Dehorning and disbudding are two common methods used for goat horn management, each with distinct procedures and timing. Disbudding is performed on young kids, usually within the first week of life, to prevent horn growth by destroying the horn-producing cells, resulting in less stress and risk of injury. Dehorning is carried out on older goats with developed horns, involving the physical removal of horns, which can be more painful and requires careful aftercare to avoid complications.
Table of Comparison
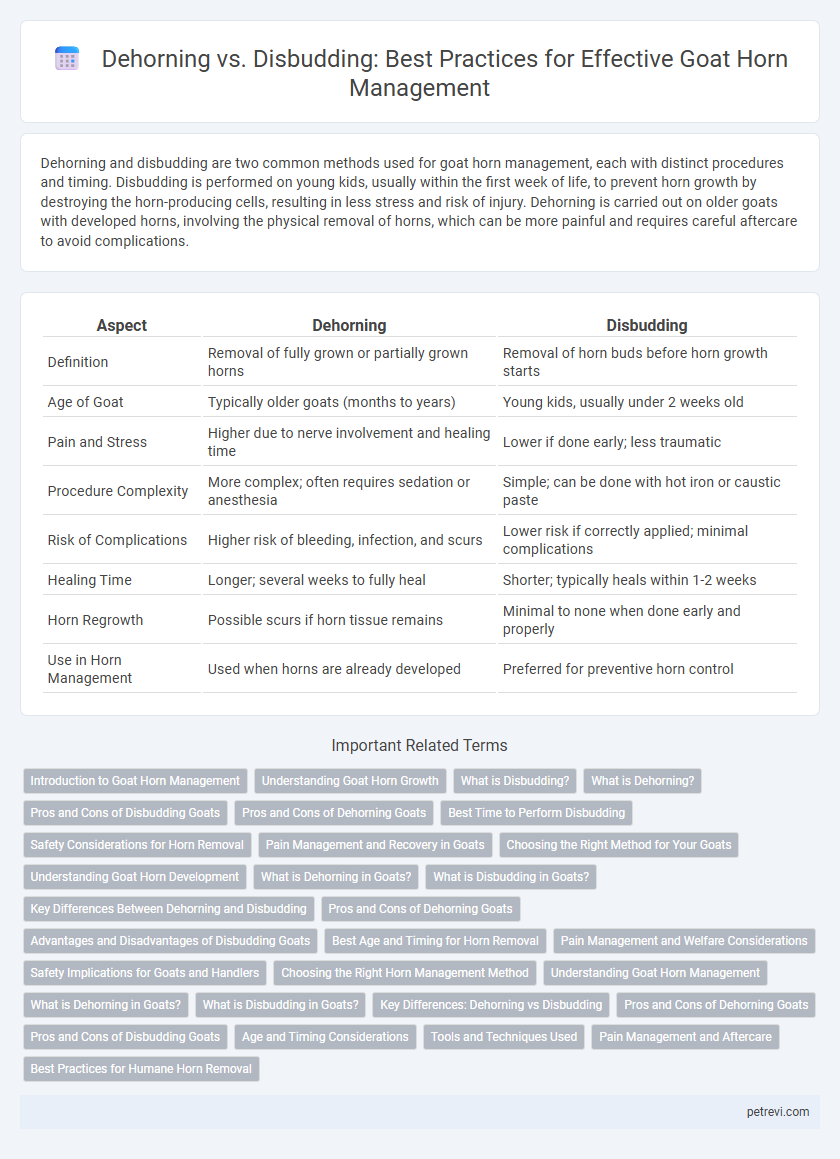
| Aspect | Dehorning | Disbudding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removal of fully grown or partially grown horns | Removal of horn buds before horn growth starts |
| Age of Goat | Typically older goats (months to years) | Young kids, usually under 2 weeks old |
| Pain and Stress | Higher due to nerve involvement and healing time | Lower if done early; less traumatic |
| Procedure Complexity | More complex; often requires sedation or anesthesia | Simple; can be done with hot iron or caustic paste |
| Risk of Complications | Higher risk of bleeding, infection, and scurs | Lower risk if correctly applied; minimal complications |
| Healing Time | Longer; several weeks to fully heal | Shorter; typically heals within 1-2 weeks |
| Horn Regrowth | Possible scurs if horn tissue remains | Minimal to none when done early and properly |
| Use in Horn Management | Used when horns are already developed | Preferred for preventive horn control |
Introduction to Goat Horn Management
Goat horn management involves controlling horn growth to prevent injuries and facilitate handling, with dehorning and disbudding as primary methods. Disbudding, performed on young kids before horn buds develop fully, uses heat or caustic agents to inhibit horn growth with minimal pain and faster recovery. Dehorning removes mature horns surgically or mechanically, requiring more skill and posing higher risks of complications.
Understanding Goat Horn Growth
Goat horn growth begins within the first days after birth, with horn buds forming beneath the skin that later develop into full horns. Disbudding involves removing or destroying these horn buds before they firmly attach to the skull, preventing horn growth and minimizing stress and injury risks. Dehorning, performed on mature goats with developed horns, requires more invasive techniques and carries higher risks such as bleeding, infection, and prolonged healing times.
What is Disbudding?
Disbudding is the process of preventing horn growth in young goat kids by destroying the horn-producing cells shortly after birth, typically within the first week. This method involves using a heated tool or caustic chemical to eliminate the horn buds before they develop into fully grown horns. Disbudding is considered less invasive and less stressful compared to dehorning adult goats, making it a preferred practice for horn management in goat farming.
What is Dehorning?
Dehorning is the process of removing fully developed horns from goats, typically performed when the animal is older and the horns have grown past the bud stage. This method often requires more caution and skill due to increased bleeding and pain compared to disbudding, which targets horn buds in young kids. Proper dehorning helps prevent injuries to other animals and handlers, contributing to safer management in goat farming.
Pros and Cons of Disbudding Goats
Disbudding goats at an early age prevents horn growth, reducing risks of injury to other goats and handlers while minimizing long-term pain compared to later dehorning procedures. The primary advantage of disbudding includes a quicker, less invasive method that promotes better healing and reduces the chance of horn regrowth. However, disbudding can cause stress and potential complications if not performed properly, requiring skilled handling and adherence to animal welfare guidelines.
Pros and Cons of Dehorning Goats
Dehorning goats involves removing fully developed horns, which can reduce injury risks in confined spaces and simplify handling but is more invasive and painful compared to disbudding, with longer recovery times. This method may cause significant bleeding, increase the risk of infection, and requires skilled technique to avoid damage to the goat's skull or brain. While dehorning provides a permanent solution when horns are large or damaged, it demands careful consideration of animal welfare and proper pain management.
Best Time to Perform Disbudding
The best time to perform disbudding on goats is within the first one to two weeks of age, ideally between 3 to 7 days old, before the horn buds fully develop. Early disbudding reduces stress and minimizes the risk of horn growth complications, promoting healthier hornless goats. Delaying beyond two weeks increases difficulty and potential for injury to the goat's skull and surrounding tissues.
Safety Considerations for Horn Removal
Dehorning and disbudding are common goat horn management practices with distinct safety considerations; disbudding is generally safer for young kids as it involves removing horn buds before they attach to the skull, minimizing bleeding and infection risks. Dehorning older goats carries higher safety risks due to the increased vascularization and root development of mature horns, requiring careful handling to prevent severe hemorrhage and pain. Proper sedation, skilled technique, and post-procedure care are critical to reducing complications and ensuring animal welfare during horn removal.
Pain Management and Recovery in Goats
Disbudding in goats involves removing horn buds at an early age, resulting in less tissue damage and faster recovery compared to dehorning, which removes fully developed horns and causes more pain and prolonged healing. Effective pain management for both procedures typically includes local anesthetics such as lidocaine, combined with analgesics like meloxicam to reduce discomfort and inflammation. Recovery from disbudding generally spans a few days, while dehorning may require weeks, highlighting the importance of proactive pain control to improve animal welfare and promote quicker healing.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Goats
Dehorning removes fully developed goat horns, typically performed on older goats, while disbudding is the prevention of horn growth in young kids by destroying the horn buds. Choosing the right method depends on the goat's age, size, and breed, with disbudding preferred for young kids due to less pain and reduced risk of complications. Effective horn management improves safety for both goats and handlers, minimizing injury and facilitating easier herd management.
Dehorning vs Disbudding for Goat Horn Management Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com