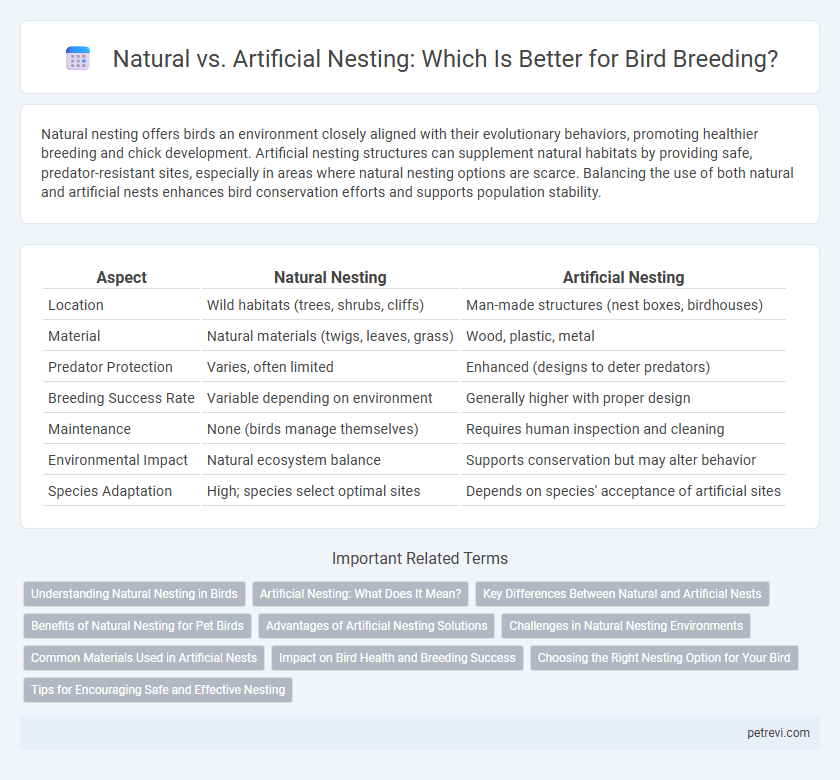
Natural nesting offers birds an environment closely aligned with their evolutionary behaviors, promoting healthier breeding and chick development. Artificial nesting structures can supplement natural habitats by providing safe, predator-resistant sites, especially in areas where natural nesting options are scarce. Balancing the use of both natural and artificial nests enhances bird conservation efforts and supports population stability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Natural Nesting | Artificial Nesting |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Wild habitats (trees, shrubs, cliffs) | Man-made structures (nest boxes, birdhouses) |
| Material | Natural materials (twigs, leaves, grass) | Wood, plastic, metal |
| Predator Protection | Varies, often limited | Enhanced (designs to deter predators) |
| Breeding Success Rate | Variable depending on environment | Generally higher with proper design |
| Maintenance | None (birds manage themselves) | Requires human inspection and cleaning |
| Environmental Impact | Natural ecosystem balance | Supports conservation but may alter behavior |
| Species Adaptation | High; species select optimal sites | Depends on species' acceptance of artificial sites |
Understanding Natural Nesting in Birds
Natural nesting in birds involves selecting sites that offer optimal protection, temperature regulation, and proximity to food sources, enhancing reproductive success. Birds instinctively choose materials and locations that blend with their environment to reduce predation risk and increase chick survival rates. Understanding these natural behaviors is crucial for conservation efforts and improving artificial nesting designs.
Artificial Nesting: What Does It Mean?
Artificial nesting for bird breeding involves providing man-made structures such as nest boxes, platforms, or cavities designed to mimic natural habitats, enhancing breeding success in urban or habitat-degraded areas. These artificial nests help support species with limited natural nesting sites, improve monitoring of bird populations, and contribute to conservation efforts by increasing reproductive rates. Properly designed and maintained artificial nests reduce predation risks and environmental stressors, ensuring safer breeding conditions for targeted bird species.
Key Differences Between Natural and Artificial Nests
Natural bird nests are constructed using organic materials like twigs, leaves, and mud, offering camouflage and temperature regulation suited to the specific habitat. Artificial nests, made from synthetic or human-provided materials, often lack the precise insulation and protection natural nests provide but can increase breeding opportunities in areas with limited natural resources. Key differences include material composition, structural complexity, and the impact on bird behavior and reproductive success.
Benefits of Natural Nesting for Pet Birds
Natural nesting environments provide pet birds with essential stimuli that promote instinctive behaviors, improving their overall well-being and breeding success. The use of natural materials and structures enhances comfort and reduces stress, leading to healthier offspring and stronger parental bonding. Exposure to natural nesting conditions supports cognitive development and boosts immune function, key factors in sustaining vibrant pet bird populations.
Advantages of Artificial Nesting Solutions
Artificial nesting solutions provide consistent protection from predators and harsh weather, improving chick survival rates and overall breeding success. These structures can be strategically placed to support endangered species and increase local bird populations, especially in areas lacking natural habitats. Customizable designs also enable scientists to study bird behavior closely and adapt environments to meet specific species' needs.
Challenges in Natural Nesting Environments
Natural nesting environments for bird breeding face challenges such as habitat loss, predation, and climate change, which reduce nesting site availability and success rates. Limited shelter and food resources in these areas increase vulnerability to predators and environmental stress. Monitoring and preserving natural habitats remain critical to support diverse bird populations despite these obstacles.
Common Materials Used in Artificial Nests
Artificial bird nests commonly utilize natural materials like wood fibers, straw, and coconut coir to mimic the insulating properties of natural nests while ensuring durability and safety for breeding. Synthetic components such as plastic mesh, foam padding, and weather-resistant fabrics enhance structural integrity and protect against predators and harsh environmental conditions. Combining organic and synthetic elements optimizes artificial nesting sites, promoting successful breeding and chick development in various bird species.
Impact on Bird Health and Breeding Success
Natural nesting sites provide optimal conditions for bird health and breeding success by offering suitable materials, protection from predators, and appropriate microclimates, which support egg incubation and chick development. Artificial nesting boxes can supplement habitat loss but may pose risks such as increased parasite infestations, exposure to extreme weather, and competition with invasive species if not properly maintained. Careful design and regular cleaning of artificial nests can mitigate negative impacts, fostering better breeding outcomes and healthier bird populations.
Choosing the Right Nesting Option for Your Bird
Selecting between natural and artificial nesting sites significantly impacts bird breeding success, as natural nests provide optimal environmental conditions closely aligned with specific bird species' instincts and behaviors. Artificial nests, including birdhouses and nesting boxes, offer controlled protection from predators and harsh weather, enhancing breeding efficiency in urban or deforested areas. Understanding species-specific nesting preferences and habitat requirements ensures that the chosen nesting option supports healthy egg incubation, chick development, and overall population sustainability.
Tips for Encouraging Safe and Effective Nesting
Providing natural nesting materials like twigs, leaves, and grasses encourages birds to build safe and effective nests. Installing well-designed artificial birdhouses with proper ventilation, appropriate entrance size, and weather protection enhances breeding success. Regularly monitoring nests without disturbing the birds helps prevent predators and ensures a secure environment for chicks.
Natural vs Artificial nesting for Bird breeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com