Organic feed, free from synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, provides ducks with natural nutrients that can enhance their growth and overall health compared to conventional feed. Ducks consuming organic feed often exhibit improved immune function and better weight gain due to the absence of chemical residues commonly found in conventional feed. Choosing organic feed supports sustainable farming practices and results in healthier duck development without compromising growth rates.
Table of Comparison
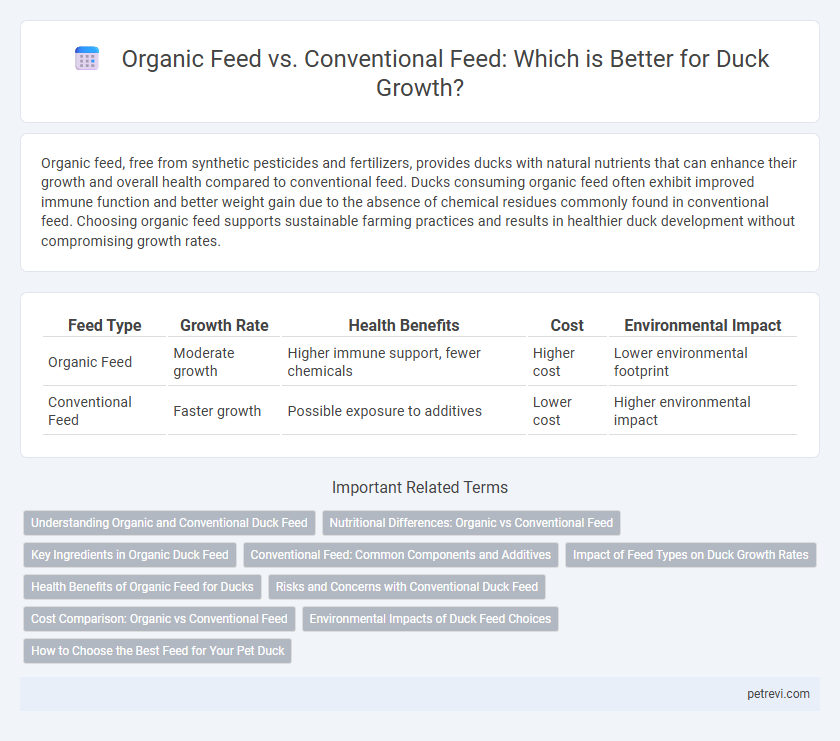
| Feed Type | Growth Rate | Health Benefits | Cost | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Feed | Moderate growth | Higher immune support, fewer chemicals | Higher cost | Lower environmental footprint |
| Conventional Feed | Faster growth | Possible exposure to additives | Lower cost | Higher environmental impact |
Understanding Organic and Conventional Duck Feed
Organic feed for ducks typically consists of non-GMO grains and natural ingredients free from synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, promoting healthier growth and reducing chemical residues in the meat. Conventional feed often includes genetically modified components and synthetic additives designed to enhance rapid growth and feed efficiency but may introduce antibiotic residues or hormones. Choosing between organic and conventional duck feed depends on priorities such as sustainability, animal welfare, and potential health benefits for both ducks and consumers.
Nutritional Differences: Organic vs Conventional Feed
Organic feed for ducks typically contains higher-quality ingredients free from synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers, leading to improved nutrient density and digestibility. Conventional feed often includes genetically modified crops and synthetic additives, which may affect nutrient absorption and overall duck health. Studies indicate organic feed can enhance growth rates and immune response in ducks due to richer vitamin and mineral content.
Key Ingredients in Organic Duck Feed
Organic duck feed primarily contains non-GMO grains such as corn and barley, enriched with natural protein sources like soybean meal and fish meal to promote optimal growth. Key ingredients also include organic vitamins and minerals that support immune function and bone development, while omitting synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers found in conventional feed. This balanced composition enhances nutrient absorption and overall health, leading to better weight gain and meat quality in ducks raised on organic diets.
Conventional Feed: Common Components and Additives
Conventional feed for ducks typically includes corn, soybean meal, wheat, and barley as primary energy and protein sources, providing a balanced nutrient profile essential for rapid growth and development. Additives such as vitamins (A, D, E), minerals (calcium, phosphorus), antibiotics, and growth promoters are commonly incorporated to enhance feed efficiency, immunity, and overall health. The inclusion of enzymes and probiotics in conventional duck feed further supports digestive health and nutrient absorption, contributing to optimized weight gain and feed conversion ratios.
Impact of Feed Types on Duck Growth Rates
Organic feed, rich in natural nutrients and free from synthetic additives, promotes healthier and more consistent growth rates in ducks compared to conventional feed. Ducks consuming organic feed often exhibit improved immune function and better weight gain efficiency due to the high-quality protein and essential vitamins present. Conventional feed, while cost-effective, may contain growth enhancers and fillers that can lead to faster but less sustainable growth and potential health issues.
Health Benefits of Organic Feed for Ducks
Organic feed for ducks promotes better health by reducing exposure to synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, and genetically modified organisms commonly found in conventional feed. Ducks fed organic diets exhibit stronger immune systems and lower incidences of diseases, supporting sustainable growth and welfare. Nutrient profiles in organic feed, rich in natural vitamins and antioxidants, enhance overall vitality and feather quality in ducks.
Risks and Concerns with Conventional Duck Feed
Conventional duck feed often contains synthetic additives, antibiotics, and genetically modified ingredients that pose health risks such as antibiotic resistance and toxin accumulation. These components can negatively impact duck growth, immune function, and overall welfare compared to organic feed options. Concerns also include environmental pollution and residue buildup in duck products, raising food safety issues for consumers.
Cost Comparison: Organic vs Conventional Feed
Organic feed for ducks typically costs 20-30% more than conventional feed due to the use of natural ingredients and certified farming practices. Despite higher initial expenses, organic feed can lead to improved duck health and potentially higher market value for organically raised ducks. Conventional feed is more economical upfront, but may result in increased veterinary costs and lower product premiums in the long term.
Environmental Impacts of Duck Feed Choices
Organic feed for ducks typically results in lower environmental pollution due to reduced pesticide and synthetic fertilizer use, promoting healthier soil and water systems. Conventional feed often relies on chemically intensive crops that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and water contamination. Choosing organic feed supports sustainable farming practices and decreases the ecological footprint of duck production.
How to Choose the Best Feed for Your Pet Duck
Choosing the best feed for your pet duck involves comparing organic feed and conventional feed based on nutritional quality, growth benefits, and safety. Organic feed typically contains no synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, promoting healthier growth and reducing exposure to harmful chemicals. Prioritize feeds with balanced protein levels, essential vitamins, and minerals to support optimal duck development and overall well-being.
Organic Feed vs Conventional Feed for Duck growth Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com