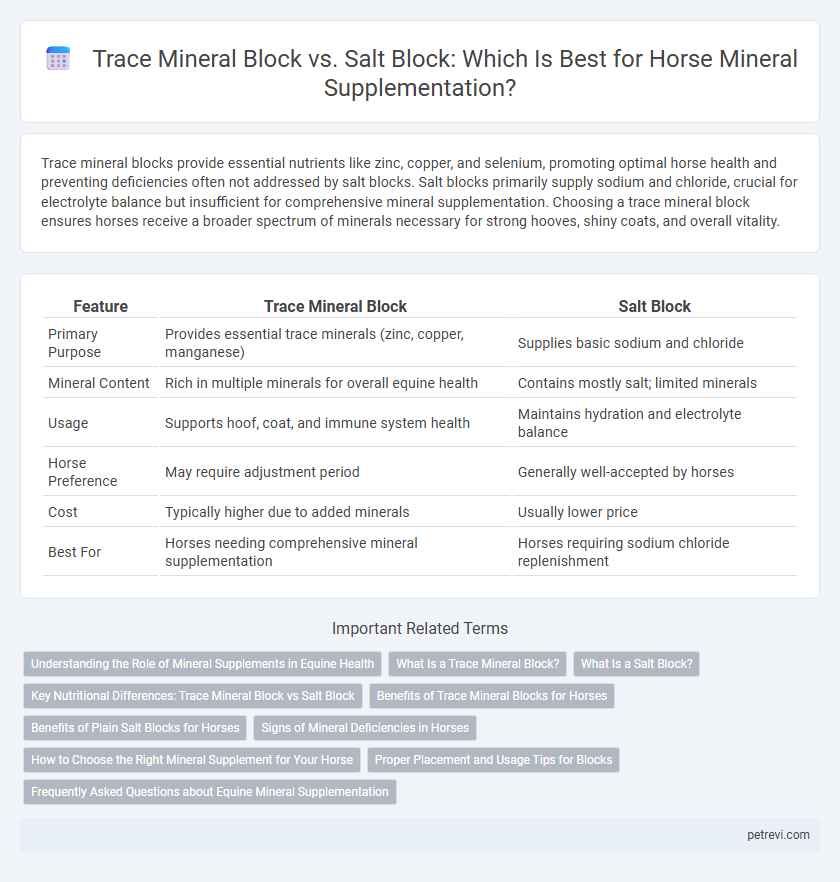
Trace mineral blocks provide essential nutrients like zinc, copper, and selenium, promoting optimal horse health and preventing deficiencies often not addressed by salt blocks. Salt blocks primarily supply sodium and chloride, crucial for electrolyte balance but insufficient for comprehensive mineral supplementation. Choosing a trace mineral block ensures horses receive a broader spectrum of minerals necessary for strong hooves, shiny coats, and overall vitality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Trace Mineral Block | Salt Block |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Provides essential trace minerals (zinc, copper, manganese) | Supplies basic sodium and chloride |
| Mineral Content | Rich in multiple minerals for overall equine health | Contains mostly salt; limited minerals |
| Usage | Supports hoof, coat, and immune system health | Maintains hydration and electrolyte balance |
| Horse Preference | May require adjustment period | Generally well-accepted by horses |
| Cost | Typically higher due to added minerals | Usually lower price |
| Best For | Horses needing comprehensive mineral supplementation | Horses requiring sodium chloride replenishment |
Understanding the Role of Mineral Supplements in Equine Health
Trace mineral blocks provide essential micronutrients like zinc, copper, and selenium that support enzyme function, immune response, and coat quality in horses, making them crucial for overall equine health. Salt blocks primarily supply sodium and chloride to maintain electrolyte balance and hydration but lack vital trace minerals necessary for metabolic processes. Optimal equine mineral supplementation involves combining trace mineral blocks with salt blocks to ensure horses receive a comprehensive range of minerals for growth, reproduction, and performance.
What Is a Trace Mineral Block?
A trace mineral block for horses is a concentrated supplement designed to provide essential trace minerals such as zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium, which support overall health, immune function, and hoof quality. Unlike plain salt blocks that primarily supply sodium chloride to maintain electrolyte balance and hydration, trace mineral blocks offer a broader spectrum of nutrients necessary for metabolic processes and tissue repair. These blocks help prevent mineral deficiencies commonly found in forage-based diets, promoting optimal growth, reproduction, and performance in horses.
What Is a Salt Block?
A salt block is a solid form of sodium chloride designed to provide horses with essential electrolytes and encourage natural licking behavior for hydration and mineral balance. It often contains minimal additional minerals, making it primarily a source of salt rather than a comprehensive trace mineral supplement. Salt blocks support proper nerve function, muscle contractions, and overall fluid regulation in horses but may require supplementation with trace mineral blocks for complete nutritional support.
Key Nutritional Differences: Trace Mineral Block vs Salt Block
Trace mineral blocks provide essential micronutrients such as zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium, supporting immune function and metabolic processes in horses, whereas salt blocks primarily supply sodium and chloride to maintain electrolyte balance and hydration. Trace mineral blocks promote bone development, enzyme activity, and reproductive health, while salt blocks help regulate nerve impulses and muscle contractions. Horses requiring comprehensive mineral supplementation benefit more from trace mineral blocks, while salt blocks suffice when the primary need is electrolyte replenishment.
Benefits of Trace Mineral Blocks for Horses
Trace mineral blocks provide essential nutrients such as zinc, copper, selenium, and manganese, which support horses' immune function, coat health, and hoof strength. These blocks help prevent common deficiencies that salt blocks alone cannot address, promoting overall metabolic and enzymatic processes critical for equine well-being. Horses consuming trace mineral blocks exhibit improved muscle function and reproductive health due to balanced mineral intake.
Benefits of Plain Salt Blocks for Horses
Plain salt blocks provide essential sodium and chloride, crucial electrolytes for maintaining proper hydration and nerve function in horses. These blocks encourage natural licking behavior, allowing horses to self-regulate their salt intake based on individual needs, reducing the risk of overconsumption. Salt blocks also support muscle function and help maintain acid-base balance, promoting overall health without the risk of mineral imbalances found in complex supplements.
Signs of Mineral Deficiencies in Horses
Signs of mineral deficiencies in horses include poor coat condition, muscle weakness, and decreased appetite, often linked to inadequate intake of essential trace minerals like copper, zinc, and selenium. Trace mineral blocks provide targeted supplementation to address these specific deficiencies, unlike salt blocks which primarily supply sodium and chloride and do not fulfill broader mineral requirements. Monitoring horses for symptoms such as lethargy or joint stiffness can indicate the need to switch from salt blocks to comprehensive trace mineral blocks for optimal health.
How to Choose the Right Mineral Supplement for Your Horse
Choosing the right mineral supplement for your horse depends on assessing their specific nutritional needs, workload, and forage quality. Trace mineral blocks provide essential micronutrients like copper, zinc, and selenium, which support immune function and metabolic processes, while salt blocks primarily fulfill sodium and chloride requirements to maintain electrolyte balance. Testing forage and water sources helps determine deficiencies, guiding the selection between a comprehensive trace mineral block or a simple salt block to optimize your horse's health and performance.
Proper Placement and Usage Tips for Blocks
Proper placement of trace mineral blocks and salt blocks is crucial to ensure horses have consistent access for optimal mineral supplementation. Blocks should be positioned in dry, shaded areas away from feeders to prevent contamination and encourage regular use. Regularly inspect blocks for wear and cleanliness, replacing them as needed to maintain consistent mineral intake.
Frequently Asked Questions about Equine Mineral Supplementation
Trace mineral blocks provide essential minerals like zinc, copper, and manganese crucial for horse metabolism, immune function, and hoof health, whereas salt blocks primarily supply sodium and chloride needed for hydration and electrolyte balance. Owners often ask if trace mineral blocks can replace complete mineral supplements; while beneficial, they should complement a balanced diet rather than substitute comprehensive mineral blends. Selecting the right block depends on forage quality, workload, and specific deficiencies diagnosed by equine nutritionists or veterinarians.
Trace Mineral Block vs Salt Block for Horse Mineral Supplementation Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com