Crossbred cows combine traits from two or more breeds, often resulting in improved hybrid vigor, better adaptability, and enhanced productivity compared to purebred cows. Purebred cows maintain genetic consistency and breed standards, making them ideal for predictable traits and specialized breeding programs. Choosing between crossbred and purebred genetics depends on goals like maximizing milk yield, disease resistance, or adaptability to environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
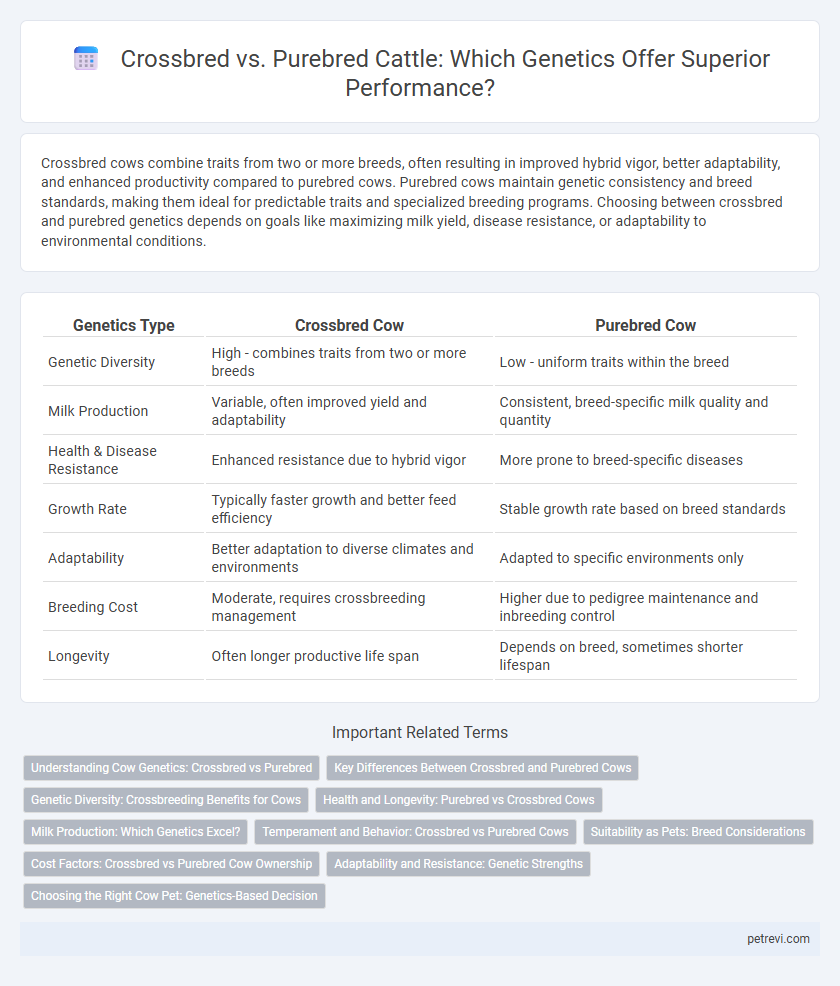
| Genetics Type | Crossbred Cow | Purebred Cow |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | High - combines traits from two or more breeds | Low - uniform traits within the breed |
| Milk Production | Variable, often improved yield and adaptability | Consistent, breed-specific milk quality and quantity |
| Health & Disease Resistance | Enhanced resistance due to hybrid vigor | More prone to breed-specific diseases |
| Growth Rate | Typically faster growth and better feed efficiency | Stable growth rate based on breed standards |
| Adaptability | Better adaptation to diverse climates and environments | Adapted to specific environments only |
| Breeding Cost | Moderate, requires crossbreeding management | Higher due to pedigree maintenance and inbreeding control |
| Longevity | Often longer productive life span | Depends on breed, sometimes shorter lifespan |
Understanding Cow Genetics: Crossbred vs Purebred
Crossbred cows possess a combination of genetic traits from two or more breeds, enhancing hybrid vigor which improves fertility, growth rate, and disease resistance compared to purebred cows. Purebred cows maintain a consistent lineage with specific breed standards, ensuring predictable traits important for specialized dairy or beef production. Understanding these genetic differences helps farmers optimize productivity, balancing adaptability and breed-specific characteristics.
Key Differences Between Crossbred and Purebred Cows
Crossbred cows exhibit greater genetic diversity, often resulting in improved hybrid vigor, disease resistance, and adaptability compared to purebred cows. Purebred cows maintain genetic consistency, ensuring predictable traits such as milk yield and growth rates, which are critical for specialized breeding programs. Farmers choose crossbreds for enhanced resilience and versatility, while purebreds are preferred for specific, uniform production goals.
Genetic Diversity: Crossbreeding Benefits for Cows
Crossbreeding in cows enhances genetic diversity by combining traits from different breeds, leading to improved health, fertility, and adaptability. Crossbred cows often exhibit hybrid vigor, resulting in higher resistance to diseases and environmental stressors compared to purebreds. This genetic variation promotes sustainable production and resilience in varying climatic conditions, benefiting overall herd performance.
Health and Longevity: Purebred vs Crossbred Cows
Crossbred cows generally exhibit greater hybrid vigor, leading to enhanced health and longer lifespans compared to purebred cows. Purebred cows may carry higher risks of inheritable diseases due to genetic uniformity, which can reduce overall longevity. Studies show crossbreeding improves resistance to common bovine diseases, contributing to more sustainable herd performance.
Milk Production: Which Genetics Excel?
Crossbred cows often outperform purebred cows in milk production due to hybrid vigor, which enhances traits like fertility, disease resistance, and overall milk yield. Purebred cows, especially specialized breeds like Holsteins, are renowned for their high milk production but may require more intensive management to maintain health and productivity. Crossbred genetics combine the strengths of multiple breeds, resulting in more consistent milk output under diverse environmental conditions.
Temperament and Behavior: Crossbred vs Purebred Cows
Crossbred cows typically exhibit more balanced temperament and adaptable behavior due to genetic diversity, making them easier to manage in diverse farming environments. Purebred cows often display more predictable but sometimes heightened temperament traits, influenced by selective breeding focused on specific breed characteristics. Understanding the behavioral differences between crossbred and purebred cows is crucial for optimizing herd management and improving animal welfare.
Suitability as Pets: Breed Considerations
Crossbred cows often exhibit hybrid vigor, resulting in enhanced adaptability and temperament, making them more suitable as pets for diverse environments compared to purebred cows. Purebred cows, while possessing consistent breed-specific traits, may require more specialized care and management, affecting their compatibility as household animals. Evaluating breed considerations, including behavioral tendencies and genetic health, is essential when selecting a cow for pet suitability.
Cost Factors: Crossbred vs Purebred Cow Ownership
Crossbred cows often present lower initial costs and improved feed efficiency compared to purebred cows, making them economically advantageous for many farmers. Purebred cows typically involve higher expenses due to specialized breeding, healthcare, and management aimed at maintaining genetic purity. Cost factors also include varied market demand and productivity levels, with crossbreds frequently offering better resilience and reduced veterinary costs over the lifespan.
Adaptability and Resistance: Genetic Strengths
Crossbred cows exhibit enhanced adaptability and resistance due to the hybrid vigor resulting from combining diverse genetic traits, making them more resilient to environmental stresses and diseases. Purebred cows, while genetically consistent, may lack the broader genetic diversity needed for optimal adaptability in varying climates or disease pressures. Emphasizing crossbreeding strategies can strengthen herd health by leveraging complementary genetic strengths for improved tolerance and immune response.
Choosing the Right Cow Pet: Genetics-Based Decision
Crossbred cows often exhibit hybrid vigor, resulting in improved health, fertility, and growth rates compared to purebred cows, which maintain consistent genetic traits but may be more prone to hereditary issues. Selecting the right cow pet depends on the purpose; crossbreds offer adaptability and resilience, while purebreds provide predictable characteristics for specialized breeding or shows. Evaluating genetic profiles, disease resistance, and temperament helps ensure the cow matches the owner's environmental conditions and management goals.
Crossbred vs Purebred for Cow Genetics Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com