Layer mash is specifically formulated to meet the nutritional needs of laying hens, providing optimal calcium and protein levels for eggshell formation and sustained egg production. Grower mash, designed for young chickens transitioning from starter feed, supports rapid growth and muscle development with a balanced mix of protein, energy, and essential vitamins. Selecting the appropriate mash at each stage enhances overall health, productivity, and feed efficiency in poultry management.
Table of Comparison
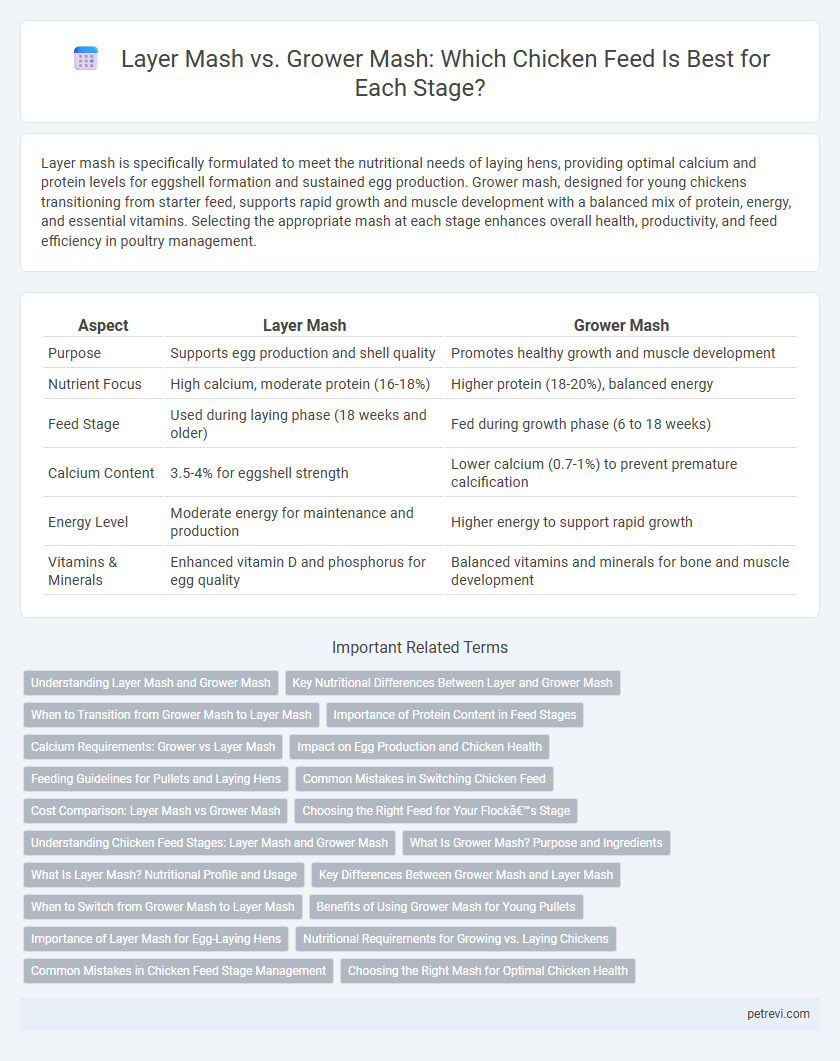
| Aspect | Layer Mash | Grower Mash |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports egg production and shell quality | Promotes healthy growth and muscle development |
| Nutrient Focus | High calcium, moderate protein (16-18%) | Higher protein (18-20%), balanced energy |
| Feed Stage | Used during laying phase (18 weeks and older) | Fed during growth phase (6 to 18 weeks) |
| Calcium Content | 3.5-4% for eggshell strength | Lower calcium (0.7-1%) to prevent premature calcification |
| Energy Level | Moderate energy for maintenance and production | Higher energy to support rapid growth |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Enhanced vitamin D and phosphorus for egg quality | Balanced vitamins and minerals for bone and muscle development |
Understanding Layer Mash and Grower Mash
Layer Mash is a nutrient-dense chicken feed formulated to support eggshell quality and sustained egg production in laying hens, enriched with higher calcium levels essential during the laying phase. Grower Mash is designed to meet the protein and energy needs of juvenile chickens during their rapid growth stage, promoting muscle development and overall health before they transition to laying. Understanding the distinct nutritional profiles of Layer Mash and Grower Mash ensures optimal feed efficiency and bird performance throughout the poultry lifecycle.
Key Nutritional Differences Between Layer and Grower Mash
Layer mash contains higher calcium levels, essential for eggshell formation and overall reproductive health in laying hens, while grower mash is formulated with increased protein and energy to support rapid growth and muscle development in young chickens. The calcium content in layer mash typically ranges from 3.5% to 4%, compared to less than 1% in grower mash, which helps prevent skeletal problems and ensures strong eggshells. Grower mash is also richer in amino acids like methionine and lysine to promote optimal weight gain and feather growth during the pre-laying stage.
When to Transition from Grower Mash to Layer Mash
Transitioning from grower mash to layer mash typically occurs at 16 to 18 weeks of age when pullets begin laying eggs, as layer mash contains higher calcium essential for eggshell formation. Providing layer mash too early can lead to excess calcium intake causing kidney issues, while delaying the transition may result in poor eggshell quality. Monitoring bird development and onset of lay ensures timely feed adjustment that supports optimal egg production and hen health.
Importance of Protein Content in Feed Stages
Layer mash contains higher protein levels, typically 16-18%, essential for egg production and maintaining hen health during laying stages. Grower mash features moderate protein content, around 14-16%, supporting muscle development and growth in juvenile chickens before reaching maturity. Proper protein adjustment in feed stages optimizes growth efficiency and maximizes egg yield in poultry production.
Calcium Requirements: Grower vs Layer Mash
Layer mash contains higher calcium levels, typically around 3.5-4%, to support eggshell formation, while grower mash has lower calcium content, about 1%, suitable for developing bones. Calcium in layer mash is crucial during the laying stage to prevent deficiencies and maintain eggshell quality. Grower mash prioritizes balanced nutrition for skeletal growth without excess calcium that could impair nutrient absorption.
Impact on Egg Production and Chicken Health
Layer Mash, formulated with higher calcium content and balanced protein levels, significantly enhances eggshell quality and overall egg production compared to Grower Mash. Grower Mash supports optimal growth and development during the pullet phase but lacks the essential nutrients needed for peak laying performance and sustained hen health. Transitioning to Layer Mash at the onset of egg production improves shell strength, reduces production gaps, and promotes long-term reproductive health in laying hens.
Feeding Guidelines for Pullets and Laying Hens
Layer Mash contains higher calcium levels essential for eggshell formation, making it ideal for laying hens during their production phase. Grower Mash is formulated with balanced protein and energy tailored to support the growth and development of pullets before they start laying. Feeding guidelines recommend transitioning pullets from grower mash to layer mash around 16 to 18 weeks of age to meet their changing nutritional requirements efficiently.
Common Mistakes in Switching Chicken Feed
Switching from grower mash to layer mash without a gradual transition can cause digestive upset and reduce feed intake in chickens. Common mistakes include introducing layer mash too early, leading to calcium overload and kidney damage, or switching too late, resulting in poor egg production and shell quality. Proper timing and mixing both feeds during the transition phase help maintain nutrient balance and support optimal growth and laying performance.
Cost Comparison: Layer Mash vs Grower Mash
Layer mash typically costs more than grower mash due to its higher protein, calcium, and vitamin content necessary for egg production. Grower mash, formulated for juveniles, is less nutrient-dense and thus cheaper, focusing on balanced growth rather than reproductive needs. Evaluating cost-effectiveness depends on the chicken's stage, with layer mash investment justified by increased egg yield and quality.
Choosing the Right Feed for Your Flock’s Stage
Layer Mash is formulated with higher calcium and protein levels to support egg production and shell quality in laying hens, while Grower Mash contains balanced nutrients tailored for developing pullets during their growth phase. Selecting Grower Mash during the pullet stage ensures optimal skeletal development and muscle growth before transitioning to Layer Mash to meet the metabolic demands of egg-laying. Proper feed selection aligned with the chicken's life stage enhances flock health, productivity, and overall feed efficiency.
Layer Mash vs Grower Mash for Chicken Feed Stages Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com