Grain-free diets for goats emphasize foraging on grasses, legumes, and browse, promoting natural digestive health and reducing the risk of acidosis and bloating. Grain-included diets provide higher energy and support rapid growth or lactation but require careful management to prevent digestive disorders. Balancing fiber-rich forage with appropriate grain supplementation ensures optimal nutrient absorption and overall goat well-being.
Table of Comparison
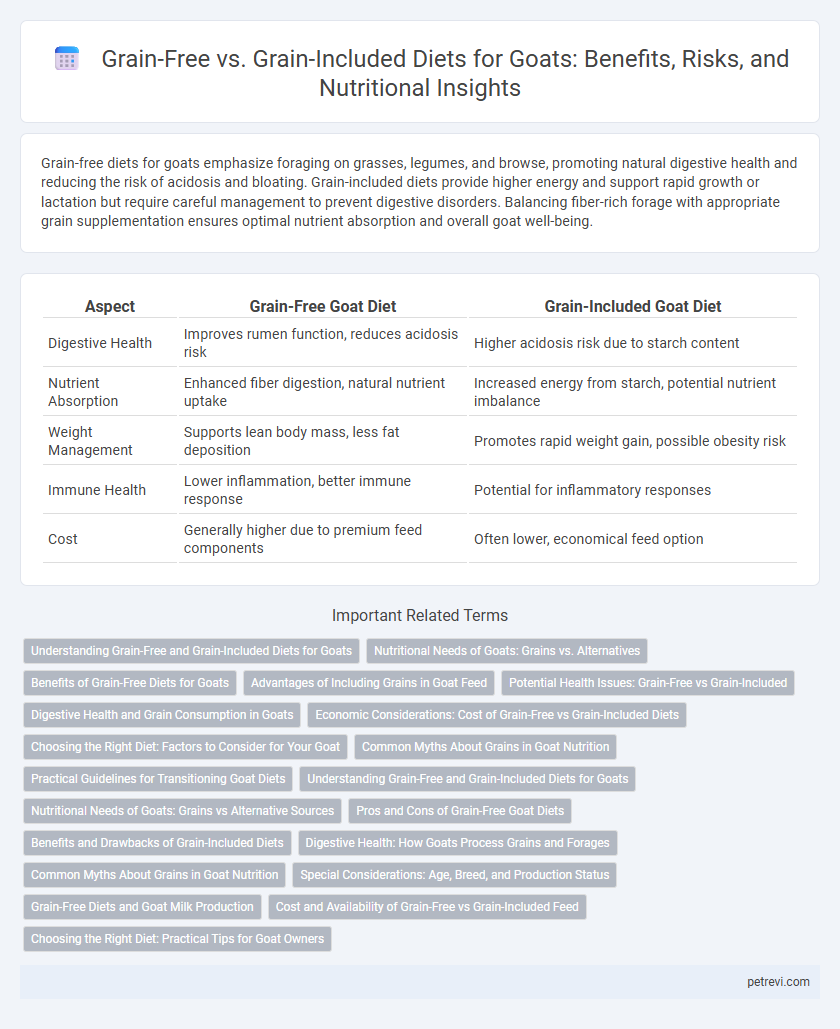
| Aspect | Grain-Free Goat Diet | Grain-Included Goat Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Digestive Health | Improves rumen function, reduces acidosis risk | Higher acidosis risk due to starch content |
| Nutrient Absorption | Enhanced fiber digestion, natural nutrient uptake | Increased energy from starch, potential nutrient imbalance |
| Weight Management | Supports lean body mass, less fat deposition | Promotes rapid weight gain, possible obesity risk |
| Immune Health | Lower inflammation, better immune response | Potential for inflammatory responses |
| Cost | Generally higher due to premium feed components | Often lower, economical feed option |
Understanding Grain-Free and Grain-Included Diets for Goats
Grain-free diets for goats emphasize forage, hay, and browse, which align closely with goats' natural browsing behaviors and digestive systems, promoting better rumen health and reducing risks of acidosis. Grain-included diets incorporate cereals such as corn, barley, and oats to provide concentrated energy and protein, supporting higher production levels in lactating or growing goats. Balancing forage with appropriate grain levels is crucial to meet nutritional needs while maintaining digestive efficiency and preventing metabolic disorders.
Nutritional Needs of Goats: Grains vs. Alternatives
Grain-free goat diets rely on high-fiber forages and alternative protein sources such as legumes and oilseeds to meet essential nutritional needs, promoting rumen health and reducing the risk of acidosis. Grain-included diets provide readily digestible carbohydrates and energy, supporting growth and lactation but may require careful balancing to avoid digestive disturbances. Understanding the specific nutritional requirements for fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals is critical when choosing between grain and grain-free feed to optimize goat health and productivity.
Benefits of Grain-Free Diets for Goats
Grain-free diets for goats enhance digestive health by reducing the risk of acidosis and promoting a stable rumen environment, which supports better nutrient absorption. These diets also lower the occurrence of obesity and metabolic disorders by emphasizing forage-based nutrition rich in fiber and essential nutrients. Improved immune function and overall vitality are observed in goats fed grain-free rations due to the natural balance of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants from diverse plant sources.
Advantages of Including Grains in Goat Feed
Including grains in goat feed enhances energy density, supporting growth, milk production, and overall health. Grains provide essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, protein, and vital vitamins like B-complex, which improve digestion and metabolic functions. The inclusion of grains also boosts feed palatability, leading to increased intake and improved feed efficiency in goats.
Potential Health Issues: Grain-Free vs Grain-Included
Grain-Free goat diets can reduce the risk of acidosis and bloating by minimizing rapid fermentation in the rumen, but may require careful balancing to prevent nutrient deficiencies such as energy and protein gaps. Grain-Included diets provide readily fermentable carbohydrates that support growth and milk production but increase the potential for ruminal pH fluctuations leading to laminitis and digestive upset. Managing the proportion and type of grains is critical to maintaining optimal rumen health and preventing metabolic disorders in goats.
Digestive Health and Grain Consumption in Goats
Grain-free diets for goats emphasize high-fiber forages that promote optimal rumen function and prevent acidosis, enhancing digestive health by maintaining stable pH levels and microbial balance. Grain-included diets provide concentrated energy sources like corn or barley but can increase the risk of digestive disorders if not balanced with adequate forage intake. Managing grain consumption with careful portion control supports efficient nutrient absorption and reduces the incidence of bloat or ruminal acidosis in goats.
Economic Considerations: Cost of Grain-Free vs Grain-Included Diets
Grain-included diets for goats generally offer a lower upfront cost due to the widespread availability and lower price of grains like corn and oats, making them economically appealing for large-scale operations. Grain-free diets, often relying on alternative forage and supplements, typically incur higher expenses, but they may reduce veterinary costs by promoting better gut health and reducing the risk of digestive disorders. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including feed efficiency, animal health, and potential productivity gains, is essential for determining the most cost-effective feeding strategy for goat herds.
Choosing the Right Diet: Factors to Consider for Your Goat
Selecting the right diet for goats involves evaluating their health status, age, and activity level to determine grain-free or grain-included options. Grain-free diets, rich in forage and fiber, support digestive health and mimic natural grazing, while grain-included diets provide higher energy levels crucial for lactating or growing goats. Balancing nutritional needs with factors like feed availability and cost ensures optimal health and productivity in goat management.
Common Myths About Grains in Goat Nutrition
Grains in goat nutrition are often misunderstood, with myths claiming they cause digestive problems or are inherently harmful. In reality, grains provide essential energy and nutrients when fed in appropriate amounts, supporting growth and milk production. Balancing grains with forage ensures optimal rumen health and prevents issues like acidosis or nutrient imbalances in goats.
Practical Guidelines for Transitioning Goat Diets
Transitioning goats from grain-included to grain-free diets requires gradual adaptation over 7 to 14 days to prevent digestive upset and maintain rumen health. Incorporate high-fiber forage such as alfalfa or grass hay to support rumination and nutrient absorption during the dietary change. Monitor body condition and stool consistency regularly to ensure goats adjust well to the new grain-free feeding regime and avoid metabolic disturbances.
Grain-Free vs Grain-Included for Goat Diet Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com