Floating feed allows ducks to eat at the water's surface, promoting natural feeding behavior and reducing contamination from debris. In contrast, sinking feed reaches the bottom, encouraging ducks to dive and forage, which can enhance their physical activity and digestion. Choosing between floating and sinking feed depends on the ducks' environment and dietary needs for optimal health.
Table of Comparison
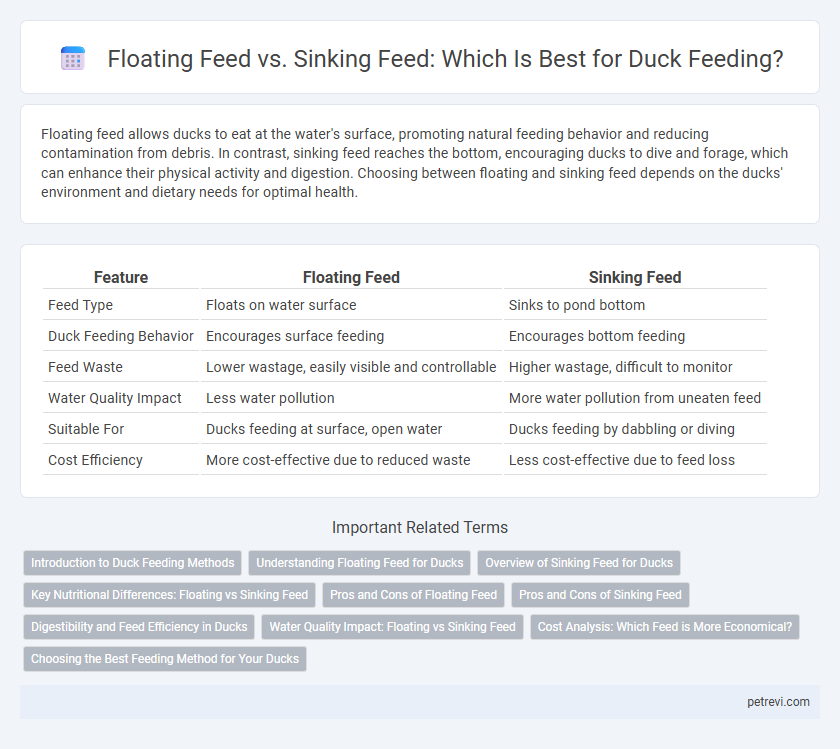
| Feature | Floating Feed | Sinking Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Type | Floats on water surface | Sinks to pond bottom |
| Duck Feeding Behavior | Encourages surface feeding | Encourages bottom feeding |
| Feed Waste | Lower wastage, easily visible and controllable | Higher wastage, difficult to monitor |
| Water Quality Impact | Less water pollution | More water pollution from uneaten feed |
| Suitable For | Ducks feeding at surface, open water | Ducks feeding by dabbling or diving |
| Cost Efficiency | More cost-effective due to reduced waste | Less cost-effective due to feed loss |
Introduction to Duck Feeding Methods
Floating feed allows ducks to consume food more naturally at the water's surface, promoting better digestion and reducing wastage compared to sinking feed. Sinking feed, designed to settle on the pond or water bottom, can be beneficial in deeper water environments where ducks forage underwater but may lead to nutrient loss due to uneaten feed. Understanding these feeding methods helps optimize nutrition absorption and maintain water quality in duck farming operations.
Understanding Floating Feed for Ducks
Floating feed for ducks improves visibility and encourages natural surface feeding behavior, promoting healthy activity levels. This feed type allows farmers to monitor consumption easily, reducing waste and preventing water contamination. Nutritionally, floating feed often contains balanced protein and energy levels tailored to support growth and egg production in ducks.
Overview of Sinking Feed for Ducks
Sinking feed for ducks is formulated to settle quickly at the bottom of water bodies, making it ideal for ducks that naturally forage underwater. This type of feed supports natural feeding behaviors and can reduce waste by preventing feed from floating away. Nutritionally balanced sinking pellets ensure essential vitamins and minerals are delivered efficiently to improve duck health and growth.
Key Nutritional Differences: Floating vs Sinking Feed
Floating feed for ducks, formulated with higher protein content and essential amino acids, promotes optimal growth and waterfowl health by ensuring nutrients remain available on the water surface. Sinking feed typically contains denser ingredients with increased fiber and energy levels suited for bottom-feeding behaviors, supporting digestive efficiency and sustained energy release. Key nutritional differences include floating feed's emphasis on rapid nutrient absorption and sinking feed's role in providing extended nutrient availability within the water column.
Pros and Cons of Floating Feed
Floating feed for ducks offers the advantage of allowing easy observation of feeding behavior, which helps in monitoring intake and reducing feed waste. This type of feed promotes natural dabbling and surface feeding habits, encouraging active foraging and better health. However, floating feed may become soggy in water, leading to potential nutrient loss and increased risk of water contamination if not managed properly.
Pros and Cons of Sinking Feed
Sinking feed for ducks offers the advantage of reducing feed wastage as it allows ducks to forage naturally at the bottom of water bodies, promoting exercise and natural feeding behavior. However, sinking feed can lead to water pollution due to uneaten particles accumulating in ponds, potentially causing poor water quality and increased maintenance. It may also be less visible to ducks compared to floating feed, resulting in uneven consumption and slower growth rates.
Digestibility and Feed Efficiency in Ducks
Floating feed enhances digestibility in ducks by promoting natural foraging behavior and preventing feed wastage, which improves feed efficiency by ensuring more nutrients are absorbed. Sinking feed may lead to lower digestibility due to feed accumulation at the pond bottom, increasing the risk of spoilage and bacterial growth that hampers nutrient uptake. Optimizing feed type based on water conditions and duck behavior directly influences growth performance and feed conversion ratios in duck production.
Water Quality Impact: Floating vs Sinking Feed
Floating feed improves water quality by minimizing feed wastage and surface residue, reducing nutrient loading and algae growth in duck habitats. Sinking feed tends to accumulate on the pond bottom, increasing organic matter and promoting anaerobic conditions that degrade water quality. Optimizing feed type based on water system management supports healthier aquatic environments and better duck health.
Cost Analysis: Which Feed is More Economical?
Floating feed for ducks often proves more economical due to reduced wastage and easier monitoring, allowing farmers to control intake and minimize overfeeding. Sinking feed can lead to higher feed loss as uneaten pellets settle and spoil on the pond bottom, increasing feed costs over time. Evaluating feed efficiency and waste management typically highlights floating feed as the cost-effective choice in duck farming operations.
Choosing the Best Feeding Method for Your Ducks
Floating feed allows ducks to exhibit natural dabbling behaviors, promoting better digestion and reducing feed waste by keeping the feed accessible on the water surface. Sinking feed can be beneficial in minimizing water contamination and controlling feed intake but may not fully support natural feeding instincts. Selecting the best feeding method depends on the duck breed, feeding environment, and management goals to optimize health and feed efficiency.
Floating feed vs Sinking feed for Duck feeding method Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com