Goslings are young geese characterized by soft down feathers and require extra care such as frequent feeding and warm shelter. Adult geese have fully developed feathers, enhanced flight abilities, and a more robust immune system, making them more resilient to environmental changes. Understanding the age difference between goslings and adults helps ensure proper nutrition and habitat adjustments for optimal goose health.
Table of Comparison
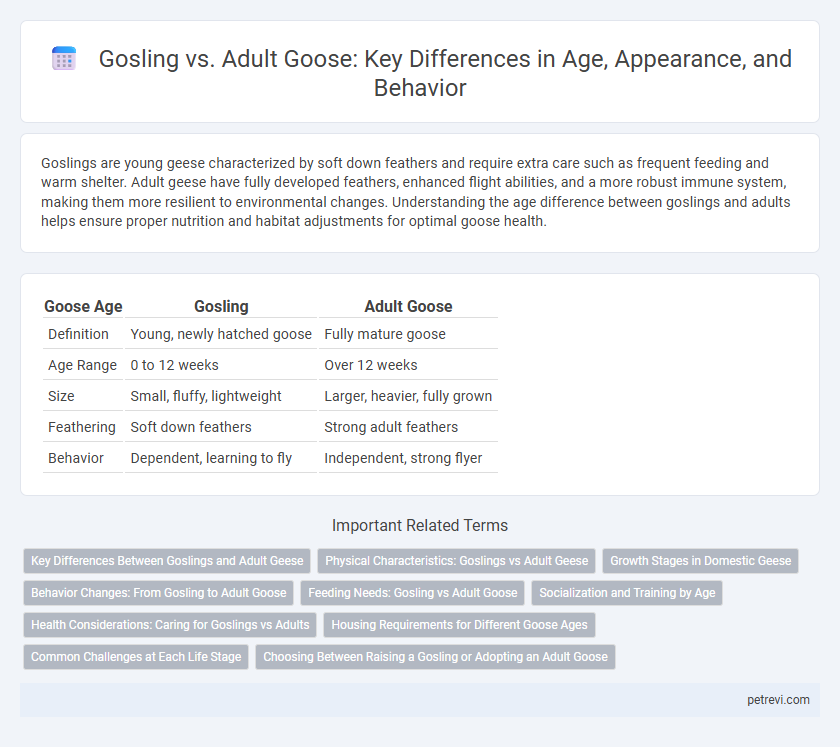
| Goose Age | Gosling | Adult Goose |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Young, newly hatched goose | Fully mature goose |
| Age Range | 0 to 12 weeks | Over 12 weeks |
| Size | Small, fluffy, lightweight | Larger, heavier, fully grown |
| Feathering | Soft down feathers | Strong adult feathers |
| Behavior | Dependent, learning to fly | Independent, strong flyer |
Key Differences Between Goslings and Adult Geese
Goslings are young geese characterized by their soft down feathers and smaller size, while adult geese have fully developed plumage and a larger body. The transition from gosling to adult involves significant growth, feather replacement, and increased independence in feeding and flight capabilities. These key differences highlight the developmental stages critical for survival and adaptation in geese populations.
Physical Characteristics: Goslings vs Adult Geese
Goslings are covered in soft, downy feathers that are yellow or light gray, while adult geese have fully developed waterproof feathers with varying patterns of brown, white, and black. Goslings have shorter necks and legs, which grow longer and more robust as they mature into adults. Adult geese also exhibit stronger beaks and larger body sizes compared to the small, fragile frame of goslings.
Growth Stages in Domestic Geese
Goslings represent the initial growth stage of domestic geese, characterized by rapid development, soft down feathers, and dependence on parental care for warmth and feeding. As they mature into adults, geese develop fully waterproof feathers, increased body size, and reproductive capability typically reached by 5 to 7 months of age. Understanding these growth stages is essential for proper feeding, housing, and management to ensure optimal health and productivity in domestic geese.
Behavior Changes: From Gosling to Adult Goose
Goslings exhibit high dependence on their parents, staying close to the family for warmth and protection while learning essential survival skills such as foraging and swimming. As geese mature into adults, their behavior shifts towards territoriality and social hierarchy establishment within flocks, often engaging in vocalizations and aggressive displays to defend nesting areas. Adult geese also develop migratory instincts, undertaking seasonal journeys that goslings experience only after full maturation.
Feeding Needs: Gosling vs Adult Goose
Goslings require a high-protein diet with about 18-20% protein content to support rapid growth, including starter feeds enriched with essential nutrients and access to fresh water. Adult geese need a balanced diet lower in protein, around 12-16%, consisting primarily of grasses, grains, and supplemented grains for energy maintenance. Feeding practices must align with age-specific nutritional requirements to ensure optimal health, development, and productivity in both goslings and adult geese.
Socialization and Training by Age
Goslings require early socialization and gentle training to develop trust and adapt to human interaction, which is crucial within the first few weeks of life. Adult geese, having established social hierarchies, benefit from consistent reinforcement of learned behaviors and social boundaries to maintain calmness and cooperation. Training practices tailored to each age group enhance bonding and reduce aggressive tendencies in geese.
Health Considerations: Caring for Goslings vs Adults
Goslings require specialized care to support their developing immune systems, including warm environments and frequent feeding to prevent hypothermia and malnutrition. Adult geese need regular exercise and a balanced diet to maintain their health and prevent obesity-related issues, such as joint problems. Monitoring both age groups for signs of respiratory infections and parasites is essential for effective health management.
Housing Requirements for Different Goose Ages
Goslings require warm, dry housing with protected brooding areas to support their rapid growth and vulnerability to cold and predators. Adult geese need spacious, well-ventilated shelters with sturdy fencing to accommodate their larger size and territorial behavior while providing easy access to outdoor grazing areas. Properly designed housing for each age group optimizes health, development, and overall welfare throughout the goose lifecycle.
Common Challenges at Each Life Stage
Goslings face vulnerability to predators and require constant parental care and a high-protein diet for proper growth, while adult geese struggle with territorial conflicts and maintaining energy reserves during migration. Immature goslings encounter challenges in learning flight and social behaviors critical for survival. Adults must also manage molting periods when they are temporarily flightless and more susceptible to threats.
Choosing Between Raising a Gosling or Adopting an Adult Goose
Choosing between raising a gosling or adopting an adult goose depends on your experience and the commitment you can provide. Goslings require intensive care, including frequent feeding, temperature control, and close monitoring to ensure proper growth and health. Adult geese are generally easier to manage, already socialized, and can adapt quickly to new environments, making them suitable for those seeking lower-maintenance birds.
Gosling vs Adult for Goose Age Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com