Tethered pigs have limited mobility, often restricted to a small area, which can lead to stress and health issues due to lack of exercise. Free-range pigs move freely within larger, natural environments, promoting better physical fitness, natural behaviors, and overall well-being. Allowing free-range movement supports improved muscle development and reduces aggressive tendencies compared to tethered systems.
Table of Comparison
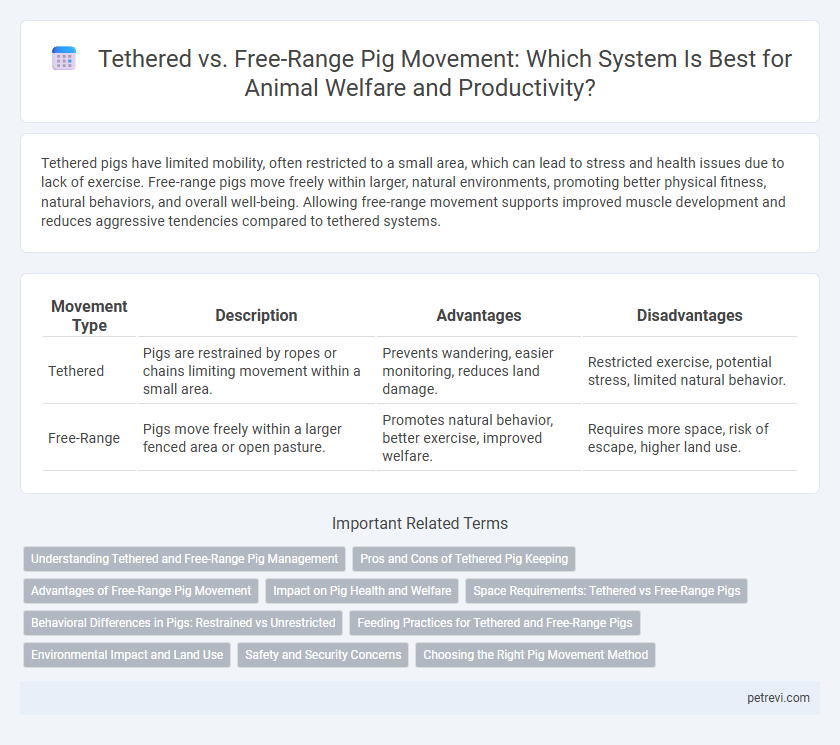
| Movement Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tethered | Pigs are restrained by ropes or chains limiting movement within a small area. | Prevents wandering, easier monitoring, reduces land damage. | Restricted exercise, potential stress, limited natural behavior. |
| Free-Range | Pigs move freely within a larger fenced area or open pasture. | Promotes natural behavior, better exercise, improved welfare. | Requires more space, risk of escape, higher land use. |
Understanding Tethered and Free-Range Pig Management
Tethered pig management involves restricting pigs with ropes or chains, limiting their movement and reducing risks of escape or damage to property, but potentially causing stress and health issues. Free-range pig management allows pigs to roam freely over a designated area, promoting natural behaviors, improved welfare, and better soil health through rooting and foraging activities. Understanding the benefits and challenges of each method helps optimize pig welfare, land use, and productivity in pig farming operations.
Pros and Cons of Tethered Pig Keeping
Tethered pig keeping allows for controlled movement, reducing the risk of crop damage and escape but can limit natural foraging behavior and cause stress due to restricted mobility. Tethering typically requires less land and infrastructure, making it cost-effective for small-scale farmers, yet it may increase vulnerability to predators and restrict social interactions among pigs. While it offers ease of monitoring, tethered pigs often experience slower growth rates compared to free-range counterparts due to limited exercise and natural foraging opportunities.
Advantages of Free-Range Pig Movement
Free-range pig movement enhances animal welfare by allowing natural behaviors such as rooting, foraging, and social interaction, which improve mental and physical health. This method reduces stress-related illnesses and promotes muscle development, resulting in higher quality meat with better flavor and texture. Free-range systems also contribute to sustainable farming by enabling pigs to naturally fertilize soil, supporting ecosystem balance and reducing the need for chemical inputs.
Impact on Pig Health and Welfare
Free-range pigs exhibit improved physical health and mental well-being due to increased movement, natural foraging behavior, and social interactions compared to tethered pigs. Tethering restricts locomotion, leading to muscle atrophy, increased stress levels, and higher susceptibility to diseases. Optimal pig welfare is achieved through environments that allow natural behaviors and exploration, significantly reducing behavioral issues and promoting cardiovascular and immune health.
Space Requirements: Tethered vs Free-Range Pigs
Tethered pigs typically require minimal space, often confined to small, designated areas that limit movement but facilitate feeding and management. Free-range pigs need substantially larger enclosures to roam freely, forage naturally, and exhibit behavioral activities essential for welfare. Space requirements for free-range systems range from 15 to 30 square meters per pig, significantly exceeding the restricted area allotted in tethered setups.
Behavioral Differences in Pigs: Restrained vs Unrestricted
Tethered pigs exhibit limited natural behaviors, often showing increased stress and aggression due to restricted movement and social interaction. Free-range pigs demonstrate enhanced exploratory activities, improved social behaviors, and reduced signs of stress, benefiting overall welfare and health. Behavioral studies confirm that unrestricted movement allows pigs to express innate behaviors crucial for psychological well-being and physical development.
Feeding Practices for Tethered and Free-Range Pigs
Tethered pigs typically rely on controlled feeding practices, receiving measured portions of commercial feed or supplements to ensure proper nutrition within limited movement areas. Free-range pigs forage naturally, consuming a diverse diet of grasses, roots, insects, and agricultural by-products, which enhances their nutrient intake through natural behavior. Feeding strategies for tethered pigs focus on maximizing feed efficiency, while free-range systems prioritize dietary variety to promote health and growth.
Environmental Impact and Land Use
Tethered pig systems restrict animal movement, leading to localized soil compaction and nutrient accumulation that can degrade pasture health and reduce biodiversity. Free-range pig farming promotes natural foraging behavior, improves soil aeration through rooting, and allows for more even nutrient distribution, resulting in healthier ecosystems and more sustainable land use. However, free-range systems require larger land areas to manage environmental impact effectively and prevent overgrazing.
Safety and Security Concerns
Tethered pigs face increased risks of injury and predation due to restricted movement, limiting their ability to escape threats. Free-range pigs benefit from enhanced safety by roaming larger areas, allowing natural behaviors that reduce stress and improve health. However, free-range systems require secure fencing and monitoring to prevent escapes and protect pigs from predators.
Choosing the Right Pig Movement Method
Tethered pig systems restrict movement, reducing land damage but increasing stress and health issues, whereas free-range setups promote natural behaviors and better welfare but require more space and management. Selecting the right pig movement method depends on farm size, environmental conditions, and welfare priorities, balancing productivity with animal well-being. Integrating rotational grazing with controlled access can optimize health outcomes and sustainable land use.
Tethered vs Free-Range for Pig Movement Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com