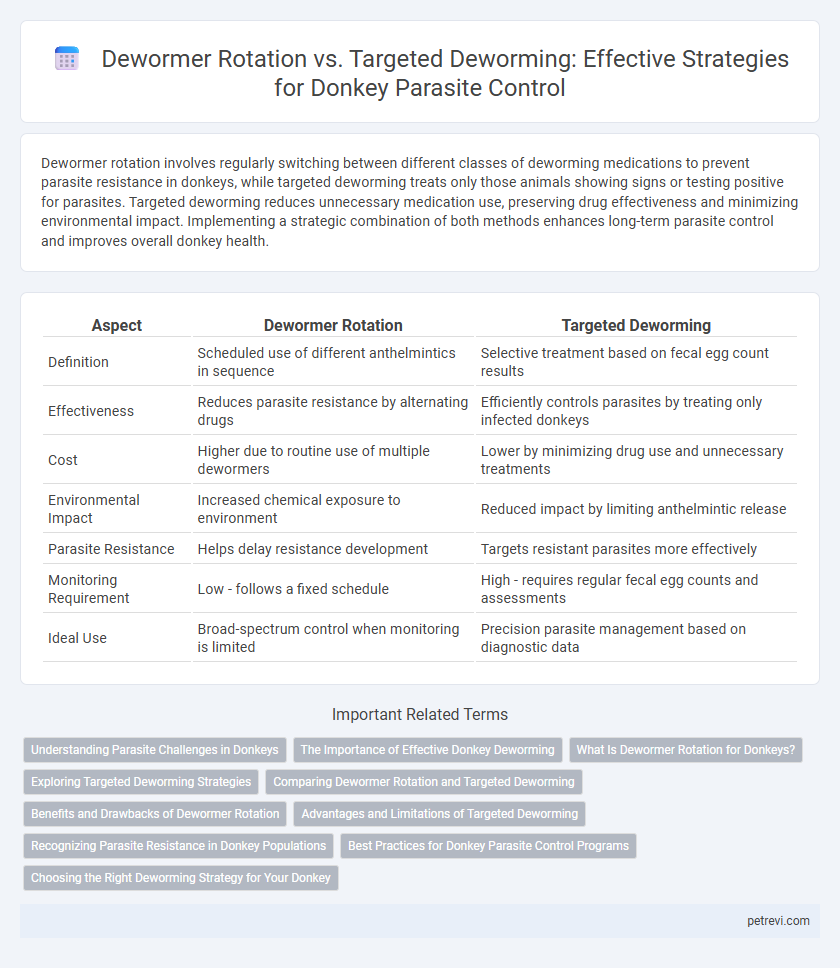
| Aspect | Dewormer Rotation | Targeted Deworming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled use of different anthelmintics in sequence | Selective treatment based on fecal egg count results |
| Effectiveness | Reduces parasite resistance by alternating drugs | Efficiently controls parasites by treating only infected donkeys |
| Cost | Higher due to routine use of multiple dewormers | Lower by minimizing drug use and unnecessary treatments |
| Environmental Impact | Increased chemical exposure to environment | Reduced impact by limiting anthelmintic release |
| Parasite Resistance | Helps delay resistance development | Targets resistant parasites more effectively |
| Monitoring Requirement | Low - follows a fixed schedule | High - requires regular fecal egg counts and assessments |
| Ideal Use | Broad-spectrum control when monitoring is limited | Precision parasite management based on diagnostic data |
Understanding Parasite Challenges in Donkeys
Donkey parasite control requires careful consideration of parasite resistance and life cycles to optimize treatment efficacy. Dewormer rotation involves systematically changing anthelmintic classes to reduce resistance development, while targeted deworming uses fecal egg counts to treat only donkeys with significant parasite burdens. Understanding parasite challenges such as cyathostomins and strongyles informs strategic decisions, minimizing drug resistance and promoting long-term health in donkeys.
The Importance of Effective Donkey Deworming
Effective donkey deworming is crucial to prevent parasite resistance and ensure long-term health by maintaining optimal gastrointestinal function and nutrient absorption. Dewormer rotation involves alternating between different classes of anthelmintics to reduce resistance development, while targeted deworming relies on fecal egg count monitoring to treat only those donkeys with high parasite loads. Implementing strategic parasite control through either method helps safeguard donkeys from debilitating worm infestations and supports sustainable parasite management.
What Is Dewormer Rotation for Donkeys?
Dewormer rotation for donkeys involves systematically changing between different classes of anthelmintic drugs to prevent parasite resistance and maintain treatment efficacy. This strategy targets a broad spectrum of internal parasites, including strongyles and roundworms, by alternating active ingredients such as ivermectin, fenbendazole, and pyrantel. Proper rotation schedules, based on fecal egg count monitoring, help optimize parasite control and promote long-term health in donkeys.
Exploring Targeted Deworming Strategies
Targeted deworming strategies for donkeys involve regular fecal egg count monitoring to identify parasite load before administering treatments, reducing unnecessary dewormer use and slowing resistance development. Dewormer rotation alternates chemical classes to combat resistance but may lead to overtreatment and increased costs. Implementing targeted deworming optimizes parasite control, enhances animal health, and supports sustainable parasite management in donkey populations.
Comparing Dewormer Rotation and Targeted Deworming
Dewormer rotation involves regularly switching between different classes of anthelmintics to prevent parasite resistance in donkeys, while targeted deworming focuses on treating only those individuals showing high parasite loads based on fecal egg counts. Studies indicate that targeted deworming reduces drug use and slows resistance development compared to routine rotation strategies. Effective parasite control in donkeys depends on monitoring infection levels and selecting treatments accordingly to maintain anthelmintic efficacy.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Dewormer Rotation
Dewormer rotation in donkey parasite control helps prevent anthelmintic resistance by alternating drugs with different modes of action, ensuring broader efficacy against multiple parasite species. However, frequent rotation may increase costs and complicate treatment schedules, potentially reducing adherence and effectiveness. It contrasts with targeted deworming, which minimizes drug use and resistance risk by treating only donkeys with confirmed parasite burdens through fecal egg counts.
Advantages and Limitations of Targeted Deworming
Targeted deworming in donkeys involves administering anthelmintics based on fecal egg count results, reducing the risk of anthelmintic resistance and lowering drug costs. This approach allows precise identification of heavily infected individuals, optimizing parasite control while minimizing environmental impact. Limitations include the need for regular fecal monitoring, potentially delaying treatment during acute infestations and requiring veterinary expertise for accurate interpretation of results.
Recognizing Parasite Resistance in Donkey Populations
Dewormer rotation involves systematically alternating anthelmintic classes to reduce parasite resistance, but frequent misuse can accelerate resistance development in donkey populations. Targeted deworming relies on fecal egg count monitoring to identify donkeys with high parasite burdens, minimizing unnecessary anthelmintic use and slowing resistance buildup. Recognizing parasite resistance requires regular fecal egg count reduction tests (FECRT) and monitoring treatment efficacy to adjust control strategies effectively.
Best Practices for Donkey Parasite Control Programs
Dewormer rotation in donkey parasite control involves alternating anthelmintic classes to reduce parasite resistance, enhancing long-term efficacy of treatments. Targeted deworming focuses on diagnosing specific parasite loads through fecal egg counts, enabling precise treatment and minimizing unnecessary drug use. Combining regular fecal monitoring with strategic rotation of anthelmintics constitutes the best practice framework for sustainable donkey parasite control programs.
Choosing the Right Deworming Strategy for Your Donkey
Choosing the right deworming strategy for your donkey involves evaluating parasite resistance patterns and overall herd health. Dewormer rotation regularly switches between drug classes to reduce resistance buildup, while targeted deworming relies on fecal egg count tests to treat only donkeys with significant parasite loads. Implementing targeted deworming optimized by fecal diagnostics enhances parasite control efficiency and minimizes unnecessary drug use, preserving anthelmintic efficacy in donkey populations.
Dewormer rotation vs Targeted deworming for Donkey Parasite Control Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com