Effective coccidiosis prevention in pet ducks involves maintaining clean living environments, proper nutrition, and routine health monitoring to minimize the risk of infection. Treatment typically requires timely administration of anticoccidial medications prescribed by a veterinarian to control symptoms and reduce parasite load. Prioritizing prevention over treatment helps sustain overall duck health and avoids the complications associated with advanced coccidiosis infections.
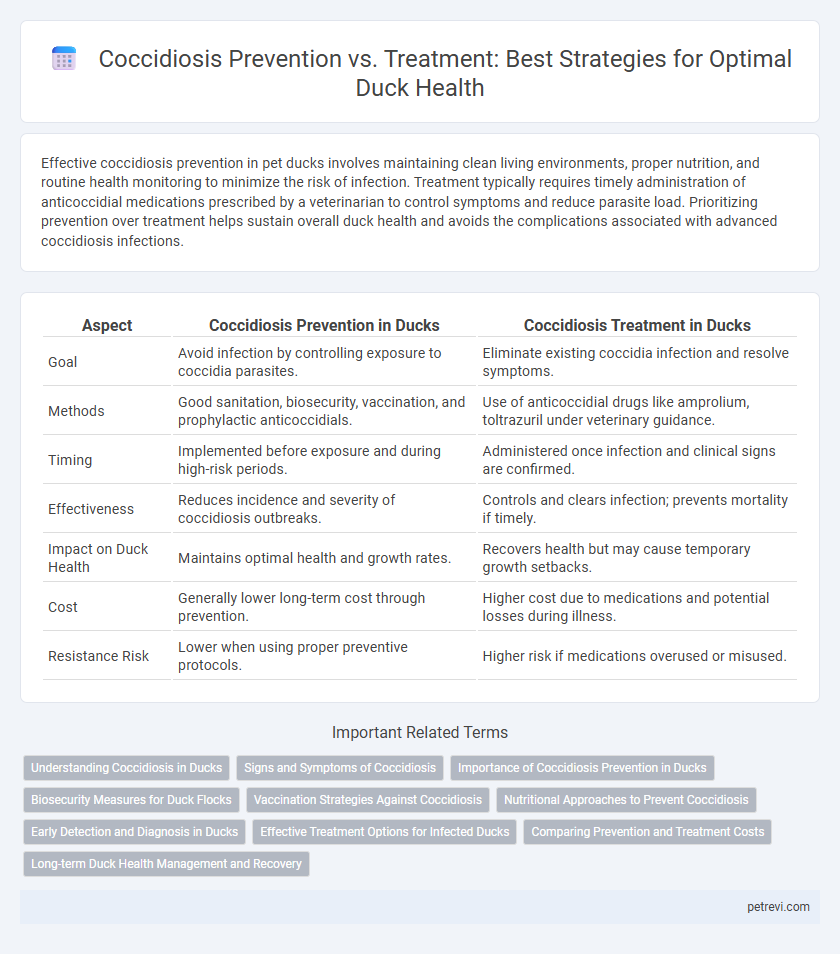
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Coccidiosis Prevention in Ducks | Coccidiosis Treatment in Ducks |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Avoid infection by controlling exposure to coccidia parasites. | Eliminate existing coccidia infection and resolve symptoms. |
| Methods | Good sanitation, biosecurity, vaccination, and prophylactic anticoccidials. | Use of anticoccidial drugs like amprolium, toltrazuril under veterinary guidance. |
| Timing | Implemented before exposure and during high-risk periods. | Administered once infection and clinical signs are confirmed. |
| Effectiveness | Reduces incidence and severity of coccidiosis outbreaks. | Controls and clears infection; prevents mortality if timely. |
| Impact on Duck Health | Maintains optimal health and growth rates. | Recovers health but may cause temporary growth setbacks. |
| Cost | Generally lower long-term cost through prevention. | Higher cost due to medications and potential losses during illness. |
| Resistance Risk | Lower when using proper preventive protocols. | Higher risk if medications overused or misused. |
Understanding Coccidiosis in Ducks
Coccidiosis in ducks is caused by microscopic parasites from the genus Eimeria, leading to intestinal damage and severe health issues like diarrhea and weight loss. Effective prevention includes maintaining clean, dry living environments and administering coccidiostats in water or feed to inhibit parasite development. Treatment requires prompt use of anticoccidial medications such as amprolium, combined with supportive care to restore hydration and nutrient absorption in infected ducks.
Signs and Symptoms of Coccidiosis
Coccidiosis in ducks presents with signs such as diarrhea, lethargy, weight loss, and ruffled feathers, often accompanied by reduced appetite and dehydration. Early detection of these symptoms is critical for effective prevention through improved sanitation and prophylactic medication. Treatment involves targeted anticoccidial drugs, but recognizing symptoms early significantly improves health outcomes and reduces mortality rates in duck populations.
Importance of Coccidiosis Prevention in Ducks
Coccidiosis prevention in ducks is essential to maintaining flock health and preventing the spread of Eimeria parasites that cause intestinal damage and mortality. Implementing biosecurity measures, maintaining clean living environments, and using anticoccidial medications proactively reduce infection risks and improve growth rates. Preventative strategies lower treatment costs and minimize the development of drug-resistant coccidia strains, ensuring sustainable duck farming.
Biosecurity Measures for Duck Flocks
Maintaining strict biosecurity measures is essential for preventing coccidiosis in duck flocks by minimizing exposure to infectious oocysts in the environment. Implementing regular cleaning and disinfection of duck housing, managing litter moisture levels, and controlling access to contaminated water sources significantly reduce parasite transmission. Early detection combined with these biosecurity protocols supports healthier flocks and reduces reliance on chemical treatments.
Vaccination Strategies Against Coccidiosis
Vaccination strategies against coccidiosis in ducks focus on stimulating immune responses to Eimeria species, the primary causative agents of the disease. Live attenuated and recombinant vaccines have shown efficacy in reducing oocyst shedding and intestinal lesions, thereby improving overall duck health and productivity. Implementing regular vaccination schedules combined with biosecurity measures offers a proactive approach that decreases reliance on anticoccidial drugs and minimizes resistance development.
Nutritional Approaches to Prevent Coccidiosis
Optimizing duck nutrition with high-quality protein sources, essential vitamins like A and E, and minerals such as zinc enhances immune function, reducing susceptibility to coccidiosis. Inclusion of probiotics and prebiotics in feed supports gut health, creating an unfavorable environment for coccidia proliferation. Maintaining balanced diets rich in antioxidants and proper hydration fortifies intestinal integrity, serving as an effective preventive strategy against coccidiosis outbreaks in duck populations.
Early Detection and Diagnosis in Ducks
Early detection of coccidiosis in ducks through regular fecal examinations and observation of symptoms such as weight loss and diarrhea is critical for effective prevention. Accurate diagnosis using microscopic identification of coccidia oocysts enables timely intervention and reduces the severity of outbreaks. Implementing routine health monitoring and hygiene practices minimizes infection risk and supports long-term duck health management.
Effective Treatment Options for Infected Ducks
Effective treatment options for coccidiosis in ducks involve the use of anticoccidial drugs such as amprolium and toltrazuril, which target the Eimeria parasites responsible for the infection. Supportive care with electrolytes and vitamins enhances recovery while minimizing secondary infections. Early diagnosis combined with proper medication significantly reduces mortality rates and improves overall duck health during outbreaks.
Comparing Prevention and Treatment Costs
Prevention of coccidiosis in ducks through vaccination and maintaining clean, dry living conditions generally incurs lower costs compared to treatment expenses, which often involve prolonged medication and veterinary care. Preventive measures reduce the risk of outbreaks, minimizing the financial burden associated with reduced growth rates, increased mortality, and loss of productivity in duck populations. Investment in high-quality feed additives and biosecurity practices represents a cost-effective strategy that outweighs the higher costs and potential losses linked to treating coccidiosis infections.
Long-term Duck Health Management and Recovery
Effective coccidiosis prevention in ducks involves maintaining clean, dry living environments and implementing routine sanitation protocols to minimize oocyst exposure. Strategic use of coccidiostats in feed supports immune resistance development, reducing infection recurrence and promoting sustainable long-term health. Treatment protocols emphasize prompt administration of anticoccidial medications, followed by supportive care and nutritional supplementation to enhance recovery and prevent chronic health issues.
Coccidiosis Prevention vs Treatment for Duck Health Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com