Flushing involves feeding cows a high-energy diet before breeding to boost ovulation rates and improve fertility compared to routine feeding, which typically maintains standard nutritional levels without targeted enhancement. This strategic increase in energy intake supports better follicle development and higher conception rates in cows. Studies show that flushing yields improved reproductive performance, making it a valuable practice in herd fertility management.
Table of Comparison
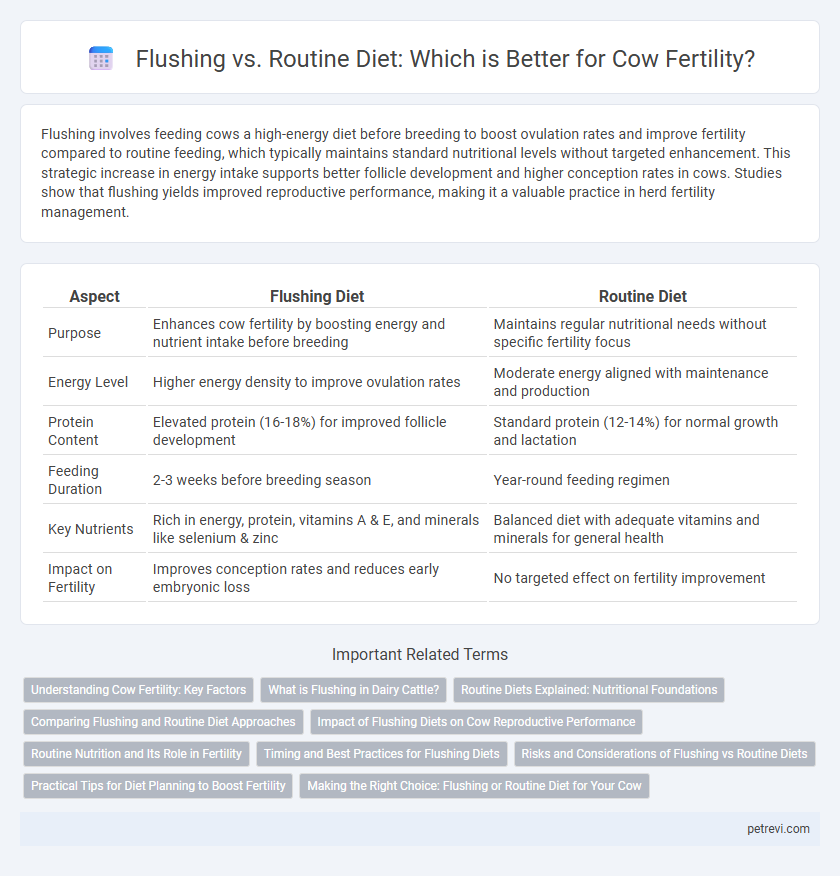
| Aspect | Flushing Diet | Routine Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances cow fertility by boosting energy and nutrient intake before breeding | Maintains regular nutritional needs without specific fertility focus |
| Energy Level | Higher energy density to improve ovulation rates | Moderate energy aligned with maintenance and production |
| Protein Content | Elevated protein (16-18%) for improved follicle development | Standard protein (12-14%) for normal growth and lactation |
| Feeding Duration | 2-3 weeks before breeding season | Year-round feeding regimen |
| Key Nutrients | Rich in energy, protein, vitamins A & E, and minerals like selenium & zinc | Balanced diet with adequate vitamins and minerals for general health |
| Impact on Fertility | Improves conception rates and reduces early embryonic loss | No targeted effect on fertility improvement |
Understanding Cow Fertility: Key Factors
Flushing involves increasing energy-rich feed before and during breeding to improve ovulation rates and conception in cows. Routine diets typically maintain baseline nutrition but may lack the enhanced energy density needed for optimal fertility performance. Key factors influencing cow fertility include body condition score, energy balance, and timing of nutrient intake relative to the breeding cycle.
What is Flushing in Dairy Cattle?
Flushing in dairy cattle refers to the practice of increasing nutrient intake, particularly energy and protein, 2 to 3 weeks prior to breeding to improve ovulation rates and enhance fertility. This technique involves feeding high-quality forage and concentrates to boost body condition and stimulate follicular development. Research shows flushing can increase conception rates by promoting better reproductive performance compared to routine diets alone.
Routine Diets Explained: Nutritional Foundations
Routine diets for cows emphasize balanced nutritional foundations essential for optimal fertility, including adequate protein, energy, vitamins, and minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, and trace elements like zinc and selenium. Consistent feeding of high-quality forages combined with strategic supplementation supports reproductive hormone regulation and improves ovarian function. Nutritional stability from routine diets enhances conception rates by maintaining body condition score and reducing metabolic stress during critical reproductive periods.
Comparing Flushing and Routine Diet Approaches
Flushing enhances cow fertility by increasing nutrient intake before breeding, promoting ovulation and improving conception rates more effectively than routine diets, which often lack the targeted nutrient boost. Research shows that flushing protocols, rich in energy and protein, lead to higher ovulation rates and increased progesterone levels compared to standard feeding regimens. Routine diets may maintain general health but rarely achieve the specific metabolic and reproductive benefits observed with flushing strategies in bovine fertility management.
Impact of Flushing Diets on Cow Reproductive Performance
Flushing diets, rich in energy and protein, significantly enhance cow fertility by improving body condition and promoting ovarian follicle development prior to breeding. This strategic nutritional boost increases ovulation rates, leading to higher conception rates compared to routine maintenance diets. Studies demonstrate that cows on flushing protocols exhibit improved reproductive performance, reduced anestrus periods, and shorter intervals to first estrus postpartum.
Routine Nutrition and Its Role in Fertility
Routine nutrition plays a critical role in optimizing cow fertility by ensuring a balanced intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and energy sources necessary for reproductive health. Consistent feeding schedules with nutrient-dense diets support hormonal balance, improve estrus expression, and enhance conception rates. Proper maintenance of body condition through routine diet management reduces the risk of metabolic disorders that can negatively impact ovulation and embryo development.
Timing and Best Practices for Flushing Diets
Flushing diets improve cow fertility by increasing body condition and ovulation rates when implemented 2-3 weeks before breeding. Best practices include providing high-energy, nutrient-dense feed such as grains and protein supplements to maximize reproductive performance. Timing is critical, as initiating the flushing diet too early or late can reduce its effectiveness compared to a routine diet.
Risks and Considerations of Flushing vs Routine Diets
Flushing cows with high-energy diets before breeding can improve fertility by increasing ovulation rates but also carries risks such as metabolic disorders and digestive upset if not carefully managed. Routine diets maintain baseline health but may not provide the elevated energy levels needed to optimize reproductive performance, potentially resulting in lower conception rates. Considerations include balancing nutrient intake to avoid excessive weight gain and monitoring individual cow responses to prevent negative health impacts during the flushing period.
Practical Tips for Diet Planning to Boost Fertility
Optimizing cow fertility through diet planning hinges on balancing energy, protein, and mineral intake, particularly ensuring adequate calcium, phosphorus, and trace minerals like selenium and zinc. Implement flushing diets with increased energy density and quality forage two to three weeks before breeding to stimulate follicular development and enhance conception rates. Regular feeding schedules, proper body condition scoring, and incorporating rumen-friendly supplements further support reproductive performance and overall herd productivity.
Making the Right Choice: Flushing or Routine Diet for Your Cow
Flushing involves feeding cows a high-energy diet approximately three weeks before breeding to enhance ovulation rates and improve fertility outcomes compared to a routine diet. Research shows that flushing can increase conception rates by boosting body condition scores and reproductive hormone levels, critical for successful breeding. Choosing between flushing and a routine diet depends on the cow's current nutritional status, but strategically implementing flushing in under-conditioned cows optimizes reproductive performance and herd productivity.
Flushing vs Routine Diet for Cow Fertility Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com