DNA testing provides a highly accurate and non-invasive method for determining bird gender by analyzing genetic material, offering reliable results from feathers, blood, or eggshells. Surgical sexing involves a minor procedure to visually inspect reproductive organs, which can yield immediate identification but carries risks related to anesthesia and potential injury. Compared to surgical sexing, DNA testing is safer, less stressful for the bird, and more suitable for a wide range of species, making it the preferred choice for avian gender determination.
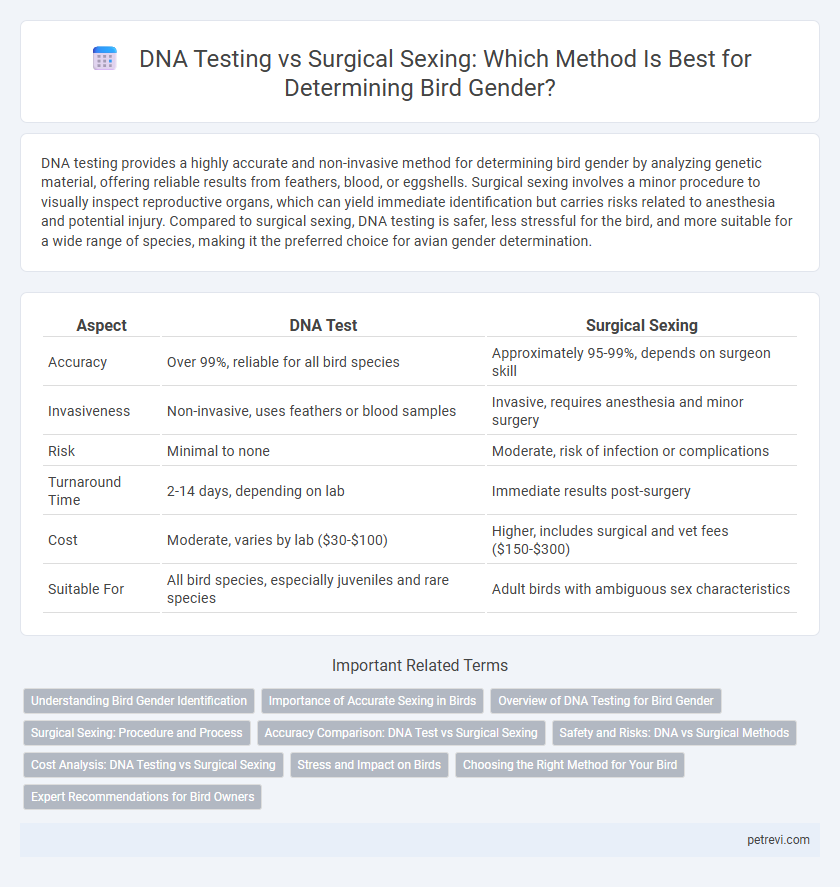
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | DNA Test | Surgical Sexing |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Over 99%, reliable for all bird species | Approximately 95-99%, depends on surgeon skill |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive, uses feathers or blood samples | Invasive, requires anesthesia and minor surgery |
| Risk | Minimal to none | Moderate, risk of infection or complications |
| Turnaround Time | 2-14 days, depending on lab | Immediate results post-surgery |
| Cost | Moderate, varies by lab ($30-$100) | Higher, includes surgical and vet fees ($150-$300) |
| Suitable For | All bird species, especially juveniles and rare species | Adult birds with ambiguous sex characteristics |
Understanding Bird Gender Identification
DNA testing for bird gender identification offers high accuracy by analyzing genetic material, making it reliable across various species, including those without visible sexual dimorphism. Surgical sexing involves endoscopic examination to visually confirm reproductive organs, providing immediate results but requiring anesthesia and specialized skills. Comparing both methods highlights DNA testing's non-invasive advantage and surgical sexing's direct observation, aiding informed decisions for breeders and avian veterinarians.
Importance of Accurate Sexing in Birds
Accurate sexing in birds is crucial for breeding programs, conservation efforts, and behavioral studies, ensuring appropriate pairing and management. DNA testing offers a highly reliable, non-invasive method by analyzing genetic markers, outperforming surgical sexing, which, though accurate, carries surgical risks and requires anesthetic expertise. Prioritizing DNA-based sex identification enhances welfare outcomes and supports precise scientific research on avian species.
Overview of DNA Testing for Bird Gender
DNA testing for bird gender identification offers a highly accurate and non-invasive method by analyzing feather, blood, or eggshell samples. This molecular technique detects sex-specific genetic markers such as the CHD gene found on Z and W chromosomes, providing definitive results regardless of species or age. Compared to surgical sexing, DNA testing significantly reduces stress on birds and the risk of complications, making it an increasingly preferred method in avian veterinary diagnostics and breeding programs.
Surgical Sexing: Procedure and Process
Surgical sexing in birds involves a precise procedure where a small incision is made to access the gonads for direct visual identification of the bird's sex, typically under general anesthesia to ensure minimal stress and pain. This method provides immediate and accurate results compared to DNA testing, especially in species with indistinguishable external sexual characteristics. The process requires expertise in avian anatomy and sterile surgical techniques to reduce risks and promote quick recovery.
Accuracy Comparison: DNA Test vs Surgical Sexing
DNA testing for bird gender identification offers near-perfect accuracy by analyzing genetic material from feathers or blood, minimizing stress and risk to the bird. Surgical sexing, although traditionally considered reliable, involves anesthesia and invasive procedures, which carry higher risks and a marginal chance of human error during visual examination. Studies indicate DNA tests achieve accuracy rates exceeding 99%, while surgical sexing accuracy can vary between 95-99% depending on species and technique.
Safety and Risks: DNA vs Surgical Methods
DNA testing for bird gender identification offers a non-invasive and safe alternative with minimal stress and zero physical risk to the bird, using feathers or blood samples for precise results. Surgical sexing, involving endoscopy, presents higher risks due to anesthesia and invasive procedures that can lead to infection, complications, or mortality. Prioritizing bird safety, DNA testing is widely recommended to avoid the inherent risks associated with surgical methods.
Cost Analysis: DNA Testing vs Surgical Sexing
DNA testing for bird gender identification generally costs between $30 and $50, offering a non-invasive and cost-effective solution with high accuracy. Surgical sexing, involving endoscopy, ranges from $200 to $400 due to anesthesia and veterinary fees, making it significantly more expensive. Considering both methods, DNA testing provides a budget-friendly option suitable for breeders and owners seeking reliable results without the risks and expenses associated with surgery.
Stress and Impact on Birds
DNA testing offers a non-invasive method for determining bird gender, minimizing stress and physical impact compared to surgical sexing. Surgical sexing, involving anesthesia and tissue extraction, poses higher risks such as infection, stress-induced behavioral changes, and longer recovery times. Opting for DNA tests reduces bird distress, promotes quicker diagnosis, and supports better welfare practices in avian care.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Bird
Choosing the right method for determining bird gender depends on species, accuracy requirements, and invasiveness tolerance. DNA testing offers a highly accurate, non-invasive solution by analyzing feathers or blood samples, suitable for all bird species. Surgical sexing, while more invasive, provides immediate results and is often reserved for cases where DNA testing is unavailable or inconclusive.
Expert Recommendations for Bird Owners
Expert recommendations emphasize DNA testing as the most accurate and non-invasive method for determining bird gender, with success rates exceeding 99%. Surgical sexing, while providing direct visual confirmation through endoscopy, carries higher risks including anesthesia complications and infection. Bird owners are advised to choose DNA testing for routine gender identification to ensure minimal stress and optimal bird welfare.
DNA test vs Surgical sexing for Bird gender Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com