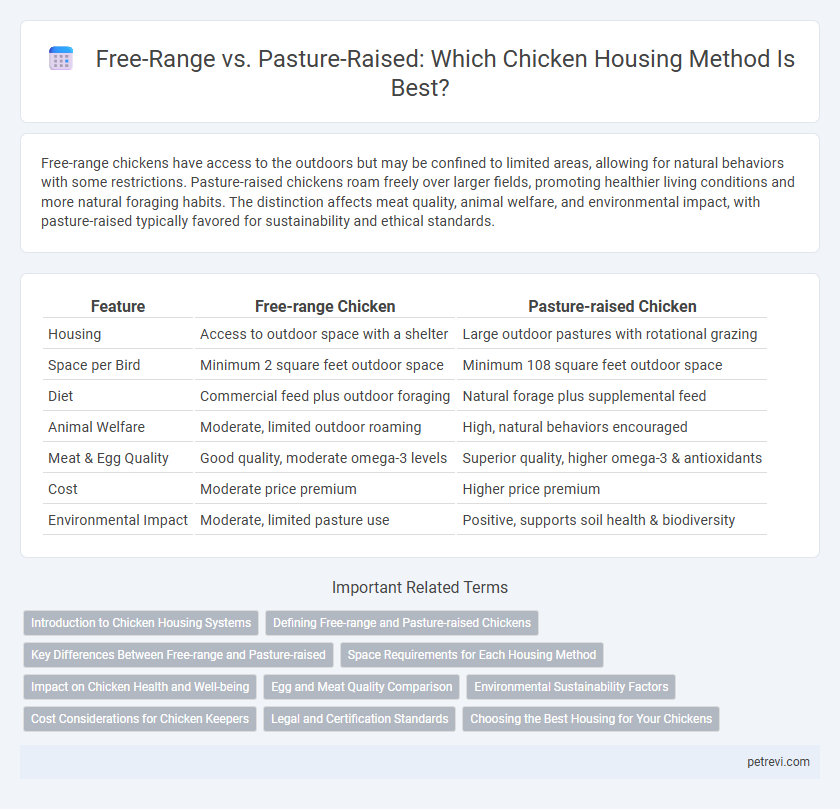
Free-range chickens have access to the outdoors but may be confined to limited areas, allowing for natural behaviors with some restrictions. Pasture-raised chickens roam freely over larger fields, promoting healthier living conditions and more natural foraging habits. The distinction affects meat quality, animal welfare, and environmental impact, with pasture-raised typically favored for sustainability and ethical standards.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Free-range Chicken | Pasture-raised Chicken |
|---|---|---|
| Housing | Access to outdoor space with a shelter | Large outdoor pastures with rotational grazing |
| Space per Bird | Minimum 2 square feet outdoor space | Minimum 108 square feet outdoor space |
| Diet | Commercial feed plus outdoor foraging | Natural forage plus supplemental feed |
| Animal Welfare | Moderate, limited outdoor roaming | High, natural behaviors encouraged |
| Meat & Egg Quality | Good quality, moderate omega-3 levels | Superior quality, higher omega-3 & antioxidants |
| Cost | Moderate price premium | Higher price premium |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, limited pasture use | Positive, supports soil health & biodiversity |
Introduction to Chicken Housing Systems
Free-range chicken housing allows birds access to outdoor areas for part of the day, promoting natural behaviors and better welfare. Pasture-raised systems provide continuous access to pasture throughout the day, enhancing nutrition through fresh forage and insects. These housing methods impact chicken health, growth rates, and product quality, influencing consumer preferences.
Defining Free-range and Pasture-raised Chickens
Free-range chickens are allowed access to the outdoors for part of the day, typically with limited space and varying environmental conditions, whereas pasture-raised chickens spend most of their lives on pasture with ample space, natural forage, and sunlight exposure. The USDA defines free-range primarily by outdoor access without specifying duration or quality of the outdoor environment, while pasture-raised standards emphasize continuous outdoor access on pasture with fresh vegetation. These distinctions affect animal welfare, nutritional values, and farming practices, with pasture-raised generally considered superior in promoting natural behaviors and providing richer omega-3 content in the meat.
Key Differences Between Free-range and Pasture-raised
Free-range chickens have access to the outdoors but the space is often limited and not guaranteed to be natural pasture. Pasture-raised chickens roam freely on a large, grassy area allowing natural foraging, which typically results in higher animal welfare and better nutritional profiles such as increased omega-3 and vitamin content. The USDA defines free-range based on outdoor access, whereas pasture-raised is more about the quality and extent of outdoor space and diet.
Space Requirements for Each Housing Method
Free-range chickens typically require a minimum of 2 square feet per bird indoors with access to at least 8-10 square feet of outdoor space, enabling natural behaviors and movement. Pasture-raised chickens, however, benefit from significantly larger outdoor space, often around 108 square feet per bird, promoting grazing and foraging on fresh pasture. These space requirements directly impact chicken welfare, growth rates, and meat quality in free-range versus pasture-raised systems.
Impact on Chicken Health and Well-being
Free-range chicken housing allows birds access to outdoor spaces, promoting natural behaviors and improving mental stimulation, which enhances overall health and immune function. Pasture-raised chickens benefit from a more nutrient-rich diet sourced from grass, insects, and worms, leading to higher omega-3 fatty acid levels and stronger skeletal development. Both systems reduce stress-related illnesses compared to conventional caged environments by providing better air quality, space, and opportunities for exercise.
Egg and Meat Quality Comparison
Free-range chickens typically have access to outdoor areas, which can enhance the flavor and nutritional profile of both eggs and meat through increased physical activity and natural foraging. Pasture-raised chickens, with more extensive outdoor grazing and diverse diet, often produce eggs richer in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin E, and beta-carotene, alongside meat with better texture and higher protein levels. Studies indicate pasture-raised poultry generally offers superior nutrient density and enhanced taste compared to conventional free-range systems.
Environmental Sustainability Factors
Free-range chickens have limited outdoor access, which can reduce soil degradation and promote natural foraging, but their environmental impact varies based on the size and management of the outdoor area. Pasture-raised chickens typically roam larger, well-managed pastures that support biodiversity, enhance soil health through natural fertilization and allow for rotational grazing, significantly lowering environmental footprint. Studies show pasture-raised systems often improve carbon sequestration and reduce reliance on synthetic inputs compared to conventional free-range housing, promoting greater overall sustainability.
Cost Considerations for Chicken Keepers
Free-range chicken housing generally involves moderate infrastructure costs, allowing birds access to outdoor spaces with minimal fencing and shelter, making it an affordable option for small to medium-scale chicken keepers. Pasture-raised systems require higher investment in movable shelters, durable fencing, and rotational grazing management to maintain pasture quality and bird health, resulting in increased operational expenses. The ongoing costs of pasture maintenance, such as reseeding and pest control, contribute significantly to the overall expenditure compared to free-range setups.
Legal and Certification Standards
Free-range chickens are legally required to have access to the outdoors but face minimal specifications on space and duration, as defined by the USDA for egg production. Pasture-raised chickens must meet more stringent certification standards, such as those from the American Humane Association or Certified Humane, which mandate continuous access to pasture with specific square footage per bird. These certifications ensure higher welfare practices, including natural behavior allowance, compared to the broader legal requirements for free-range labeling.
Choosing the Best Housing for Your Chickens
Free-range chickens have access to outdoor areas but may still be confined to a coop or yard, while pasture-raised chickens roam freely on fresh pasture, promoting natural behaviors and improved welfare. Pasture-raised housing typically results in healthier birds with higher omega-3 fatty acid content and enhanced flavor compared to free-range. Selecting the best housing depends on balancing space, environmental enrichment, and biosecurity to optimize chicken health and productivity.
Free-range vs Pasture-raised for Chicken Housing Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com