Ration feeding provides precise control over the nutritional intake of sheep, ensuring each animal receives balanced meals tailored to their specific growth and health requirements. Self-feeding allows sheep to graze or access feed freely, promoting natural feeding behaviors and reducing labor costs but may result in uneven nutrient consumption. Choosing between these methods depends on flock size, management goals, and available resources to optimize meal delivery and overall sheep productivity.
Table of Comparison
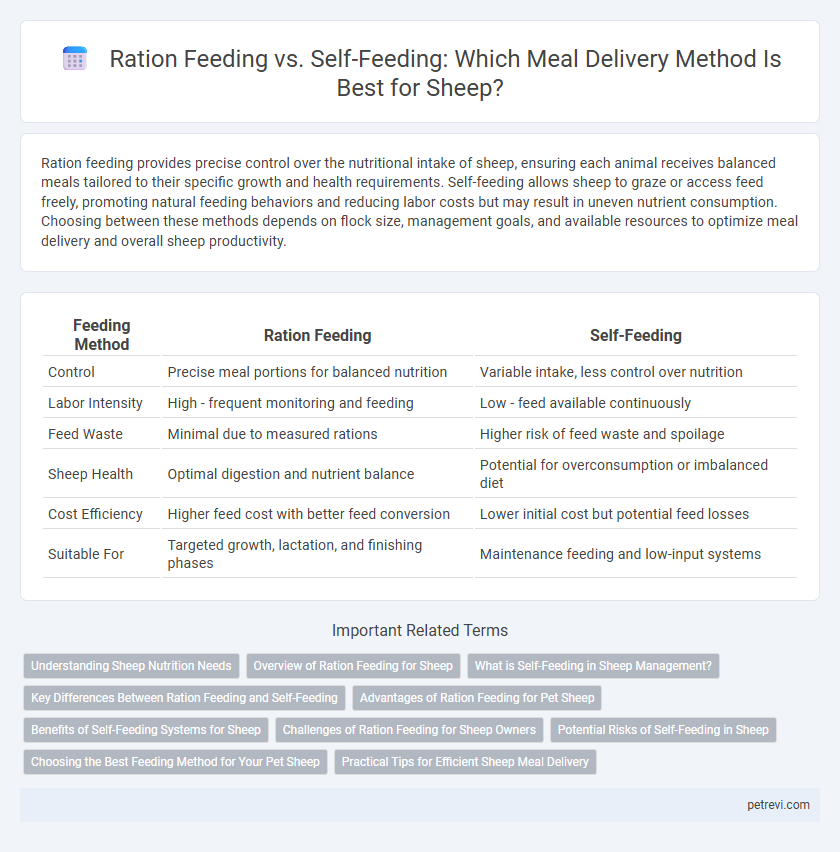
| Feeding Method | Ration Feeding | Self-Feeding |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Precise meal portions for balanced nutrition | Variable intake, less control over nutrition |
| Labor Intensity | High - frequent monitoring and feeding | Low - feed available continuously |
| Feed Waste | Minimal due to measured rations | Higher risk of feed waste and spoilage |
| Sheep Health | Optimal digestion and nutrient balance | Potential for overconsumption or imbalanced diet |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher feed cost with better feed conversion | Lower initial cost but potential feed losses |
| Suitable For | Targeted growth, lactation, and finishing phases | Maintenance feeding and low-input systems |
Understanding Sheep Nutrition Needs
Ration feeding provides precise control over nutrient intake, ensuring that sheep receive balanced levels of protein, energy, vitamins, and minerals essential for growth, reproduction, and wool production. Self-feeding allows sheep to consume feed ad libitum, but risks nutrient imbalances and overconsumption of concentrates, potentially causing digestive disturbances like acidosis. Understanding sheep nutrition needs requires analyzing factors such as physiological stage, forage quality, and individual variability to optimize ration formulations and promote health and productivity.
Overview of Ration Feeding for Sheep
Ration feeding for sheep involves providing a controlled and measured amount of feed, ensuring consistent nutrient intake tailored to the flock's specific requirements. This method improves feed efficiency, supports optimal growth and production, and reduces waste compared to self-feeding systems. By delivering balanced rations based on factors such as age, weight, and production stage, ration feeding enhances overall flock health and performance.
What is Self-Feeding in Sheep Management?
Self-feeding in sheep management refers to a method where sheep have continuous access to feed, allowing them to consume meals at their own pace throughout the day. This system reduces labor costs and minimizes feed waste by enabling natural grazing behaviors, leading to improved animal welfare and consistent nutritional intake. Common self-feeding setups include troughs or feeder bins strategically placed in the paddock, ensuring sheep can regulate their diet and maintain optimal health and productivity.
Key Differences Between Ration Feeding and Self-Feeding
Ration feeding in sheep involves delivering precise, controlled meal portions to ensure balanced nutrient intake, minimizing feed wastage and optimizing growth performance. Self-feeding allows sheep free access to feed, promoting natural eating behaviors but can lead to uneven nutrient consumption and increased risk of overfeeding or underfeeding. Understanding these key differences helps optimize feed efficiency, animal health, and farm profitability in sheep management.
Advantages of Ration Feeding for Pet Sheep
Ration feeding ensures precise control over nutrient intake for pet sheep, improving health and growth by preventing overfeeding and nutrient imbalances. It reduces feed wastage and allows easy monitoring of individual consumption, supporting tailored dietary adjustments. This method enhances feed efficiency and supports better management of digestive health in pet sheep.
Benefits of Self-Feeding Systems for Sheep
Self-feeding systems for sheep promote consistent nutrient intake by allowing animals to eat ad libitum, reducing feeding stress and improving overall growth rates. These systems enhance feed efficiency by minimizing wastage and ensuring sheep receive a balanced diet tailored to their individual needs. Improved animal welfare and labor cost reduction are significant advantages, making self-feeding a practical option for efficient sheep meal delivery.
Challenges of Ration Feeding for Sheep Owners
Ration feeding for sheep presents challenges such as the need for precise measurement and mixing of feed components to ensure balanced nutrition, which can be time-consuming for owners. Variability in individual sheep's feed intake often leads to uneven nutrient distribution, causing some animals to be underfed or overfed. Managing feed storage and preventing spoilage further complicate the consistency and quality of ration-based meal delivery.
Potential Risks of Self-Feeding in Sheep
Self-feeding in sheep can lead to uneven nutrient intake, resulting in overconsumption or deficiencies that affect growth and wool quality. Risks include increased incidence of bloat and acidosis due to rapid ingestion of high-concentrate feeds, posing significant health threats. Proper ration feeding ensures controlled portion sizes, balanced nutrient delivery, and reduces the likelihood of metabolic disorders in sheep flocks.
Choosing the Best Feeding Method for Your Pet Sheep
Ration feeding allows precise control of nutrient intake, ensuring balanced nutrition tailored to individual sheep's needs, which supports optimal growth and health. Self-feeding provides freedom for sheep to consume feed ad libitum, promoting natural grazing behavior but may risk overconsumption or nutritional imbalances. Selecting the best feeding method depends on factors like flock size, management goals, feed quality, and the specific health requirements of your pet sheep.
Practical Tips for Efficient Sheep Meal Delivery
Ration feeding involves providing measured amounts of feed, ensuring precise nutrient intake and minimizing waste, which supports consistent flock health and productivity. Self-feeding allows sheep to consume feed ad libitum, promoting natural eating behaviors but requires careful monitoring to prevent overconsumption and uneven nutrition. Implementing timed feeding schedules, investing in durable feeders, and regularly assessing sheep body condition scores optimize efficiency and maintain balanced nutrient delivery in both feeding methods.
Ration Feeding vs Self-feeding for Sheep Meal Delivery Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com