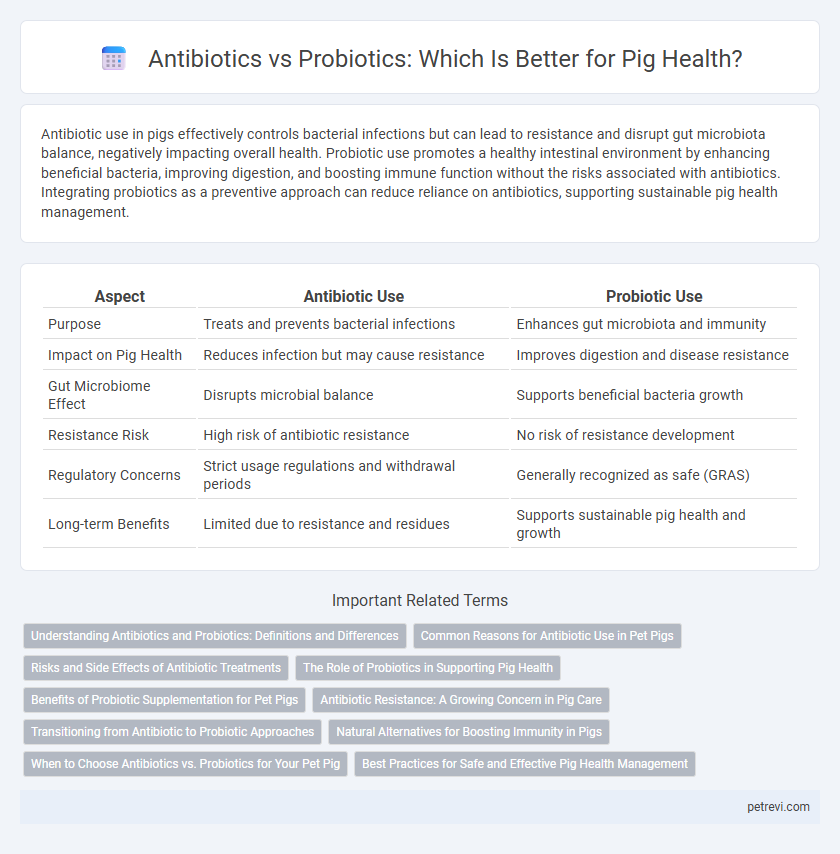
Antibiotic use in pigs effectively controls bacterial infections but can lead to resistance and disrupt gut microbiota balance, negatively impacting overall health. Probiotic use promotes a healthy intestinal environment by enhancing beneficial bacteria, improving digestion, and boosting immune function without the risks associated with antibiotics. Integrating probiotics as a preventive approach can reduce reliance on antibiotics, supporting sustainable pig health management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Antibiotic Use | Probiotic Use |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Treats and prevents bacterial infections | Enhances gut microbiota and immunity |
| Impact on Pig Health | Reduces infection but may cause resistance | Improves digestion and disease resistance |
| Gut Microbiome Effect | Disrupts microbial balance | Supports beneficial bacteria growth |
| Resistance Risk | High risk of antibiotic resistance | No risk of resistance development |
| Regulatory Concerns | Strict usage regulations and withdrawal periods | Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) |
| Long-term Benefits | Limited due to resistance and residues | Supports sustainable pig health and growth |
Understanding Antibiotics and Probiotics: Definitions and Differences
Antibiotics in pig health are medications designed to kill or inhibit harmful bacteria, often used to treat or prevent infections but can disrupt gut microbiota balance. Probiotics consist of live beneficial microorganisms that promote intestinal health by enhancing microbial diversity and supporting immune function. Unlike antibiotics, probiotics aim to maintain or restore gut flora equilibrium without contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Common Reasons for Antibiotic Use in Pet Pigs
Antibiotics are commonly used in pet pigs to treat bacterial infections such as respiratory diseases, gastrointestinal infections, and wound infections, aiming to reduce mortality and morbidity. Probiotics offer a natural alternative by enhancing gut health, improving digestion, and boosting the immune system, potentially reducing the need for antibiotics. Overuse of antibiotics in pet pigs can lead to antibiotic resistance, making probiotics a crucial component in sustainable health management.
Risks and Side Effects of Antibiotic Treatments
Antibiotic use in pigs carries significant risks, including the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and disruption of the gut microbiota, which can lead to decreased immunity and growth performance. Side effects often include gastrointestinal disturbances and increased susceptibility to secondary infections. In contrast, probiotics promote a balanced intestinal environment, enhancing gut health without the adverse consequences associated with antibiotics.
The Role of Probiotics in Supporting Pig Health
Probiotics play a crucial role in supporting pig health by enhancing gut microbiota balance, improving nutrient absorption, and boosting the immune system, which reduces the reliance on antibiotics. Unlike antibiotics that may contribute to antimicrobial resistance, probiotics promote natural disease resistance and improve growth performance in pigs through beneficial bacterial colonization. Incorporating probiotics in pig diets supports gastrointestinal health, decreases pathogen load, and leads to healthier, more resilient swine populations.
Benefits of Probiotic Supplementation for Pet Pigs
Probiotic supplementation in pet pigs enhances gut health by promoting beneficial microflora and improving nutrient absorption, leading to stronger immune responses compared to traditional antibiotic use. Unlike antibiotics, which may cause resistance and disrupt microbial balance, probiotics support long-term digestive health and reduce the incidence of gastrointestinal disorders. This natural approach contributes to improved growth rates, reduced diarrhea, and overall better well-being in pet pigs.
Antibiotic Resistance: A Growing Concern in Pig Care
Excessive antibiotic use in pig farming contributes significantly to the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a major threat to animal and human health. Probiotics offer a sustainable alternative by enhancing gut health and immunity without promoting resistance. Implementing probiotics in pig diets reduces reliance on antibiotics, mitigating the spread of resistant pathogens in swine production.
Transitioning from Antibiotic to Probiotic Approaches
Transitioning from antibiotic to probiotic approaches in pig health management reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance and promotes gut microbiota balance, enhancing immune function and nutrient absorption. Probiotic supplementation with strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium supports intestinal integrity and lowers incidences of diarrhea during weaning, a critical phase in pig development. Emphasizing probiotics aligns with sustainable farming practices by improving growth performance and minimizing the environmental impact of antibiotic residues.
Natural Alternatives for Boosting Immunity in Pigs
Probiotic use in pigs enhances gut microbiota balance, promoting stronger immune responses compared to traditional antibiotic treatments that risk resistance development. Natural alternatives such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains improve nutrient absorption and reduce pathogenic bacteria, leading to healthier, more resilient pigs. Incorporating probiotics supports sustainable pig farming by minimizing antibiotic residues and fostering long-term animal well-being.
When to Choose Antibiotics vs. Probiotics for Your Pet Pig
Antibiotics are most effective for treating bacterial infections in pigs when symptoms such as fever, lethargy, and localized inflammation are present, ensuring rapid recovery and preventing disease spread. Probiotics serve as preventive supplements that enhance gut microbiota balance, boost immunity, and improve digestion in healthy pigs or those recovering from illness. Choosing antibiotics is critical during active infections, while probiotics are ideal for promoting long-term health and preventing future gastrointestinal disturbances.
Best Practices for Safe and Effective Pig Health Management
Antibiotic use in pigs must follow strict guidelines to prevent resistance, emphasizing targeted treatments based on veterinary diagnosis and adherence to withdrawal periods. Probiotics offer a natural alternative by enhancing gut health, boosting immunity, and improving nutrient absorption without contributing to antimicrobial resistance. Integrating probiotics with judicious antibiotic use supports optimal pig growth and health while maintaining food safety and regulatory compliance.
Antibiotic use vs Probiotic use for Pig health Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com