Probiotics support cow gut health by promoting beneficial bacteria balance and enhancing digestion, reducing the risk of infections naturally. Antibiotics, while effective in treating bacterial infections, can disrupt gut flora and lead to antibiotic resistance if overused. Prioritizing probiotics helps maintain a healthy microbiome, improving overall cow health and productivity.
Table of Comparison
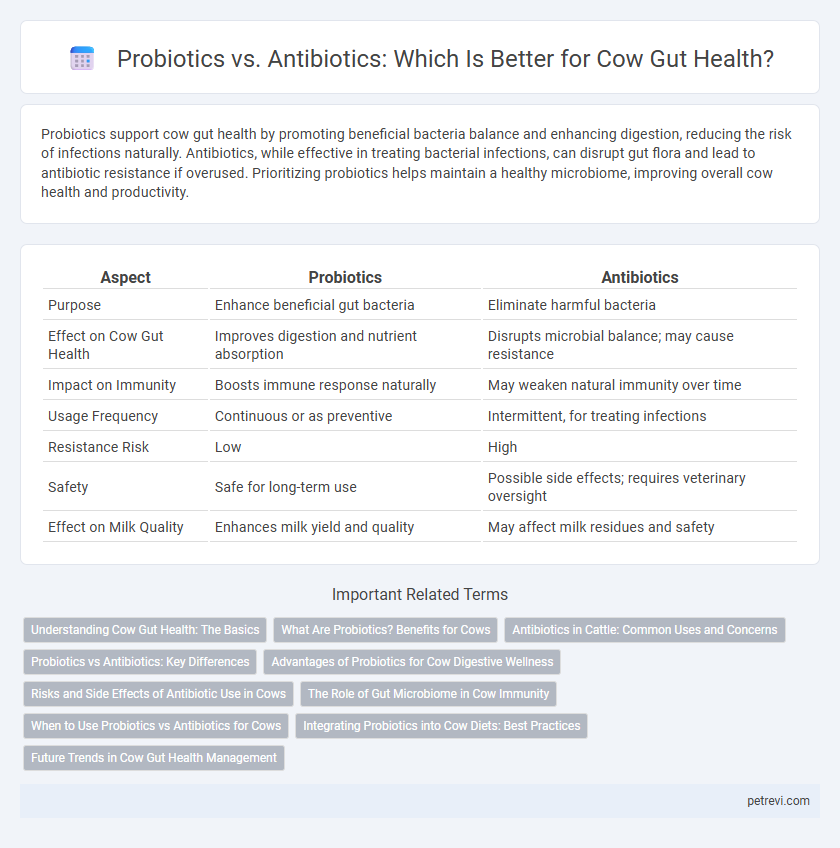
| Aspect | Probiotics | Antibiotics |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance beneficial gut bacteria | Eliminate harmful bacteria |
| Effect on Cow Gut Health | Improves digestion and nutrient absorption | Disrupts microbial balance; may cause resistance |
| Impact on Immunity | Boosts immune response naturally | May weaken natural immunity over time |
| Usage Frequency | Continuous or as preventive | Intermittent, for treating infections |
| Resistance Risk | Low | High |
| Safety | Safe for long-term use | Possible side effects; requires veterinary oversight |
| Effect on Milk Quality | Enhances milk yield and quality | May affect milk residues and safety |
Understanding Cow Gut Health: The Basics
Cow gut health relies on a balanced microbial ecosystem where probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria that enhance digestion and nutrient absorption, promoting overall immune function. Antibiotics target harmful bacteria but can disrupt this delicate microbiome, potentially leading to reduced microbial diversity and digestive issues. Maintaining optimal cow gut health involves prioritizing probiotics to support rumen fermentation and nutrient utilization while using antibiotics judiciously to prevent resistance and preserve beneficial microbes.
What Are Probiotics? Benefits for Cows
Probiotics are live beneficial microorganisms that enhance the microbial balance in the cow's digestive system, promoting improved nutrient absorption and stronger immune function. These beneficial bacteria help prevent gastrointestinal infections, reduce the incidence of diarrhea, and support overall gut health, leading to better feed efficiency and weight gain in cattle. Incorporating probiotics into cow diets can reduce reliance on antibiotics, lowering the risk of antibiotic resistance while maintaining optimal digestive health.
Antibiotics in Cattle: Common Uses and Concerns
Antibiotics in cattle are primarily used to treat bacterial infections and prevent disease outbreaks, ensuring herd health and productivity. Overuse or misuse can lead to antibiotic resistance, posing risks to animal welfare and public health. Monitoring antibiotic application and exploring alternative treatments are essential for sustainable cattle management.
Probiotics vs Antibiotics: Key Differences
Probiotics and antibiotics play distinct roles in cow gut health, with probiotics enhancing beneficial gut microbiota by introducing live microorganisms, while antibiotics target and eliminate harmful bacteria. Probiotics support digestion and immune function without disrupting the natural balance of the gut flora, whereas antibiotics can cause dysbiosis by indiscriminately killing both harmful and beneficial bacteria. Understanding these key differences helps optimize gut health strategies to improve nutrient absorption and reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance in dairy and beef cattle.
Advantages of Probiotics for Cow Digestive Wellness
Probiotics enhance cow digestive wellness by promoting a balanced gut microbiota, which improves nutrient absorption and immune function. Unlike antibiotics, probiotics reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance and help maintain long-term gut health. Consistent probiotic use supports digestive efficiency, leading to better feed conversion and overall herd productivity.
Risks and Side Effects of Antibiotic Use in Cows
Antibiotic use in cows carries significant risks including the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which can compromise both animal and human health. Side effects may also include disruption of the natural gut microbiota, leading to digestive issues and reduced nutrient absorption. In contrast, probiotics support gut health by promoting beneficial microbes without these adverse effects, making them a safer option for maintaining optimal intestinal function in cows.
The Role of Gut Microbiome in Cow Immunity
The gut microbiome in cows plays a crucial role in modulating immune functions by enhancing pathogen resistance and supporting nutrient absorption. Probiotics promote a balanced microbial community, improving gut barrier integrity and stimulating immune responses, while antibiotics can disrupt this delicate ecosystem, potentially leading to dysbiosis and weakened immunity. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through probiotics ensures optimal cow health and productivity by reinforcing natural defense mechanisms against infections.
When to Use Probiotics vs Antibiotics for Cows
Probiotics are best used in cows to promote gut health during periods of stress or dietary changes, enhancing beneficial bacteria and improving digestion. Antibiotics should be reserved for treating bacterial infections when clinical signs like fever, diarrhea, or systemic illness are evident, as overuse can disrupt the gut microbiome. Implementing probiotics for maintenance and antibiotics strictly for infections helps maintain balanced gut flora and reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance in cattle.
Integrating Probiotics into Cow Diets: Best Practices
Integrating probiotics into cow diets enhances gut health by promoting beneficial microbiota that improve digestion and nutrient absorption. Optimal practices include selecting strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, ensuring proper dosage, and maintaining consistent administration through feed or water. Regular monitoring of cow performance and adjusting probiotic formulations based on herd response maximizes health benefits and reduces dependency on antibiotics.
Future Trends in Cow Gut Health Management
Emerging research highlights the shift from traditional antibiotics to probiotics in cow gut health management, driven by rising concerns over antibiotic resistance and regulatory restrictions. Next-generation probiotics, designed with precision microbiome engineering, offer targeted modulation of the bovine gut ecosystem to enhance nutrient absorption, immunity, and disease resistance. Future trends emphasize integrated approaches combining advanced genomic tools and personalized probiotic formulations to sustain lifelong gut health and optimize dairy production efficiency.
Probiotics vs Antibiotics for Cow Gut Health Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com