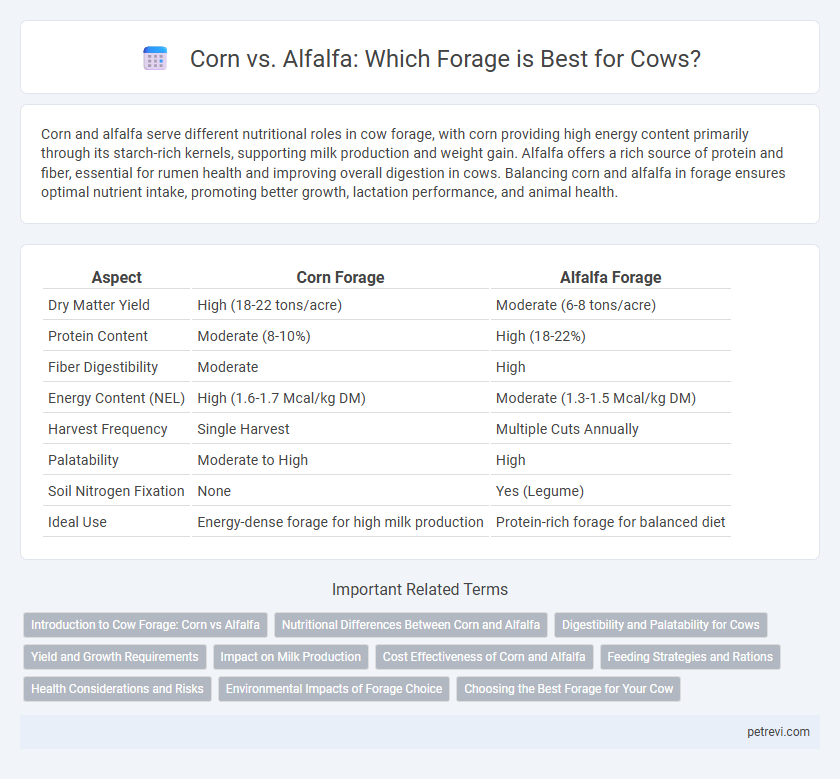
Corn and alfalfa serve different nutritional roles in cow forage, with corn providing high energy content primarily through its starch-rich kernels, supporting milk production and weight gain. Alfalfa offers a rich source of protein and fiber, essential for rumen health and improving overall digestion in cows. Balancing corn and alfalfa in forage ensures optimal nutrient intake, promoting better growth, lactation performance, and animal health.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Corn Forage | Alfalfa Forage |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Matter Yield | High (18-22 tons/acre) | Moderate (6-8 tons/acre) |
| Protein Content | Moderate (8-10%) | High (18-22%) |
| Fiber Digestibility | Moderate | High |
| Energy Content (NEL) | High (1.6-1.7 Mcal/kg DM) | Moderate (1.3-1.5 Mcal/kg DM) |
| Harvest Frequency | Single Harvest | Multiple Cuts Annually |
| Palatability | Moderate to High | High |
| Soil Nitrogen Fixation | None | Yes (Legume) |
| Ideal Use | Energy-dense forage for high milk production | Protein-rich forage for balanced diet |
Introduction to Cow Forage: Corn vs Alfalfa
Corn forage offers high-energy feed rich in starch, promoting rapid weight gain and milk production in cows, while alfalfa provides a protein-dense, fiber-rich diet essential for rumen health and efficient digestion. Balancing corn's high digestibility with alfalfa's nutrient density optimizes cow performance and supports sustainable forage systems. Selecting the appropriate forage depends on factors like soil type, climate, and specific nutritional requirements of the herd.
Nutritional Differences Between Corn and Alfalfa
Corn forage provides high energy through its starch-rich kernels, supporting increased milk production and weight gain in cows. Alfalfa offers superior protein content and essential minerals, promoting better rumen health and overall cow immunity. Balancing corn and alfalfa in cow diets optimizes nutrient intake, enhancing both growth and lactation performance.
Digestibility and Palatability for Cows
Corn forage offers higher digestibility due to its increased starch content, which provides cows with readily available energy for milk production and growth. Alfalfa, known for its superior palatability, encourages greater feed intake from cows, promoting better nutrient absorption and overall health. Balancing corn and alfalfa in a cow's diet optimizes digestibility while maintaining palatability, enhancing feed efficiency and animal performance.
Yield and Growth Requirements
Corn forage offers higher dry matter yield per acre compared to alfalfa, often reaching 15 to 25 tons per acre, while alfalfa typically produces 6 to 10 tons per acre. Corn requires warmer temperatures, well-drained soils, and a longer growing season, whereas alfalfa thrives in cooler climates, tolerates a wider range of soils, and includes nitrogen-fixing properties that improve soil fertility. Growth rate for corn is faster, enabling quicker forage availability within a single season, unlike alfalfa which establishes more slowly but supports multi-year harvest cycles.
Impact on Milk Production
Corn forage typically provides higher energy content compared to alfalfa, which can lead to increased milk yield in dairy cows. Alfalfa, rich in protein and fiber, supports better rumen health and milk quality, especially in terms of milk fat and protein percentages. Balancing corn and alfalfa in cow diets optimizes nutrient intake, enhancing overall milk production and composition.
Cost Effectiveness of Corn and Alfalfa
Corn forage offers higher yield per acre and is generally more cost-effective than alfalfa due to lower establishment and maintenance expenses. Alfalfa, while providing superior protein content and digestibility, entails higher seed costs, irrigation requirements, and risk of stand loss, impacting overall profitability. Farmers prioritizing feed cost reduction often favor corn, but integrating alfalfa can improve milk production efficiency despite increased input costs.
Feeding Strategies and Rations
Corn offers high energy content and digestibility ideal for lactating cows requiring increased milk production, while alfalfa provides rich protein and fiber essential for rumen health and reproduction. Balanced rations combining corn and alfalfa optimize nutrient intake by supporting energy demands and maintaining adequate fiber levels to prevent digestive disorders. Strategic feeding protocols adjust proportions based on lactation stage, ensuring enhanced feed efficiency and overall herd performance.
Health Considerations and Risks
Corn forage provides high-energy content essential for dairy cow milk production but may lead to metabolic disorders such as acidosis if consumed excessively. Alfalfa offers superior protein levels and calcium, promoting hoof health and reducing the risk of milk fever, yet it can cause bloat if not managed properly. Balancing corn and alfalfa in cow diets optimizes nutrient intake while minimizing health risks associated with digestive disturbances and mineral imbalances.
Environmental Impacts of Forage Choice
Corn forage requires higher water and nitrogen fertilizer inputs, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions and potential nutrient runoff compared to alfalfa. Alfalfa improves soil nitrogen levels through biological fixation, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and lowering environmental pollution. Choosing alfalfa over corn forage can enhance sustainable livestock production by minimizing water use and mitigating environmental impact on adjacent ecosystems.
Choosing the Best Forage for Your Cow
Corn forage provides high energy and digestible fiber, promoting rapid weight gain and milk production in cows, while alfalfa offers superior protein content and essential minerals that support overall health and reproduction. Selecting the best forage depends on the cow's nutritional needs, stage of production, and forage availability, with corn preferred for energy-intensive periods and alfalfa favored for balanced nutrition and rumen health. Evaluating forage quality through nutrient analysis and considering factors like soil type and climate ensures optimal feed efficiency and livestock performance.
Corn vs Alfalfa for Cow Forage Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com