A flushing diet for goat breeding involves increasing the nutritional intake, particularly energy and protein, before and during the breeding season to enhance ovulation rates and improve conception chances. In contrast, a maintenance diet provides the essential nutrients required to sustain the goat's current body condition without promoting weight gain or reproductive stimulation. Optimizing the balance between flushing and maintenance diets is crucial for maximizing reproductive performance and overall herd health.
Table of Comparison
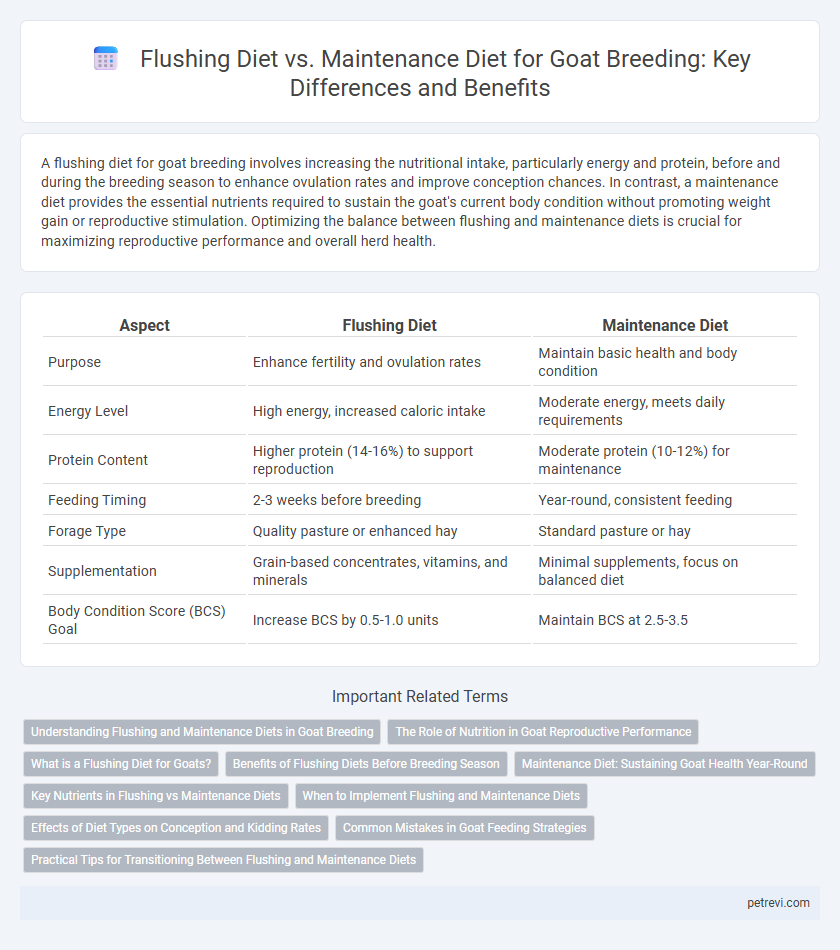
| Aspect | Flushing Diet | Maintenance Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance fertility and ovulation rates | Maintain basic health and body condition |
| Energy Level | High energy, increased caloric intake | Moderate energy, meets daily requirements |
| Protein Content | Higher protein (14-16%) to support reproduction | Moderate protein (10-12%) for maintenance |
| Feeding Timing | 2-3 weeks before breeding | Year-round, consistent feeding |
| Forage Type | Quality pasture or enhanced hay | Standard pasture or hay |
| Supplementation | Grain-based concentrates, vitamins, and minerals | Minimal supplements, focus on balanced diet |
| Body Condition Score (BCS) Goal | Increase BCS by 0.5-1.0 units | Maintain BCS at 2.5-3.5 |
Understanding Flushing and Maintenance Diets in Goat Breeding
Flushing diet in goat breeding involves increasing the energy and protein intake to enhance ovulation rates and improve conception success, typically initiated 2-3 weeks before breeding. Maintenance diet provides adequate nutrition to sustain body condition and health without excess energy or protein, ensuring goats remain in optimal condition for breeding cycles. Understanding the balance between flushing and maintenance diets is crucial for maximizing reproductive efficiency and successful kidding outcomes.
The Role of Nutrition in Goat Reproductive Performance
Proper nutritional management during the flushing and maintenance diet phases significantly impacts goat reproductive performance by enhancing ovulation rates and conception success. Flushing diets, rich in energy and protein, stimulate increased follicular development and improve body condition scores, which directly correlate with higher kidding rates. Maintenance diets ensure sustained health and optimal metabolic function, supporting successful gestation and overall fertility.
What is a Flushing Diet for Goats?
A flushing diet for goats involves increasing the nutritional intake, especially energy and protein, about two to three weeks before breeding to boost ovulation rates and improve conception success. This diet typically includes higher-quality forage, grains, and supplements to enhance body condition and reproductive performance. Proper flushing can lead to larger kidding rates and healthier offspring compared to a maintenance diet that simply meets basic nutritional needs.
Benefits of Flushing Diets Before Breeding Season
Flushing diets, rich in energy and protein, enhance ovulation rates and improve conception success in goats by rapidly boosting body condition scores before breeding season. This nutritional strategy increases follicular development and hormone production, leading to higher kidding rates and healthier offspring. Compared to maintenance diets, flushing promotes reproductive efficiency, maximizing herd productivity and genetic potential.
Maintenance Diet: Sustaining Goat Health Year-Round
A maintenance diet for goats prioritizes balanced nutrient intake to sustain overall health and body condition throughout the year without promoting excessive weight gain. This diet typically includes adequate forage quality, consistent mineral supplementation, and controlled energy levels to support metabolic functions and immune resilience. Ensuring proper hydration and regular health monitoring also plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal goat well-being beyond the breeding cycle.
Key Nutrients in Flushing vs Maintenance Diets
Flushing diets for goat breeding emphasize higher energy levels, with increased concentrates rich in carbohydrates and proteins to enhance ovulation rates and fertility. Maintenance diets prioritize balanced fiber from forages and adequate protein to sustain body condition without promoting excessive weight gain. Key nutrients in flushing include increased crude protein (16-18%) and energy density, while maintenance focuses on moderate protein (10-12%) and fiber to support basic metabolic functions.
When to Implement Flushing and Maintenance Diets
Flushing diets for goats should be implemented 3 to 4 weeks before breeding to enhance ovulation rates and improve conception efficiency. Maintenance diets are essential throughout the non-breeding period to sustain body condition and support overall health. Proper timing ensures optimal reproductive performance and maximizes kidding rates.
Effects of Diet Types on Conception and Kidding Rates
Flushing diet, rich in energy and protein, significantly improves conception and kidding rates by enhancing ovulation and embryo survival in goats, whereas maintenance diet sustains basic nutritional needs without optimizing reproductive performance. Studies show goats on a flushing diet exhibit increased ovulation rates and higher twinning percentages compared to those on a maintenance diet. Proper flushing before breeding is critical to maximize fecundity and improve overall herd productivity in goat breeding programs.
Common Mistakes in Goat Feeding Strategies
Flushing goats with high-energy grains before breeding is crucial to improve ovulation rates, but a common mistake is overfeeding, leading to excessive weight gain and reduced fertility. Maintenance diets often lack the nutritional density required to support optimal reproductive performance during flushing, causing failure in conception or poor kidding outcomes. Neglecting to balance protein, energy, and mineral intake during these phases disrupts hormonal balance and lowers breeding success in goats.
Practical Tips for Transitioning Between Flushing and Maintenance Diets
Flushing diets for goats typically involve increased energy and protein intake to stimulate ovulation, often using grains and lush forage. Maintenance diets emphasize balanced nutrition with adequate fiber to support health without excessive weight gain, focusing on hay and pasture. Practical tips include gradually adjusting feed over 7-10 days, monitoring body condition scores, and ensuring clean water availability to ease metabolic transitions and optimize reproductive performance.
Flushing vs Maintenance diet for Goat breeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com