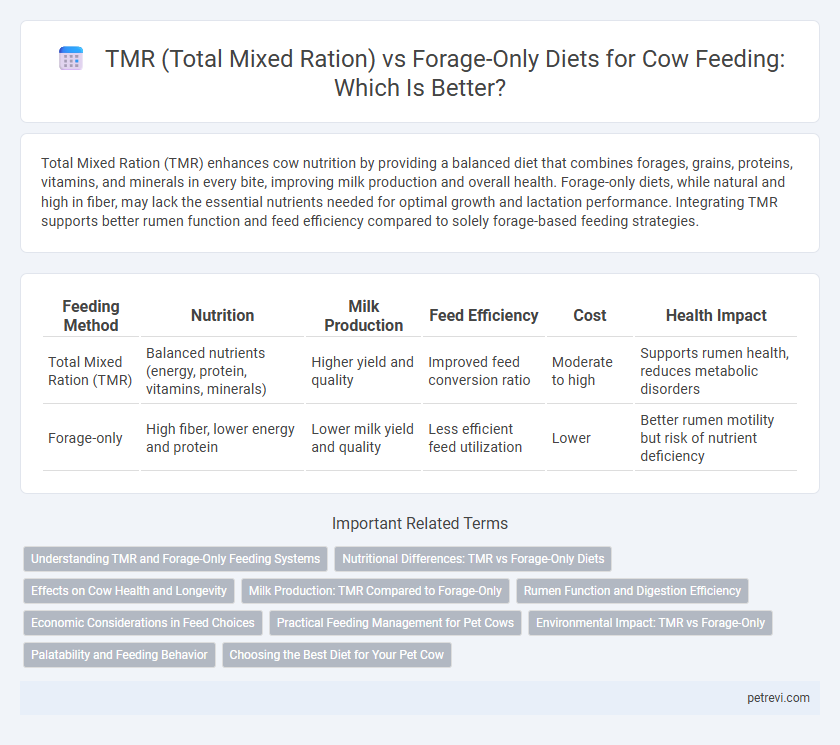
Total Mixed Ration (TMR) enhances cow nutrition by providing a balanced diet that combines forages, grains, proteins, vitamins, and minerals in every bite, improving milk production and overall health. Forage-only diets, while natural and high in fiber, may lack the essential nutrients needed for optimal growth and lactation performance. Integrating TMR supports better rumen function and feed efficiency compared to solely forage-based feeding strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Feeding Method | Nutrition | Milk Production | Feed Efficiency | Cost | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Mixed Ration (TMR) | Balanced nutrients (energy, protein, vitamins, minerals) | Higher yield and quality | Improved feed conversion ratio | Moderate to high | Supports rumen health, reduces metabolic disorders |
| Forage-only | High fiber, lower energy and protein | Lower milk yield and quality | Less efficient feed utilization | Lower | Better rumen motility but risk of nutrient deficiency |
Understanding TMR and Forage-Only Feeding Systems
Total Mixed Ration (TMR) combines forage, grains, protein sources, vitamins, and minerals into a balanced diet that ensures uniform nutrient intake and improves milk production efficiency in dairy cows. Forage-only feeding relies exclusively on pasture or stored forage, which may lead to nutrient variability and lower energy density, potentially reducing milk yield and growth performance. Understanding the differences between TMR and forage-only systems helps optimize feed strategies for improved cow health, productivity, and overall farm profitability.
Nutritional Differences: TMR vs Forage-Only Diets
Total Mixed Ration (TMR) diets provide cows with a balanced blend of forage, grains, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, optimizing nutrient intake and enhancing milk production compared to forage-only diets. Forage-only feeding primarily supplies fiber and energy but often lacks sufficient protein and energy density, potentially limiting milk yield and cow health. Nutritional differences between TMR and forage-only diets significantly impact rumen function, nutrient absorption, and overall dairy cow performance.
Effects on Cow Health and Longevity
Feeding cows a Total Mixed Ration (TMR) improves nutrient balance, leading to enhanced digestion and reduced risk of metabolic disorders compared to forage-only diets. TMR supports stable rumen pH levels, decreasing incidences of acidosis and promoting better immune function, which contributes to longer productive lifespans. Forage-only feeding often results in inconsistent nutrient intake and higher susceptibility to digestive issues, negatively impacting cow health and longevity.
Milk Production: TMR Compared to Forage-Only
Total Mixed Ration (TMR) diets provide a balanced blend of forage, grains, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, resulting in enhanced milk yield and improved nutrient utilization compared to forage-only feeding. Studies show cows on TMR produce up to 15-20% more milk with higher fat and protein content due to consistent energy and nutrient intake. Forage-only diets often lead to lower milk production because of variability in nutrient availability and inadequate energy density.
Rumen Function and Digestion Efficiency
Total Mixed Ration (TMR) feeding enhances rumen function by providing a balanced blend of forage, grains, and supplements, which promotes optimal microbial activity and improves fiber digestion. In contrast, forage-only diets often result in less consistent nutrient intake and reduced rumen fermentation efficiency, potentially limiting microbial protein synthesis. TMR supports higher feed intake and better nutrient utilization, leading to improved digestion efficiency and milk production in dairy cows.
Economic Considerations in Feed Choices
TMR (Total Mixed Ration) feeding systems optimize nutrient intake by blending forages, grains, protein supplements, and minerals, often leading to higher milk yields and improved feed efficiency compared to forage-only diets. Although TMR requires higher initial investment in feed ingredients and mixing equipment, the enhanced productivity can result in lower cost per unit of milk produced, improving overall farm profitability. Forage-only feeding reduces feed costs but may limit milk production potential, posing economic trade-offs depending on forage quality, market prices, and herd production goals.
Practical Feeding Management for Pet Cows
TMR (Total Mixed Ration) offers balanced nutrient intake by combining forage, grains, vitamins, and minerals, promoting consistent weight maintenance and improved digestion in pet cows. Forage-only diets primarily provide fiber but may lack essential nutrients, leading to potential deficiencies and uneven energy supply. Practical feeding management for pet cows emphasizes TMR to ensure optimal health, enhance milk production, and support overall well-being.
Environmental Impact: TMR vs Forage-Only
Total Mixed Ration (TMR) feeding in cows reduces methane emissions per unit of milk produced compared to forage-only diets by improving feed digestibility and nutrient absorption. Forage-only diets often result in higher methane emissions due to increased fiber content leading to more enteric fermentation. Studies indicate that TMR systems contribute to lower greenhouse gas intensity in dairy production, enhancing environmental sustainability.
Palatability and Feeding Behavior
Total Mixed Ration (TMR) enhances palatability by blending forages, grains, vitamins, and minerals uniformly, encouraging consistent intake and minimizing selective feeding among cows. In contrast, forage-only diets may lead to selective grazing, resulting in uneven nutrient consumption and reduced overall feed efficiency. Feeding behavior studies show that cows fed TMR exhibit more stable rumination patterns and less sorting activity, promoting better digestion and milk production.
Choosing the Best Diet for Your Pet Cow
Choosing the best diet for your pet cow involves comparing Total Mixed Ration (TMR) and forage-only feeding strategies. TMR provides a balanced mix of nutrients by combining forages, grains, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, optimizing digestion and milk production in dairy cows. Forage-only diets promote natural grazing behavior and rumen health but may lack certain essential nutrients, potentially requiring supplementation to meet energy and protein needs effectively.
TMR (Total Mixed Ration) vs Forage-only for Cow feeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com