Effective manure management for ducks involves regular collection and controlled storage to prevent odors and water contamination, while composting transforms duck waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments that enhance garden fertility. Composting requires proper balance of carbon and nitrogen, adequate aeration, and moisture control to accelerate decomposition and reduce pathogens. Both methods minimize environmental impact, but composting provides a sustainable solution by recycling duck manure into valuable organic fertilizer.
Table of Comparison
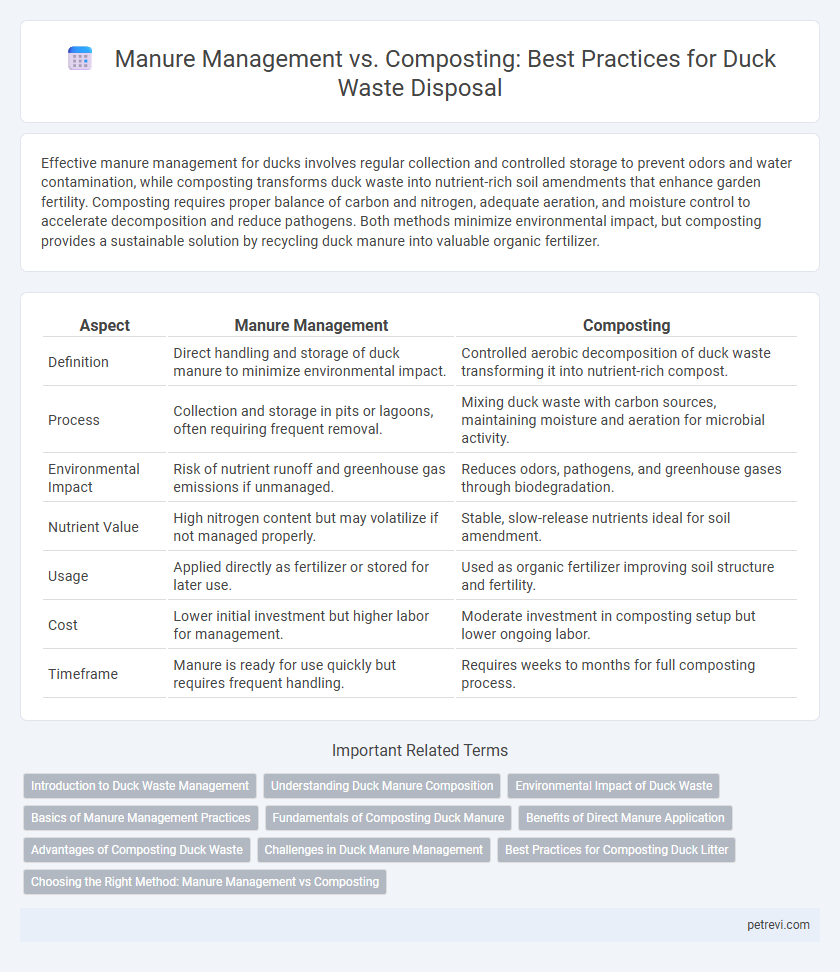
| Aspect | Manure Management | Composting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct handling and storage of duck manure to minimize environmental impact. | Controlled aerobic decomposition of duck waste transforming it into nutrient-rich compost. |
| Process | Collection and storage in pits or lagoons, often requiring frequent removal. | Mixing duck waste with carbon sources, maintaining moisture and aeration for microbial activity. |
| Environmental Impact | Risk of nutrient runoff and greenhouse gas emissions if unmanaged. | Reduces odors, pathogens, and greenhouse gases through biodegradation. |
| Nutrient Value | High nitrogen content but may volatilize if not managed properly. | Stable, slow-release nutrients ideal for soil amendment. |
| Usage | Applied directly as fertilizer or stored for later use. | Used as organic fertilizer improving soil structure and fertility. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment but higher labor for management. | Moderate investment in composting setup but lower ongoing labor. |
| Timeframe | Manure is ready for use quickly but requires frequent handling. | Requires weeks to months for full composting process. |
Introduction to Duck Waste Management
Effective duck waste management is essential for maintaining healthy poultry environments and minimizing environmental impact. Manure management involves the collection, storage, and treatment of duck droppings to prevent nutrient runoff and odor issues, while composting converts duck waste into nutrient-rich organic fertilizer through controlled aerobic decomposition. Implementing proper composting techniques enhances nutrient recycling, reduces pathogens, and supports sustainable agriculture practices.
Understanding Duck Manure Composition
Duck manure is high in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making it a valuable resource for both manure management and composting processes. Understanding its composition is crucial because fresh duck manure has a strong ammonia presence that can harm plants if applied directly, whereas composting stabilizes nutrients and reduces pathogens. Proper composting transforms duck waste into a nutrient-rich soil amendment that supports sustainable agricultural practices.
Environmental Impact of Duck Waste
Proper manure management of duck waste reduces nitrogen runoff and methane emissions, preserving water quality and decreasing greenhouse gases. Composting duck waste stabilizes nutrients, promotes beneficial microbial activity, and minimizes odor, resulting in a more sustainable environmental footprint. Both approaches improve soil health but composting offers enhanced pathogen reduction and carbon cycling benefits.
Basics of Manure Management Practices
Effective manure management practices for duck waste involve regular collection, proper storage, and timely application to fields to minimize environmental impact and nutrient loss. Maintaining appropriate moisture levels and aeration during storage prevents odor and pathogen buildup, ensuring safer handling and better nutrient retention. Implementing these basics supports sustainable farming by recycling nutrients while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Fundamentals of Composting Duck Manure
Composting duck manure leverages microbial activity to break down organic waste into nutrient-rich humus, effectively reducing pathogens and odors compared to raw manure. Temperature control between 55-65degC during the thermophilic phase ensures pathogen kill-off while maintaining beneficial microbial growth. Proper carbon-to-nitrogen ratios (around 25:1 to 30:1) optimize decomposition, transforming duck waste into a safe, valuable soil amendment that supports sustainable agriculture.
Benefits of Direct Manure Application
Direct manure application from ducks enhances soil fertility by supplying essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in an immediately bioavailable form for crops. This method reduces the time and labor associated with composting while promoting microbial activity directly in the soil, which improves soil structure and water retention. Furthermore, direct application minimizes nutrient losses during decomposition, ensuring efficient nutrient cycling and boosting agricultural productivity.
Advantages of Composting Duck Waste
Composting duck waste transforms harmful pathogens and ammonia into nutrient-rich organic fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility and reducing environmental pollution. This process accelerates the breakdown of waste, decreases odor, and minimizes greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional manure management methods. Utilizing composted duck waste improves water retention in soil and supports sustainable agricultural practices by recycling valuable nutrients.
Challenges in Duck Manure Management
Duck manure management faces challenges such as high moisture content and strong odor, which complicate storage and application. Excessive nutrient runoff from improperly managed manure can lead to water pollution and eutrophication. Unlike composting, direct manure handling often struggles with pathogen control and slow nutrient stabilization, increasing environmental risks.
Best Practices for Composting Duck Litter
Effective composting of duck litter requires maintaining a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio of approximately 25:1 to optimize microbial activity and minimize odors. Regularly turning the compost pile enhances aeration, accelerates decomposition, and reduces harmful pathogens often associated with unmanaged manure. Maintaining moisture levels between 40-60% and ensuring the internal temperature reaches 131-170degF (55-77degC) are critical best practices for producing high-quality, nutrient-rich compost from duck waste.
Choosing the Right Method: Manure Management vs Composting
Effective duck waste disposal requires careful manure management or composting to minimize environmental impact and maximize nutrient recycling. Manure management techniques involve direct application in controlled amounts to fields, reducing runoff and maintaining soil health, while composting transforms duck waste into nutrient-rich organic matter, enhancing soil structure and fertility over time. Selecting the right method depends on factors like available space, odor control, processing time, and desired end-product quality for sustainable duck farming.
Manure management vs Composting for Duck waste Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com