Chutes and head gates serve distinct purposes in cow restraint, with chutes providing full-body immobilization for procedures requiring safety and precision. Head gates specifically secure the cow's head, allowing for easier access during treatments like vaccinations or examinations. Choosing between a chute and a head gate depends on the level of restraint needed, animal size, and the specific handling task.
Table of Comparison
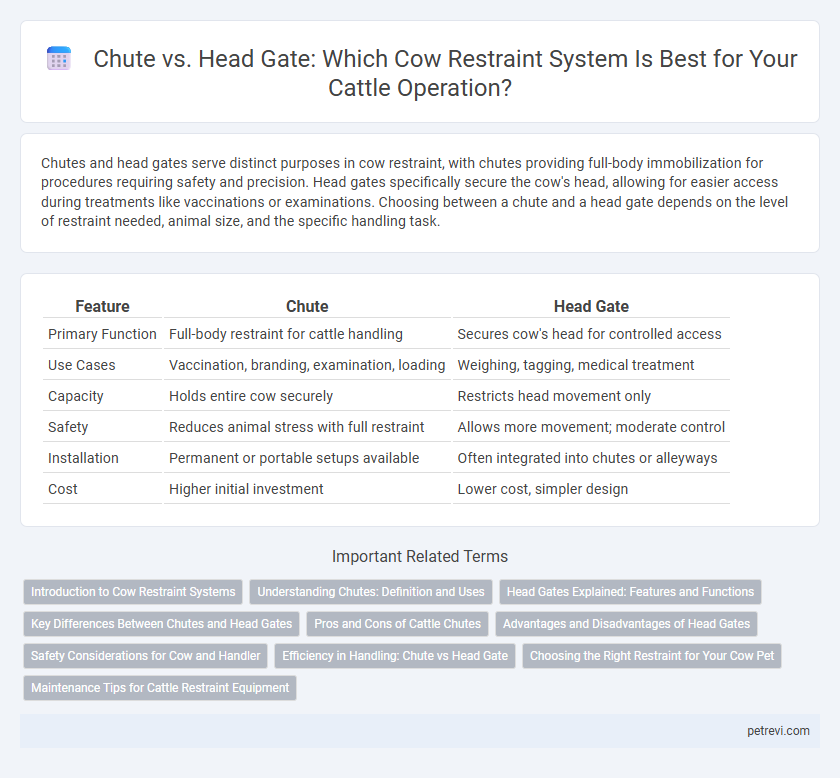
| Feature | Chute | Head Gate |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Full-body restraint for cattle handling | Secures cow's head for controlled access |
| Use Cases | Vaccination, branding, examination, loading | Weighing, tagging, medical treatment |
| Capacity | Holds entire cow securely | Restricts head movement only |
| Safety | Reduces animal stress with full restraint | Allows more movement; moderate control |
| Installation | Permanent or portable setups available | Often integrated into chutes or alleyways |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, simpler design |
Introduction to Cow Restraint Systems
Cow restraint systems are essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of livestock handling. Chutes provide a narrow passageway that limits cow movement, allowing for controlled access during medical treatments or sorting. Head gates secure the animal's head, stabilizing it to prevent injury and facilitate procedures like vaccinations or tagging.
Understanding Chutes: Definition and Uses
Chutes are sturdy, narrow enclosures designed to safely restrain cattle during medical treatment, sorting, or loading, minimizing stress and injury. Their design ensures controlled movement by guiding cows through a confined passage, facilitating efficient handling. Proper chute use improves animal welfare and worker safety, making them essential in livestock management.
Head Gates Explained: Features and Functions
Head gates offer secure cow restraint by firmly holding the animal's head, allowing safe handling during medical exams, vaccinations, or grooming. These devices are designed with adjustable bars or clamps to accommodate varying cow sizes while minimizing stress and movement. Head gates enhance safety for both handlers and cattle by providing controlled access to the animal's head area.
Key Differences Between Chutes and Head Gates
Chutes provide full-body restraint for cows, allowing safe and efficient handling during medical treatments or branding, while head gates secure only the cow's head to limit movement. Chutes offer more comprehensive control, reducing stress and the risk of injury for both animals and handlers, whereas head gates are simpler devices often used for tasks requiring minimal restraint. The choice between chute and head gate depends on the specific procedure, with chutes preferred for more invasive or extensive handling and head gates suitable for quick, targeted interventions.
Pros and Cons of Cattle Chutes
Cattle chutes provide effective restraint for handling, sorting, and medical procedures, minimizing animal stress and injury through firm, controlled confinement. However, they can be expensive, bulky, and require proper maintenance to ensure smooth operation and animal safety. Despite these challenges, chutes offer superior strength and stability compared to head gates, making them ideal for larger herds and more demanding cattle management tasks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Head Gates
Head gates provide superior control over cattle by securely restraining the cow's head, minimizing movement for safer handling during procedures such as vaccinations and veterinary exams. They offer quick release mechanisms, reducing stress and injury risk to both animals and handlers, but may be less effective with very large or aggressive cows compared to more robust chute systems. The main disadvantage of head gates lies in their potential for causing neck or head injuries if not used properly, requiring careful adjustment and operator training to ensure animal welfare.
Safety Considerations for Cow and Handler
Chutes provide secure, enclosed restraint that minimizes cattle movement, reducing injury risks for both cow and handler during procedures. Head gates allow controlled access to the animal's neck, facilitating quick interventions but may increase the chance of sudden movement if not properly monitored. Safety considerations prioritize sturdy construction, proper sizing, and handler training to ensure effective restraint while minimizing stress and injury.
Efficiency in Handling: Chute vs Head Gate
Chutes provide superior efficiency in handling cows by securely restraining the entire animal, minimizing movement and reducing stress during procedures like vaccinations and examinations. Head gates focus on controlling the cow's head, allowing quicker access but less overall restraint, which can lead to more frequent adjustments and longer handling times. For large-scale operations requiring fast, safe containment, chutes enhance workflow and animal welfare more effectively than head gates.
Choosing the Right Restraint for Your Cow Pet
Choosing the right cow restraint depends on the specific needs of your cow pet and the tasks involved. A chute offers secure, full-body immobilization ideal for comprehensive veterinary procedures and handling larger cattle, while a head gate provides targeted restraint primarily for head control, making it suitable for milking or routine examinations. Prioritize safety, ease of use, and the animal's comfort to ensure effective management and stress reduction during handling.
Maintenance Tips for Cattle Restraint Equipment
Regular lubrication of moving parts on both chutes and head gates prevents rust and ensures smooth operation, extending equipment lifespan. Inspect welds and hinges weekly for signs of wear or cracks to avoid unexpected failures during cattle handling. Clean surfaces thoroughly after use to remove dirt and manure, reducing corrosion and maintaining hygienic conditions for animal safety.
Chute vs Head Gate for Cow Restraint Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com