Selective breeding in geese enhances desirable traits such as size, temperament, and egg production through controlled mating, resulting in predictable and consistent offspring qualities. Natural breeding relies on instinctive mate choice, promoting genetic diversity and adaptability but often yields less uniformity in traits. Choosing between selective and natural breeding depends on goals for flock performance, genetic health, and breeding management.
Table of Comparison
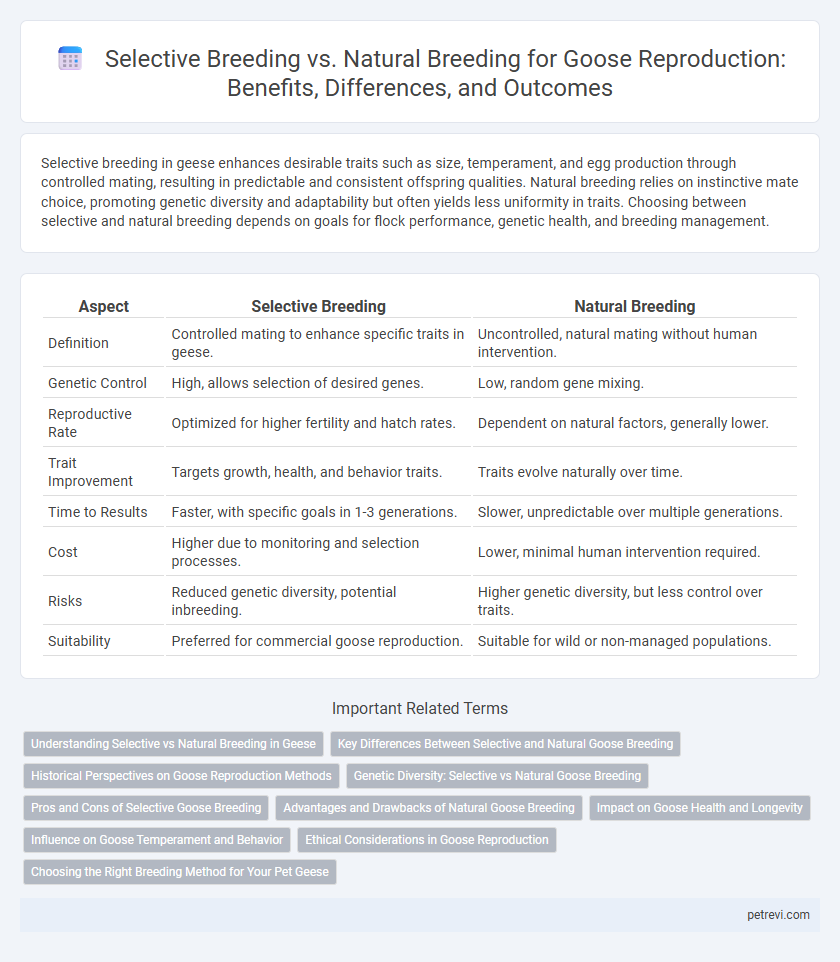
| Aspect | Selective Breeding | Natural Breeding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled mating to enhance specific traits in geese. | Uncontrolled, natural mating without human intervention. |
| Genetic Control | High, allows selection of desired genes. | Low, random gene mixing. |
| Reproductive Rate | Optimized for higher fertility and hatch rates. | Dependent on natural factors, generally lower. |
| Trait Improvement | Targets growth, health, and behavior traits. | Traits evolve naturally over time. |
| Time to Results | Faster, with specific goals in 1-3 generations. | Slower, unpredictable over multiple generations. |
| Cost | Higher due to monitoring and selection processes. | Lower, minimal human intervention required. |
| Risks | Reduced genetic diversity, potential inbreeding. | Higher genetic diversity, but less control over traits. |
| Suitability | Preferred for commercial goose reproduction. | Suitable for wild or non-managed populations. |
Understanding Selective vs Natural Breeding in Geese
Selective breeding in geese involves choosing specific pairs with desirable traits such as growth rate, egg production, or plumage quality, resulting in enhanced productivity and uniform offspring. Natural breeding relies on geese mating without human intervention, promoting genetic diversity and natural adaptation to the environment. Understanding these methods enables optimization of reproduction strategies for both commercial yield and ecological balance in goose populations.
Key Differences Between Selective and Natural Goose Breeding
Selective breeding for geese involves human intervention to enhance specific traits such as growth rate, egg production, and disease resistance, resulting in more predictable and uniform offspring. Natural breeding relies on environmental factors and mate selection without human control, leading to greater genetic diversity but less consistency in desired characteristics. The key difference lies in controlled trait selection versus organic genetic variation and adaptability.
Historical Perspectives on Goose Reproduction Methods
Selective breeding of geese began centuries ago, driven by human desires to enhance traits like size, feather quality, and egg production, contrasting with natural breeding where environmental pressures shaped survival traits. Historical records from ancient China and Europe document early attempts to control mating for desirable characteristics, leading to domesticated breeds distinct from their wild ancestors. Over time, selective breeding transformed geese reproduction by prioritizing productivity and temperament, whereas natural breeding maintained genetic diversity and adaptability within wild populations.
Genetic Diversity: Selective vs Natural Goose Breeding
Selective breeding in geese concentrates on specific traits such as growth rate, egg production, and plumage quality, often reducing genetic diversity by favoring a limited gene pool. Natural breeding preserves higher genetic variability as mate choice occurs without human intervention, promoting resilience and adaptation to environmental changes. Maintaining genetic diversity through natural breeding enhances disease resistance and long-term sustainability of goose populations.
Pros and Cons of Selective Goose Breeding
Selective goose breeding enhances traits such as growth rate, egg production, and disease resistance, leading to higher productivity and economic value. However, it can reduce genetic diversity, increasing vulnerability to environmental changes and hereditary health issues. Natural breeding maintains genetic variability and adaptability but may result in slower improvements in desired traits and lower overall yields.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Natural Goose Breeding
Natural goose breeding ensures genetic diversity and adaptability, enhancing the flock's resilience to environmental changes. It requires less human intervention and maintains natural behaviors, supporting healthier offspring development. However, natural breeding can result in slower reproductive rates and less control over desirable traits compared to selective breeding methods.
Impact on Goose Health and Longevity
Selective breeding in geese enhances specific traits like growth rate and feather quality but can increase susceptibility to genetic disorders, impacting overall health and longevity. Natural breeding maintains genetic diversity, promoting stronger immune systems and adaptability to environmental changes. Balancing both methods ensures optimal health and lifespan outcomes for goose populations.
Influence on Goose Temperament and Behavior
Selective breeding in geese often results in docile and predictable temperaments, as breeders prioritize traits like calmness and reduced aggression to facilitate easier handling and management. Natural breeding preserves a broader range of behavioral traits, including increased territoriality, instinct-driven responsiveness, and social hierarchy dynamics that are crucial for survival in wild environments. The influence of breeding methods on goose temperament directly impacts their adaptability, social interactions, and suitability for various farming or conservation purposes.
Ethical Considerations in Goose Reproduction
Selective breeding in goose reproduction raises ethical concerns regarding genetic diversity reduction and potential animal welfare compromises due to inbreeding. Natural breeding preserves genetic variation by allowing geese to mate without human intervention, promoting healthier populations and more robust resilience to diseases. Ethical considerations emphasize balancing productivity goals with the well-being and natural behaviors of geese to ensure sustainable and humane breeding practices.
Choosing the Right Breeding Method for Your Pet Geese
Selective breeding in geese focuses on enhancing desired traits such as growth rate, egg production, and temperament by controlling mating pairs, resulting in predictable and improved offspring quality. Natural breeding allows geese to reproduce without human intervention, promoting genetic diversity and maintaining robust health but with less control over specific traits. Choosing the right breeding method depends on the breeder's goals, whether prioritizing specific characteristics through selective breeding or valuing genetic variation and natural behaviors with natural breeding.
Selective breeding vs Natural breeding for Goose reproduction Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com