Zero grazing in goat management involves confining goats to a limited area and providing cut fodder, which helps control diet quality and reduces parasite exposure. Free-range systems allow goats to forage naturally, promoting exercise and diverse nutrient intake but increasing the risk of predation and disease. Choosing between these methods depends on resource availability, land size, and management goals for optimal goat health and productivity.
Table of Comparison
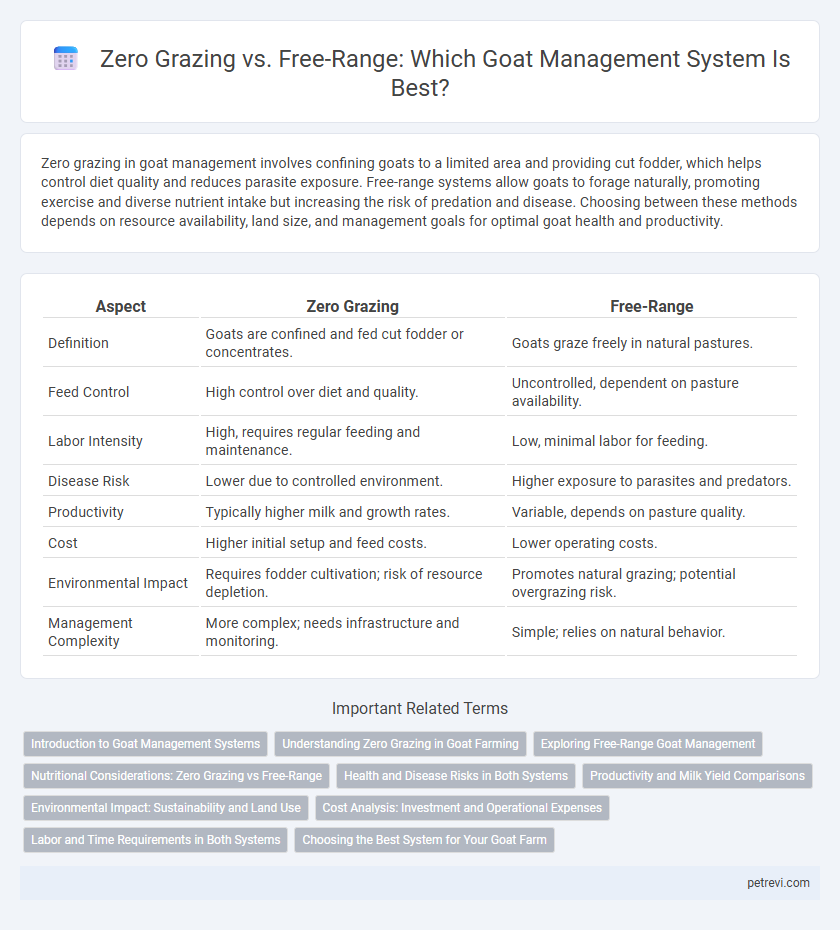
| Aspect | Zero Grazing | Free-Range |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Goats are confined and fed cut fodder or concentrates. | Goats graze freely in natural pastures. |
| Feed Control | High control over diet and quality. | Uncontrolled, dependent on pasture availability. |
| Labor Intensity | High, requires regular feeding and maintenance. | Low, minimal labor for feeding. |
| Disease Risk | Lower due to controlled environment. | Higher exposure to parasites and predators. |
| Productivity | Typically higher milk and growth rates. | Variable, depends on pasture quality. |
| Cost | Higher initial setup and feed costs. | Lower operating costs. |
| Environmental Impact | Requires fodder cultivation; risk of resource depletion. | Promotes natural grazing; potential overgrazing risk. |
| Management Complexity | More complex; needs infrastructure and monitoring. | Simple; relies on natural behavior. |
Introduction to Goat Management Systems
Zero grazing and free-range represent two primary goat management systems with distinct approaches to feeding and housing. Zero grazing confines goats to a controlled environment where forage is cut and brought to them, optimizing feed efficiency and reducing land degradation. Free-range systems allow goats to roam freely, promoting natural behaviors and diverse diet intake but requiring larger land areas and vigilant predator management.
Understanding Zero Grazing in Goat Farming
Zero grazing in goat farming involves confining goats in a controlled environment where forage is cut and brought to them, minimizing land degradation and increasing feed efficiency. This system enhances disease control and nutrient management by allowing close monitoring of animal health and precise feeding schedules. Zero grazing supports sustainable goat farming by optimizing resource use and improving productivity, especially in regions with limited grazing land.
Exploring Free-Range Goat Management
Free-range goat management allows goats to forage naturally, improving their diet diversity and overall health by consuming a variety of grasses, shrubs, and legumes. This system reduces feed costs and promotes natural behaviors, enhancing animal welfare and potentially leading to higher-quality meat and milk products. Challenges include increased exposure to predators and parasites, requiring strategic fencing and regular health monitoring to maintain productivity.
Nutritional Considerations: Zero Grazing vs Free-Range
Zero grazing systems provide controlled, high-quality forage, ensuring consistent nutrient intake essential for optimal goat growth and milk production. Free-range goats benefit from diverse forage availability, which supports natural foraging behaviors but may result in variable nutrient consumption and potential deficiencies. Proper supplementation in free-range systems is critical to balance dietary protein, fiber, and minerals for maintaining goat health and productivity.
Health and Disease Risks in Both Systems
Zero grazing systems minimize exposure to parasites and infectious diseases by confining goats to controlled environments with regular veterinary monitoring. Free-range management increases the risk of contact with wild animals and contaminated pastures, leading to higher susceptibility to parasitic infestations and zoonotic diseases. Strategic vaccination, hygiene practices, and nutritional support are critical in both systems to maintain optimal goat health and reduce disease outbreaks.
Productivity and Milk Yield Comparisons
Zero grazing systems for goat management often lead to higher productivity and increased milk yield due to controlled feeding and reduced energy expenditure. Free-range goats typically exhibit lower milk production but benefit from natural foraging, which can improve overall health and resilience. Comparing both, zero grazing maximizes milk output efficiency, while free-range supports sustainability and animal welfare with moderate yield performance.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Land Use
Zero grazing in goat management reduces land degradation by confining goats to controlled feeding areas, minimizing soil erosion and overgrazing compared to free-range systems. Free-range grazing promotes biodiversity by allowing natural vegetation recovery but can lead to habitat destruction if unmanaged, increasing carbon footprint. Sustainable land use favors zero grazing for intensive farming with smaller land footprint, while free-range supports ecological balance in extensive grazing areas.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Operational Expenses
Zero grazing systems require higher initial investment costs for infrastructure such as pens and feed storage, but offer controlled feeding that reduces feed wastage and disease incidence. Free-range systems have lower setup expenses, relying on natural grazing, but incur higher operational costs due to supplemental feeding, increased veterinary care, and potential loss from predation. Cost analysis reveals zero grazing maximizes resource efficiency and long-term savings despite upfront investments, while free-range offers lower entry costs but variable ongoing expenses.
Labor and Time Requirements in Both Systems
Zero grazing goat management demands intensive labor for daily feeding, cleaning, and health monitoring within confined spaces, resulting in higher time investment per animal. Free-range systems reduce daily labor as goats forage naturally, but require more time for supervision, boundary maintenance, and occasional health checks to prevent predation and disease. Efficiency in labor and time depends on scale, with zero grazing benefiting small-scale producers and free-range suiting extensive operations.
Choosing the Best System for Your Goat Farm
Zero grazing goat management enhances feed efficiency by providing controlled nutrition and reducing pasture degradation, ideal for limited land areas. Free-range systems allow goats to exhibit natural behaviors and access diverse forage, improving overall health and meat quality but require ample space and predator protection. Selecting the best system depends on farm size, resource availability, and production goals to balance productivity and animal welfare effectively.
Zero Grazing vs Free-Range for Goat Management Systems Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com