AI (Artificial Insemination) in cow breeding offers controlled genetic improvements and reduces the risk of disease transmission compared to natural service. Natural service, involving a bull, allows for natural mating behaviors and may be more effective in environments where AI resources or expertise are limited. Choosing between AI and natural service depends on factors like farm management, genetic goals, and available infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
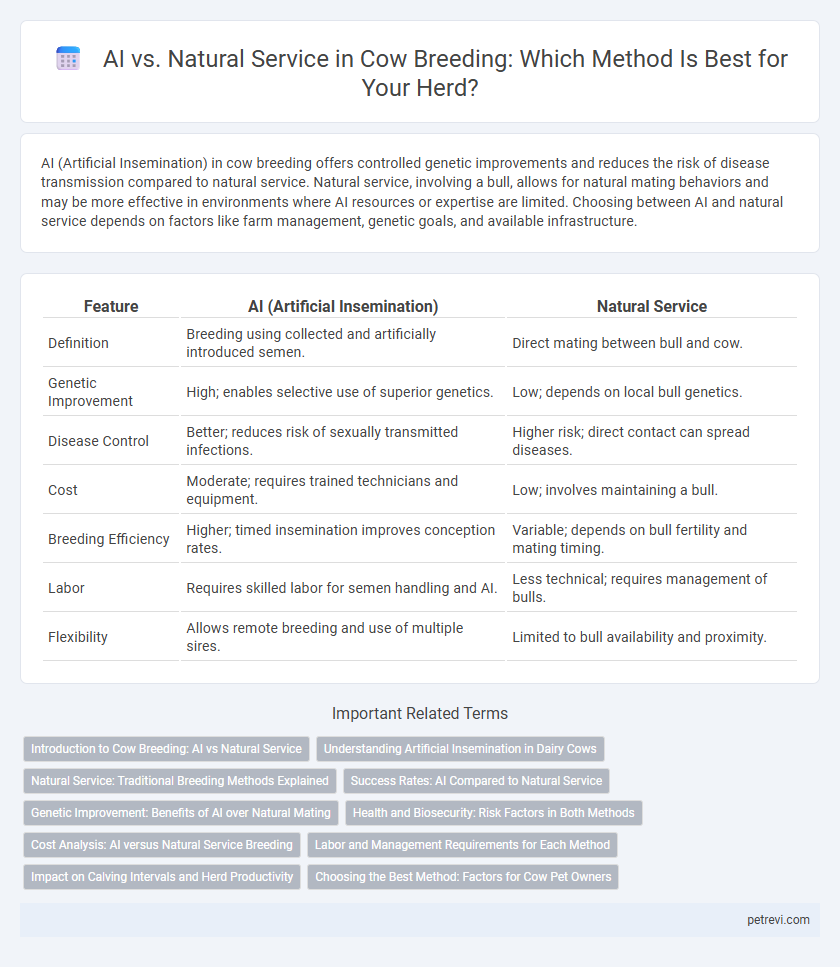
| Feature | AI (Artificial Insemination) | Natural Service |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Breeding using collected and artificially introduced semen. | Direct mating between bull and cow. |
| Genetic Improvement | High; enables selective use of superior genetics. | Low; depends on local bull genetics. |
| Disease Control | Better; reduces risk of sexually transmitted infections. | Higher risk; direct contact can spread diseases. |
| Cost | Moderate; requires trained technicians and equipment. | Low; involves maintaining a bull. |
| Breeding Efficiency | Higher; timed insemination improves conception rates. | Variable; depends on bull fertility and mating timing. |
| Labor | Requires skilled labor for semen handling and AI. | Less technical; requires management of bulls. |
| Flexibility | Allows remote breeding and use of multiple sires. | Limited to bull availability and proximity. |
Introduction to Cow Breeding: AI vs Natural Service
In cow breeding, Artificial Insemination (AI) offers precise genetic selection and disease control advantages over Natural Service, enhancing herd improvement. Natural Service provides natural mating behaviors and lower initial costs but poses risks of disease transmission and less controlled genetic outcomes. Balancing AI and Natural Service benefits can optimize reproductive efficiency and genetic progress in cattle operations.
Understanding Artificial Insemination in Dairy Cows
Artificial insemination (AI) in dairy cows offers precise control over genetic traits, improving herd quality and milk production efficiency by using semen from superior bulls. Natural service relies on bull mating, which can lead to unpredictable fertility rates and increased disease transmission risks. Implementing AI enhances reproductive management through timed inseminations, accurate heat detection, and comprehensive genetic evaluation, fostering sustainable dairy breeding programs.
Natural Service: Traditional Breeding Methods Explained
Natural service in cow breeding relies on natural mating between a bull and a cow, preserving genetic diversity and reducing the need for expensive technology. This method supports strong animal instincts and behaviors, often resulting in healthier calves with higher survival rates. Traditional breeding enhances herd adaptability to local environments without the dependency on artificial insemination or advanced reproductive technologies.
Success Rates: AI Compared to Natural Service
Artificial Insemination (AI) in cow breeding offers precise genetic selection and a success rate typically ranging from 50% to 60%, which can surpass natural service success rates of about 40% to 50% under controlled conditions. AI enables widespread use of superior sire genetics without the risks associated with natural mating, such as injury or disease transmission, enhancing herd improvement efficiency. Success rates in AI heavily depend on factors like timing of insemination, cow fertility, and semen quality, while natural service success may be influenced by bull fertility and mating behavior.
Genetic Improvement: Benefits of AI over Natural Mating
Artificial insemination (AI) enhances genetic improvement in cow breeding by enabling selective use of superior sire genetics, which accelerates desirable trait propagation more efficiently than natural service. AI reduces the risk of disease transmission and allows for extensive genetic diversity by accessing elite sperm from global sources, improving herd performance and productivity. Employing AI minimizes inbreeding and supports precise genetic management, resulting in healthier calves with enhanced milk yield, growth rates, and reproductive traits compared to natural mating.
Health and Biosecurity: Risk Factors in Both Methods
AI (Artificial Insemination) in cow breeding minimizes direct contact between animals, reducing the transmission of infectious diseases and enhancing biosecurity protocols on farms. Natural service carries higher risks of spreading reproductive diseases due to physical mounting and interaction, which can compromise herd health and fertility rates. Implementing stringent health monitoring and quarantine measures is essential to mitigate risk factors in both breeding methods.
Cost Analysis: AI versus Natural Service Breeding
Artificial Insemination (AI) in cow breeding typically reduces overall costs by minimizing the need for maintaining bulls and enabling selective genetic improvements. Natural service involves expenses related to bull upkeep, including feed, veterinary care, and housing, often resulting in higher long-term costs compared to AI. Cost analysis reveals AI offers enhanced economic efficiency through controlled breeding schedules and reduced risk of disease transmission, despite initial investment in technology and skilled labor.
Labor and Management Requirements for Each Method
AI breeding in cows requires skilled technicians and detailed record-keeping, increasing labor intensity but allowing precise genetic selection and scheduling flexibility. Natural service relies on maintaining bulls, which demands ongoing animal care, space, and management effort but involves less technical expertise. Efficient labor allocation and management strategies differ significantly between AI and natural breeding, impacting operational costs and reproductive outcomes.
Impact on Calving Intervals and Herd Productivity
AI (Artificial Insemination) in cow breeding reduces calving intervals by enabling precise timing of fertilization, enhancing reproductive efficiency compared to natural service. Shorter calving intervals achieved through AI contribute to increased herd productivity by accelerating the generation turnover and improving genetic progress. Herds utilizing AI typically exhibit higher conception rates and more consistent calving patterns, directly boosting milk output and overall farm profitability.
Choosing the Best Method: Factors for Cow Pet Owners
Choosing between AI and natural service for cow breeding depends on factors like herd genetics, cost, labor availability, and breeding goals. Artificial insemination offers precise genetic improvement, disease control, and wider sire selection, while natural service ensures ease of management and lower initial investment. Cow pet owners must evaluate herd size, reproductive efficiency, and long-term breeding program strategies to select the most effective method.
AI vs Natural Service for Cow Breeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com