Hand feeding allows closer interaction with ducks, promoting trust and quicker taming by associating humans with positive experiences. Scatter feeding encourages natural foraging behavior but may slow taming as ducks remain wary of human presence. Combining both methods can balance social bonding and natural instincts, enhancing overall duck taming success.
Table of Comparison
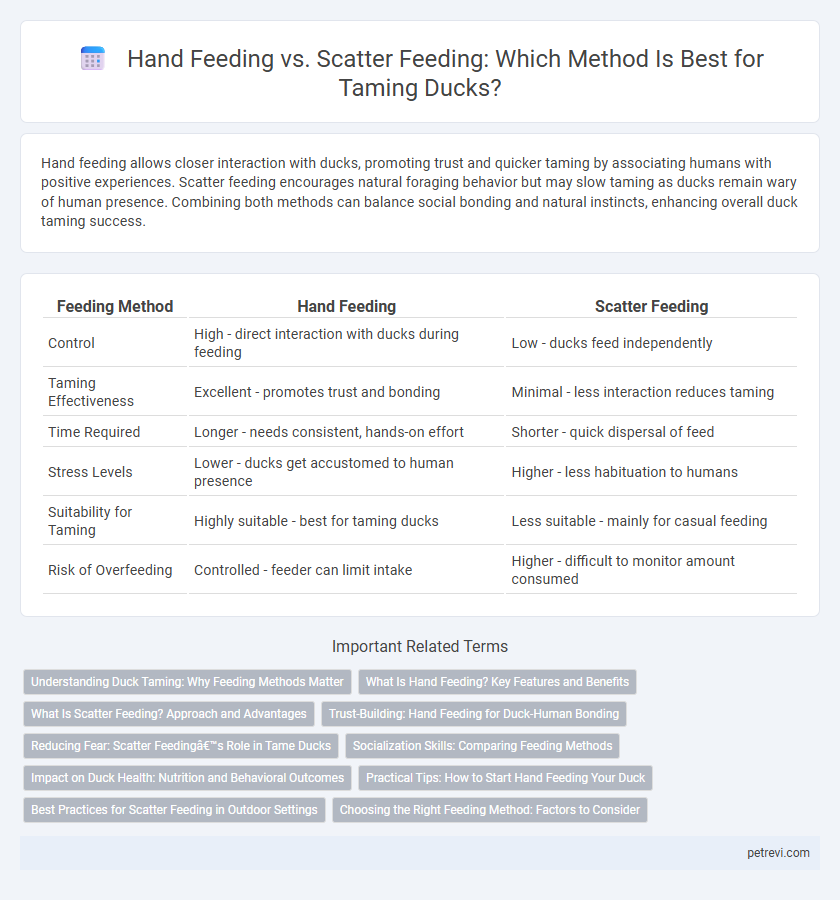
| Feeding Method | Hand Feeding | Scatter Feeding |
|---|---|---|
| Control | High - direct interaction with ducks during feeding | Low - ducks feed independently |
| Taming Effectiveness | Excellent - promotes trust and bonding | Minimal - less interaction reduces taming |
| Time Required | Longer - needs consistent, hands-on effort | Shorter - quick dispersal of feed |
| Stress Levels | Lower - ducks get accustomed to human presence | Higher - less habituation to humans |
| Suitability for Taming | Highly suitable - best for taming ducks | Less suitable - mainly for casual feeding |
| Risk of Overfeeding | Controlled - feeder can limit intake | Higher - difficult to monitor amount consumed |
Understanding Duck Taming: Why Feeding Methods Matter
Hand feeding establishes trust and strengthens the bond between humans and ducks by encouraging close interaction and positive reinforcement. Scatter feeding promotes natural foraging behaviors but may limit direct contact, slowing the taming process. Selecting hand feeding as a taming method accelerates socialization, making ducks more comfortable and responsive to handlers.
What Is Hand Feeding? Key Features and Benefits
Hand feeding involves directly offering food to ducks by hand, fostering trust and improving taming efficiency. This method allows close interaction, facilitating quicker behavioral conditioning and stronger bonds between ducks and handlers. Key benefits include enhanced socialization, easier management, and reduced fear response, making hand feeding an effective technique for domesticated and wild ducks alike.
What Is Scatter Feeding? Approach and Advantages
Scatter feeding involves dispersing food over a wide area to encourage natural foraging behaviors in ducks, promoting mental stimulation and physical exercise. This approach mimics their wild feeding habits, helping to reduce aggression and dominance hierarchies among flock members. Scatter feeding enhances duck taming by fostering trust and reducing the need for direct human interaction, leading to calmer, more confident birds.
Trust-Building: Hand Feeding for Duck-Human Bonding
Hand feeding ducks significantly enhances trust-building by fostering direct interaction and positive associations between humans and ducks, making them more comfortable and responsive. This method encourages ducks to approach willingly, strengthening the bond through consistent, personal attention. In contrast, scatter feeding lacks this close contact, resulting in slower taming and reduced trust development.
Reducing Fear: Scatter Feeding’s Role in Tame Ducks
Scatter feeding encourages natural foraging behavior in ducks, which helps reduce fear by allowing them to approach food at their own pace and feel less threatened. This method fosters trust as ducks associate their environment with positive experiences without direct human interference. In contrast, hand feeding may cause stress or hesitation in wild or less socialized ducks due to the close human contact involved.
Socialization Skills: Comparing Feeding Methods
Hand feeding ducks enhances socialization skills by fostering direct interaction and building trust between the duck and handler, promoting a stronger bond. Scatter feeding stimulates natural foraging behaviors and encourages group cohesion but may limit individual duck recognition and interaction. Selecting hand feeding supports targeted socialization, while scatter feeding prioritizes ecological behaviors essential for flock dynamics.
Impact on Duck Health: Nutrition and Behavioral Outcomes
Hand feeding ducks allows for controlled portion sizes and customized nutrition, promoting optimal health and preventing obesity, while encouraging close human interaction that enhances taming success. Scatter feeding mimics natural foraging behavior, supporting mental stimulation and exercise but risks overfeeding or nutrient imbalance if not monitored carefully. Balancing both methods can optimize duck health by combining precise dietary management with behaviors that reduce stress and encourage natural instincts.
Practical Tips: How to Start Hand Feeding Your Duck
Start hand feeding your duck by offering small, soft treats like peas or corn kernels to build trust and encourage gentle interaction. Use a shallow, clean container or your palm to present food, keeping your movements slow and calm to avoid startling the duck. Consistent daily sessions create a positive association, gradually increasing the duck's comfort and responsiveness to hand feeding.
Best Practices for Scatter Feeding in Outdoor Settings
Scatter feeding in outdoor duck taming promotes natural foraging behavior and reduces aggressive competition among ducks. Distributing feed evenly across a wide area encourages movement and mimics natural feeding patterns, enhancing physical health and social interaction. Regularly cleaning feeding areas and using high-quality grains or pellets support optimal nutrition and hygiene during scatter feeding.
Choosing the Right Feeding Method: Factors to Consider
Hand feeding ducks promotes trust and closer interaction, making it ideal for taming and bonding, especially with young or newly acquired birds. Scatter feeding encourages natural foraging behavior and reduces dependency on humans, suitable for outdoor or free-range environments where ducks can graze freely. Factors like the duck's age, temperament, environment, and your taming goals determine the most effective feeding method to ensure healthy growth and socialization.
Hand feeding vs Scatter feeding for Duck taming Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com