Natural mating in pig breeding allows for natural behavior expression and can be cost-effective but may pose risks such as disease transmission and limited genetic diversity. Artificial insemination (AI) offers precise genetic selection, improved biosecurity, and higher reproductive efficiency, enhancing productivity. Choosing between natural mating and AI depends on farm management goals, herd size, and desired genetic improvement.
Table of Comparison
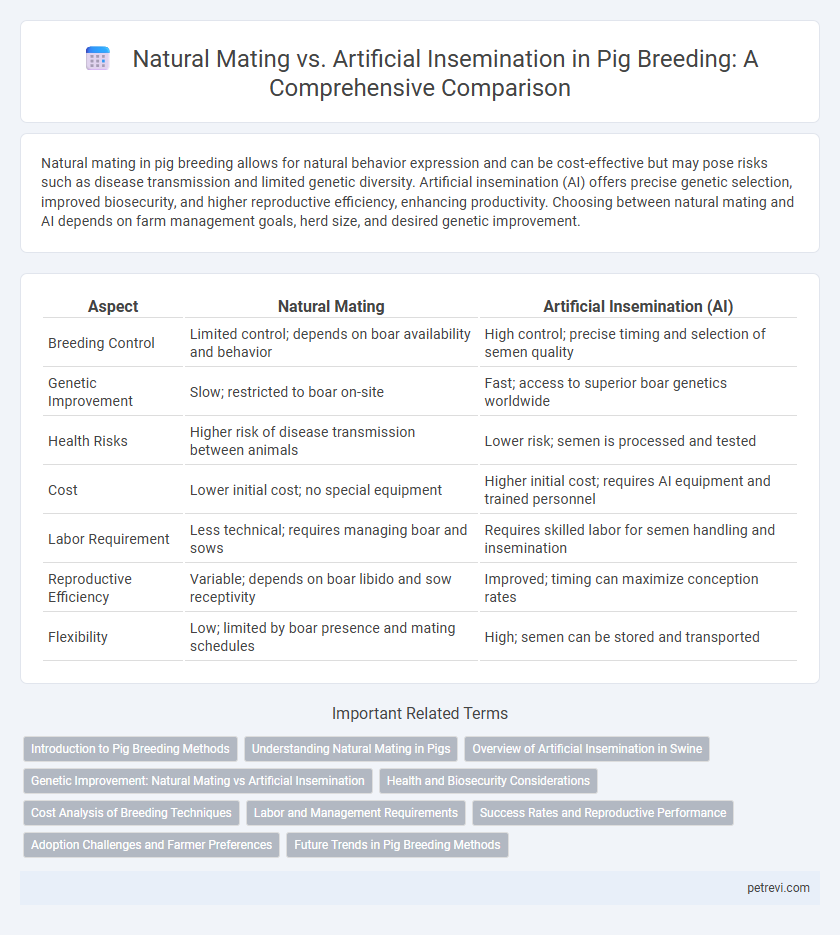
| Aspect | Natural Mating | Artificial Insemination (AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Breeding Control | Limited control; depends on boar availability and behavior | High control; precise timing and selection of semen quality |
| Genetic Improvement | Slow; restricted to boar on-site | Fast; access to superior boar genetics worldwide |
| Health Risks | Higher risk of disease transmission between animals | Lower risk; semen is processed and tested |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; no special equipment | Higher initial cost; requires AI equipment and trained personnel |
| Labor Requirement | Less technical; requires managing boar and sows | Requires skilled labor for semen handling and insemination |
| Reproductive Efficiency | Variable; depends on boar libido and sow receptivity | Improved; timing can maximize conception rates |
| Flexibility | Low; limited by boar presence and mating schedules | High; semen can be stored and transported |
Introduction to Pig Breeding Methods
Natural mating in pig breeding involves direct contact between the boar and sow, ensuring natural selection and behavioral compatibility, which can enhance offspring vigor. Artificial insemination (AI) allows precise control over genetic traits by using collected semen from superior boars, improving herd genetics and biosecurity. Both methods play critical roles in modern pig production, with AI increasingly favored for genetic advancement and disease prevention.
Understanding Natural Mating in Pigs
Natural mating in pigs involves direct copulation between a boar and a sow, allowing natural selection to influence breeding outcomes through behavioral cues and physical compatibility. This method supports natural estrus detection and can enhance fertility rates by synchronizing the insemination with the sow's optimal reproductive phase. Understanding the physiological and behavioral patterns during natural mating helps improve breeding efficiency and genetic diversity in pig populations.
Overview of Artificial Insemination in Swine
Artificial insemination (AI) in swine breeding involves the controlled deposition of semen into the reproductive tract of sows, enabling improved genetic selection and disease control. AI allows efficient use of superior boar genetics, enhances reproductive performance, and increases herd productivity by reducing the need for maintaining multiple boars. The technique requires precise timing relative to estrus and careful semen handling to maximize conception rates in pig breeding programs.
Genetic Improvement: Natural Mating vs Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination in pig breeding accelerates genetic improvement by enabling selective use of superior boars, increasing genetic diversity and reducing disease transmission risks. Natural mating limits genetic progress due to fewer mating opportunities and reliance on local boar availability, which may constrain breeding options. Utilizing artificial insemination allows for precise genetic selection, enhancing traits like growth rate, feed efficiency, and litter size more effectively than natural mating.
Health and Biosecurity Considerations
Natural mating in pig breeding minimizes stress on sows but increases the risk of disease transmission due to direct contact and potential introduction of pathogens from multiple boars. Artificial insemination enhances biosecurity by reducing physical interactions and enabling strict control over semen quality, thereby lowering the likelihood of spreading sexually transmitted infections and other diseases. Implementing rigorous health screening protocols for AI boars and maintaining sanitized equipment are critical for preventing biosecurity breaches in pig breeding operations.
Cost Analysis of Breeding Techniques
Natural mating in pig breeding typically incurs higher costs related to boar maintenance, housing, and labor, making it less economical for large-scale operations. Artificial insemination significantly reduces expenses by minimizing the number of boars required and optimizing semen use, leading to improved cost-efficiency. Studies report AI can decrease per litter breeding costs by up to 30%, enhancing profitability in intensive pig production systems.
Labor and Management Requirements
Natural mating in pig breeding demands continuous labor for heat detection, boar management, and mating supervision, requiring experienced staff and flexible scheduling. Artificial insemination significantly reduces labor intensity by allowing scheduled inseminations with stored semen, optimizing boar usage, and facilitating genetic improvement with less frequent physical handling. Efficient AI programs rely on trained technicians and meticulous estrus monitoring, enhancing overall herd management and reducing the need for maintaining multiple boars on-site.
Success Rates and Reproductive Performance
Natural mating in pig breeding often yields success rates influenced by boar fertility and the sow's estrus cycle, typically resulting in high conception rates but limited by boar availability and mating frequency. Artificial insemination (AI) enhances reproductive performance by enabling precise timing and genetic selection, achieving comparable or higher conception rates while increasing litter size and piglet viability. Both methods impact pig reproductive efficiency, with AI offering improved disease control and genetic advancement potential.
Adoption Challenges and Farmer Preferences
Natural mating in pig breeding faces challenges such as limited boar availability and higher risks of disease transmission, influencing farmer hesitation in widespread adoption. Artificial insemination offers controlled genetic improvement and reduced physical labor but requires investment in training and facilities, which can deter small-scale farmers. Preference often leans toward natural mating in regions with limited resources, while commercial operations favor artificial insemination for efficiency and herd health management.
Future Trends in Pig Breeding Methods
Future trends in pig breeding methods emphasize a shift towards integrating advanced genetic technologies with natural mating and artificial insemination (AI). Precision breeding using genomic selection combined with AI enhances reproductive efficiency, genetic diversity, and disease resistance in pig populations. Innovations such as real-time monitoring of estrus and automated AI systems are expected to further optimize breeding outcomes and reduce labor costs.
Natural mating vs Artificial insemination for Pig breeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com