Cashmere and Angora fibers from goats offer distinct qualities for textile use, with Cashmere known for its exceptional softness and warmth due to fine, dense undercoat fibers, while Angora provides a silky texture with a characteristic sheen from long, curly locks. Cashmere goats produce fiber primarily for insulation, making the material ideal for luxury winter garments, whereas Angora goats yield mohair, valued for its strength and luster, perfect for lightweight, durable fabrics. Choosing between Cashmere and Angora fibers depends on the desired balance of softness, durability, and appearance in goat fiber products.
Table of Comparison
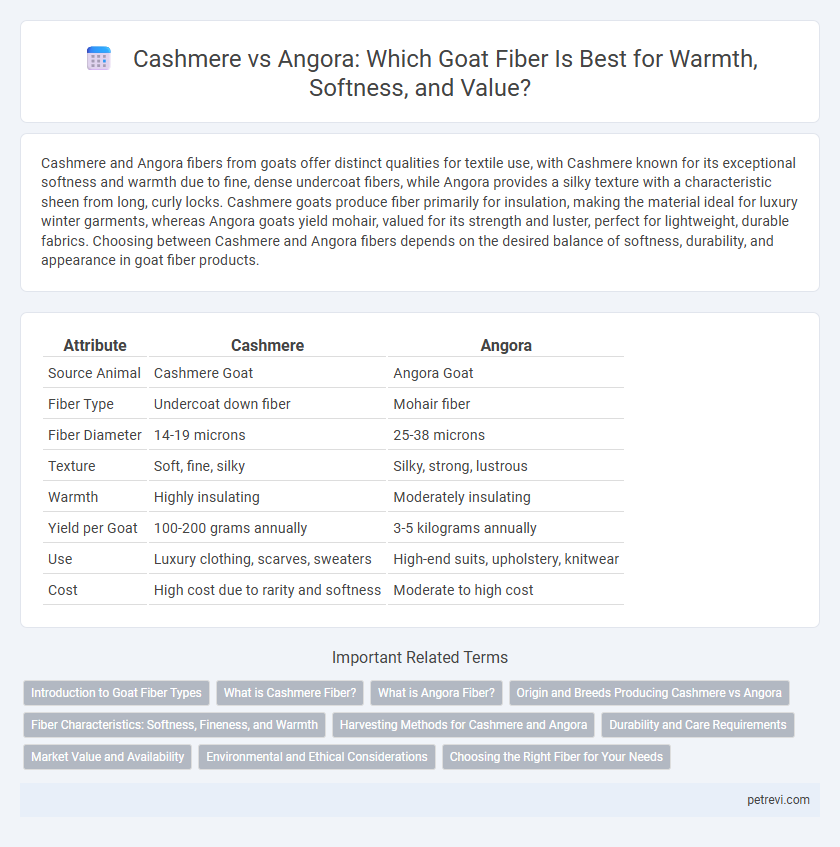
| Attribute | Cashmere | Angora |
|---|---|---|
| Source Animal | Cashmere Goat | Angora Goat |
| Fiber Type | Undercoat down fiber | Mohair fiber |
| Fiber Diameter | 14-19 microns | 25-38 microns |
| Texture | Soft, fine, silky | Silky, strong, lustrous |
| Warmth | Highly insulating | Moderately insulating |
| Yield per Goat | 100-200 grams annually | 3-5 kilograms annually |
| Use | Luxury clothing, scarves, sweaters | High-end suits, upholstery, knitwear |
| Cost | High cost due to rarity and softness | Moderate to high cost |
Introduction to Goat Fiber Types
Cashmere and Angora fibers come from distinct goat breeds, each producing unique luxurious wool known for softness and warmth. Cashmere is obtained from the undercoat of Cashmere goats, prized for its fine, silky texture and excellent insulation properties. Angora fiber, sourced from Angora goats, is characterized by its lustrous, fluffy appearance and is commonly used in high-end textiles like mohair blends.
What is Cashmere Fiber?
Cashmere fiber is a luxurious natural wool obtained from the undercoat of cashmere goats, primarily found in regions such as Mongolia, China, and Iran. This fiber is known for its exceptional softness, warmth, and lightweight properties, making it highly sought after in the textile industry. The fine diameter of cashmere fibers, typically measuring between 14 to 19 microns, distinguishes it from coarser goat fibers like Angora, which comes from a different breed producing mohair.
What is Angora Fiber?
Angora fiber is a luxury natural fiber obtained from Angora goats, renowned for its exceptional softness, luster, and warmth. Unlike Cashmere, which comes from Cashmere goats, Angora fiber is characterized by its long, silky strands that create a lightweight yet insulating fabric. This fiber is highly sought after in textile industries for its unique sheen and smooth texture, making it ideal for premium clothing and accessories.
Origin and Breeds Producing Cashmere vs Angora
Cashmere fiber originates primarily from the Changthangi and Inner Mongolian goat breeds, prized for their fine undercoat harvested during seasonal molting. Angora fiber comes exclusively from the Angora goat breed, native to the Ankara region of Turkey, known for its long, lustrous mohair fibers. Differences in geographic origin and breed characteristics significantly influence the texture and value of these luxurious goat fibers.
Fiber Characteristics: Softness, Fineness, and Warmth
Cashmere fiber, derived from the undercoat of Cashmere goats, is renowned for its exceptional softness, fineness typically around 14-19 microns, and excellent insulation properties that provide superior warmth. Angora fiber, obtained from Angora goats, tends to be coarser and thicker, with a fiber diameter usually between 24-30 microns, offering moderate softness and warmth but higher durability. The finer micron count of Cashmere makes it softer and warmer than Angora, which is better suited for more rugged and durable textile applications.
Harvesting Methods for Cashmere and Angora
Cashmere fiber is harvested by combing the undercoat of Cashmere goats during their molting season, typically in spring, which ensures the collection of soft, fine fibers without harming the animal. Angora fiber is obtained by shearing Angora goats every 3 to 4 months, producing locks of long, lustrous fiber known as mohair. The combing method for Cashmere targets the fine undercoat for softness, while the Angora's shearing process collects the entire fleece, emphasizing length and sheen.
Durability and Care Requirements
Cashmere fiber, harvested from the undercoat of Cashmere goats, is renowned for its exceptional softness and moderate durability, requiring gentle hand washing or dry cleaning to maintain its quality. Angora fiber, derived from the Angora goat, is less durable than Cashmere and demands meticulous care, including delicate hand washing and careful drying to prevent felting and damage. Both fibers offer luxurious textures, but Cashmere provides better longevity and easier maintenance compared to the more fragile and high-maintenance Angora wool.
Market Value and Availability
Cashmere fiber, derived from the undercoat of Cashmere goats, commands a higher market value due to its exceptional softness, warmth, and scarcity, with global production concentrated in regions like Mongolia and China. Angora goat fiber, known as mohair, tends to be more abundant and affordable, offering durability and a silky texture that appeals to diverse textile markets. Limited supply and labor-intensive harvesting of Cashmere significantly elevate its price compared to the more readily available mohair from Angora goats.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Cashmere fiber from goats is often favored for its lower environmental footprint compared to angora, as cashmere production typically requires less intensive grooming and results in less animal stress. Angora goats need frequent shearing to prevent painful matting, raising ethical concerns about animal welfare in some farming practices. Sustainable sourcing of both fibers involves ensuring humane treatment, minimizing habitat disruption, and supporting regenerative agriculture to reduce environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Needs
Cashmere fiber, sourced from the undercoat of Cashmere goats, offers exceptional softness, warmth, and durability, making it ideal for luxury garments and cold climates. Angora fiber, derived from Angora goats, is prized for its silky texture and distinct luster, often used in lightweight, breathable fabrics suited for mild weather. Selecting between Cashmere and Angora fibers depends on desired fabric characteristics such as insulation level, softness, and garment use, with Cashmere favored for warmth and Angora preferred for sheen and lightness.
Cashmere vs Angora for Goat fiber Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com