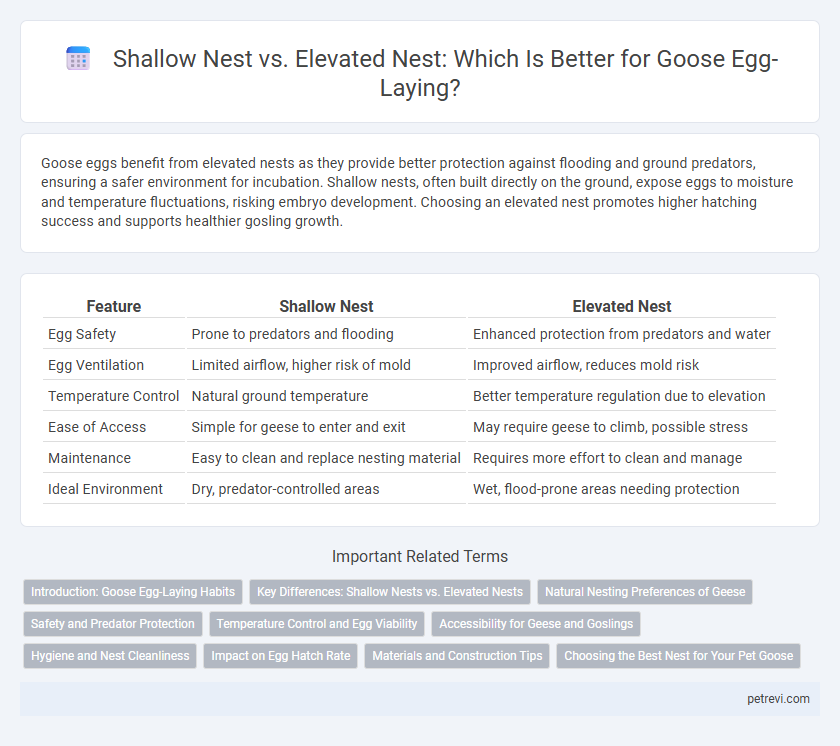
Goose eggs benefit from elevated nests as they provide better protection against flooding and ground predators, ensuring a safer environment for incubation. Shallow nests, often built directly on the ground, expose eggs to moisture and temperature fluctuations, risking embryo development. Choosing an elevated nest promotes higher hatching success and supports healthier gosling growth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shallow Nest | Elevated Nest |
|---|---|---|
| Egg Safety | Prone to predators and flooding | Enhanced protection from predators and water |
| Egg Ventilation | Limited airflow, higher risk of mold | Improved airflow, reduces mold risk |
| Temperature Control | Natural ground temperature | Better temperature regulation due to elevation |
| Ease of Access | Simple for geese to enter and exit | May require geese to climb, possible stress |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and replace nesting material | Requires more effort to clean and manage |
| Ideal Environment | Dry, predator-controlled areas | Wet, flood-prone areas needing protection |
Introduction: Goose Egg-Laying Habits
Goose egg-laying habits vary between shallow nest and elevated nest preferences, impacting hatchling survival rates. Shallow nests, typically constructed on ground vegetation, offer easy access but increase vulnerability to predators and flooding. Elevated nests, built on raised platforms or natural elevations, provide better protection and drainage, enhancing egg viability in diverse habitats.
Key Differences: Shallow Nests vs. Elevated Nests
Shallow nests for goose egg-laying are typically located on the ground, providing easy access but increased vulnerability to predators and flooding. Elevated nests, built on raised platforms or natural structures like rocky outcrops, offer better protection from ground-level threats and moisture, enhancing egg survival rates. The key differences lie in safety, moisture exposure, and accessibility, with elevated nests generally favored in wet or predator-rich environments.
Natural Nesting Preferences of Geese
Geese naturally prefer elevated nests to reduce the risk of flooding and predation, ensuring greater egg survival rates. Shallow nests, often found on ground-level vegetation, expose eggs to environmental hazards and predators, decreasing hatch success. Elevated nesting sites provide better ventilation and visibility, aligning with geese's instinctual behaviors for protecting their offspring.
Safety and Predator Protection
Shallow nests for goose egg-laying offer limited protection, making eggs more vulnerable to predators such as foxes and raccoons due to easy access. Elevated nests improve safety by providing a physical barrier that deters ground-based predators and reduces flooding risks, enhancing egg survival rates. Studies show geese using elevated nesting sites experience higher hatching success because of enhanced predator protection and environmental stability.
Temperature Control and Egg Viability
Shallow nests for goose egg-laying provide limited insulation, resulting in greater temperature fluctuations that can negatively impact egg viability. Elevated nests offer improved temperature control by promoting better air circulation and reducing moisture buildup, creating a stable microclimate essential for embryo development. Optimal temperature regulation in elevated nests enhances hatch rates and ensures higher survival chances for goslings.
Accessibility for Geese and Goslings
Elevated nests provide enhanced protection from ground predators and flooding, improving egg and gosling survival rates by keeping the nest dry and secure. Shallow nests offer easier accessibility for geese and newly hatched goslings, reducing the risk of injury during movement to and from the nest site. Balancing nest elevation with ease of access supports optimal breeding success by accommodating the mobility of both adult geese and vulnerable goslings.
Hygiene and Nest Cleanliness
Elevated nests for goose egg-laying significantly improve hygiene by reducing exposure to ground moisture and parasites, which are common in shallow nests. These elevated structures allow for better airflow, minimizing bacterial growth and maintaining cleaner eggs. Proper nest cleanliness in elevated nests directly contributes to higher hatchability rates and healthier goslings.
Impact on Egg Hatch Rate
Elevated nests for geese create a safer environment by reducing exposure to predators and flooding, significantly improving the egg hatch rate compared to shallow nests. Shallow nests are more vulnerable to temperature fluctuations and moisture, which can negatively impact embryo development and decrease hatch success. Studies indicate that elevated nesting sites can increase goose egg hatch rates by up to 20%, highlighting the importance of nest placement for reproductive outcomes.
Materials and Construction Tips
Goose shallow nests typically use soft grasses, straw, and feathers for cushioning, constructed as simple ground depressions lined with insulating materials to protect eggs from moisture and temperature fluctuations. Elevated nests require sturdy platforms or baskets made from wood or wire, ensuring secure placement above ground to deter predators and improve airflow, with added bedding of hay or dried grass for comfort. When building nests, choose natural, breathable materials to maintain warmth and dryness, and secure elevated nests firmly to withstand wind and prevent tipping.
Choosing the Best Nest for Your Pet Goose
Elevated nests for goose egg-laying offer better protection from predators and moisture, promoting healthier hatch rates compared to shallow nests. Shallow nests can cause eggs to roll and risk damage, while elevated designs provide stability and improved ventilation that mimic natural nesting environments. Choosing an elevated nest enhances your pet goose's comfort and increases the likelihood of successful incubation.
Shallow nest vs Elevated nest for Goose egg-laying Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com