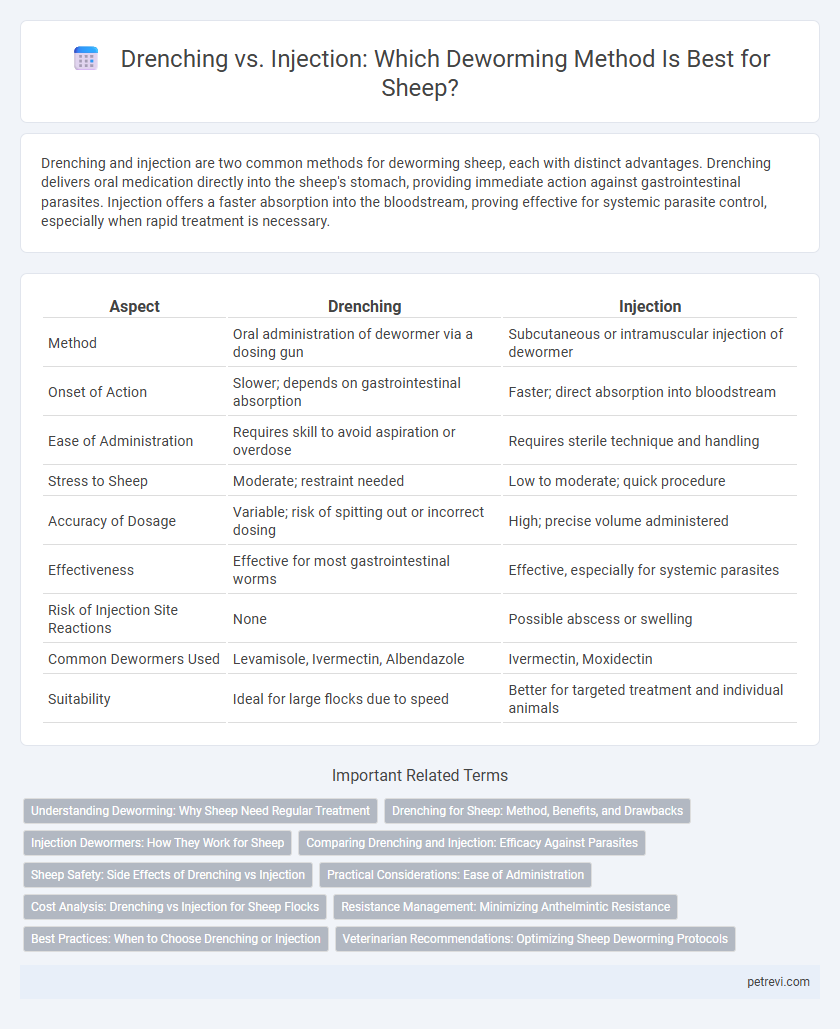
Drenching and injection are two common methods for deworming sheep, each with distinct advantages. Drenching delivers oral medication directly into the sheep's stomach, providing immediate action against gastrointestinal parasites. Injection offers a faster absorption into the bloodstream, proving effective for systemic parasite control, especially when rapid treatment is necessary.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Drenching | Injection |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Oral administration of dewormer via a dosing gun | Subcutaneous or intramuscular injection of dewormer |
| Onset of Action | Slower; depends on gastrointestinal absorption | Faster; direct absorption into bloodstream |
| Ease of Administration | Requires skill to avoid aspiration or overdose | Requires sterile technique and handling |
| Stress to Sheep | Moderate; restraint needed | Low to moderate; quick procedure |
| Accuracy of Dosage | Variable; risk of spitting out or incorrect dosing | High; precise volume administered |
| Effectiveness | Effective for most gastrointestinal worms | Effective, especially for systemic parasites |
| Risk of Injection Site Reactions | None | Possible abscess or swelling |
| Common Dewormers Used | Levamisole, Ivermectin, Albendazole | Ivermectin, Moxidectin |
| Suitability | Ideal for large flocks due to speed | Better for targeted treatment and individual animals |
Understanding Deworming: Why Sheep Need Regular Treatment
Sheep require regular deworming to control internal parasites that can cause weight loss, anemia, and reduced wool quality. Drenching administers liquid anthelmintics directly into the sheep's mouth, offering immediate gastrointestinal parasite control, whereas injectable treatments deliver systemic protection by targeting parasites circulating in the bloodstream. Understanding the benefits and limitations of both methods ensures effective parasite management, maintaining sheep health and productivity.
Drenching for Sheep: Method, Benefits, and Drawbacks
Drenching for sheep involves orally administering liquid dewormers using a dosing gun, allowing precise dosage based on the animal's weight to effectively combat internal parasites. This method offers ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and immediate dewormer delivery to the gastrointestinal tract, promoting rapid parasite control. However, drawbacks include potential aspiration pneumonia if improperly administered and the need for skill to ensure correct dosing, making careful handling critical for animal safety and treatment efficacy.
Injection Dewormers: How They Work for Sheep
Injection dewormers for sheep deliver active ingredients directly into the bloodstream, offering rapid and efficient parasite elimination. This method ensures precise dosing and better absorption compared to drenching, reducing the risk of improper administration and improving overall treatment efficacy. Injection dewormers target internal parasites such as gastrointestinal nematodes, liver flukes, and lungworms by disrupting their nervous system or metabolic pathways.
Comparing Drenching and Injection: Efficacy Against Parasites
Drenching delivers an oral anthelmintic directly to the gastrointestinal tract, targeting internal parasites effectively but requiring precise dosing and frequency to prevent resistance. Injection provides systemic absorption of dewormers, offering rapid and consistent efficacy against a broad spectrum of parasites, including those less accessible to drenched medications. Studies indicate injections often achieve higher bioavailability and longer-lasting protection compared to drenching, but selection depends on parasite type, farm management, and animal welfare considerations.
Sheep Safety: Side Effects of Drenching vs Injection
Drenching in sheep can cause stress and aspiration pneumonia if not performed correctly, posing risks to animal safety during deworming. Injection methods minimize the risk of aspiration but may lead to injection site reactions such as swelling or abscesses, affecting sheep welfare. Selecting the appropriate deworming technique depends on weighing the potential side effects on sheep safety and the skill level required for administration.
Practical Considerations: Ease of Administration
Drenching is favored for sheep deworming due to its ease of administration, requiring minimal handling and allowing rapid treatment of large flocks. Injection demands more skill, sterile equipment, and careful dosage, increasing labor time and stress on animals. Selecting the method depends on flock size, available labor, and the specific parasite targeted for effective control.
Cost Analysis: Drenching vs Injection for Sheep Flocks
Drenching is generally more cost-effective for large sheep flocks due to lower labor and equipment expenses compared to injections. Although injections may have higher upfront costs, they often provide longer-lasting efficacy, potentially reducing the frequency of treatment over time. Evaluating flock size, labor availability, and long-term parasite control goals is essential for an optimized deworming strategy balancing cost and effectiveness.
Resistance Management: Minimizing Anthelmintic Resistance
Drenching allows precise dosing based on weight but risks under-dosing if improperly administered, contributing to anthelmintic resistance in sheep. Injection ensures accurate delivery and absorption, reducing the likelihood of sub-lethal drug levels that promote resistant parasite strains. Strategic rotation of anthelmintic classes and targeted treatment based on fecal egg counts are essential to minimizing resistance regardless of administration method.
Best Practices: When to Choose Drenching or Injection
Drenching is best suited for routine worm control and delivers broad-spectrum anthelmintics directly to the gastrointestinal tract, ensuring rapid parasite clearance. Injection is preferred for severe infestations or when precise dosing is critical, as it allows for better absorption and reduces the risk of oral administration errors. Choosing between drenching and injection depends on parasite load, sheep health status, and the specific anthelmintic pharmacokinetics.
Veterinarian Recommendations: Optimizing Sheep Deworming Protocols
Veterinarians recommend selecting deworming methods based on parasite types, sheep health status, and environmental factors to optimize treatment efficacy. Drenching allows precise dosing against gastrointestinal parasites but requires skillful administration to avoid aspiration risks, while injections provide systemic action, especially for larvae in tissues or resistant parasites. Combining strategic drenching and targeted injections under veterinary guidance enhances parasite control, reduces resistance development, and promotes sheep welfare and productivity.
Drenching vs Injection for Sheep Deworming Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com