Natural mating in duck breeding allows for instinctive behaviors and stronger pair bonds, often resulting in higher fertility rates and healthier offspring. Artificial insemination offers controlled breeding opportunities, enabling genetic diversity and reducing disease transmission risks. Choosing between these methods depends on the breeder's goals, flock size, and health management priorities.
Table of Comparison
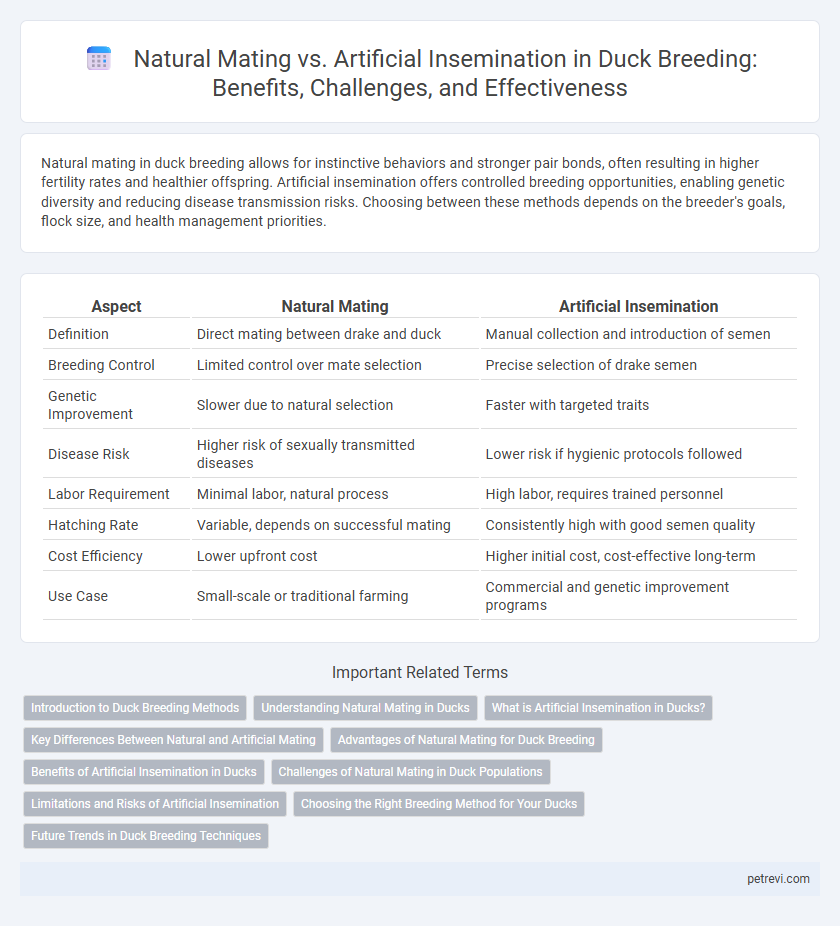
| Aspect | Natural Mating | Artificial Insemination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct mating between drake and duck | Manual collection and introduction of semen |
| Breeding Control | Limited control over mate selection | Precise selection of drake semen |
| Genetic Improvement | Slower due to natural selection | Faster with targeted traits |
| Disease Risk | Higher risk of sexually transmitted diseases | Lower risk if hygienic protocols followed |
| Labor Requirement | Minimal labor, natural process | High labor, requires trained personnel |
| Hatching Rate | Variable, depends on successful mating | Consistently high with good semen quality |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective long-term |
| Use Case | Small-scale or traditional farming | Commercial and genetic improvement programs |
Introduction to Duck Breeding Methods
Natural mating in duck breeding involves direct interaction between drakes and hens, promoting natural selection and behavioral cues that enhance fertility rates. Artificial insemination (AI) allows precise control over genetic traits by manually introducing semen, increasing hatchability and reducing disease transmission risks. Both methods play crucial roles in optimizing duck production, with AI gaining popularity for commercial breeding due to its efficiency and genetic management advantages.
Understanding Natural Mating in Ducks
Natural mating in ducks involves the direct copulation process where the male mounts the female to transfer sperm, ensuring fertilization occurs naturally without human intervention. This method maintains genetic diversity and exhibits natural selection advantages by allowing mate choice based on behavioral and physical cues. Understanding natural mating behaviors, such as courtship displays and nesting habits, helps optimize breeding success and duck welfare in both wild and managed environments.
What is Artificial Insemination in Ducks?
Artificial insemination in ducks involves collecting semen from a drake and manually depositing it into the hen's reproductive tract to facilitate fertilization without natural mating. This technique enhances genetic selection, boosts fertilization rates, and allows breeding in controlled environments, reducing the risks associated with aggressive mating behaviors. Advanced semen evaluation and handling protocols are crucial to maintaining ejaculate viability and maximizing reproductive success in duck breeding programs.
Key Differences Between Natural and Artificial Mating
Natural mating in ducks involves direct copulation, ensuring natural selection and genetic diversity, whereas artificial insemination (AI) allows controlled sperm delivery, increasing breeding precision and reducing disease transmission. Natural mating depends on environmental factors and duck behavior, often limiting breeding frequency and timing, while AI enables year-round breeding with enhanced fertility rates. AI requires specialized equipment and trained personnel, providing a scalable solution for commercial duck farming compared to the labor-intensive natural mating process.
Advantages of Natural Mating for Duck Breeding
Natural mating in duck breeding promotes genetic diversity and ensures natural selection, leading to healthier offspring with improved survival rates. It allows for better detection of behavioral traits and mating compatibility, which enhances reproductive success. This method reduces the need for specialized equipment and technical expertise, making it more cost-effective and accessible for small-scale farmers.
Benefits of Artificial Insemination in Ducks
Artificial insemination in duck breeding enhances genetic diversity by allowing selective mating from superior males regardless of location. This method increases fertilization rates and hatchability, leading to improved flock productivity. It also reduces disease transmission risks compared to natural mating, promoting better flock health management.
Challenges of Natural Mating in Duck Populations
Natural mating in duck populations faces challenges such as limited mate availability due to territorial behavior and aggressive interactions, leading to decreased breeding efficiency. Environmental factors like water quality and habitat disruption can further hinder successful copulation. These issues contribute to inconsistent fertility rates and complicate population management, often necessitating alternative breeding methods.
Limitations and Risks of Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination in duck breeding presents limitations such as lower fertility rates compared to natural mating, due to the delicate handling required for semen collection and insemination. Risks include increased chances of disease transmission through contaminated equipment and potential stress-induced injuries to both males and females during the procedure. Furthermore, artificial insemination demands specialized skills and infrastructure, which can result in higher costs and inconsistent breeding outcomes.
Choosing the Right Breeding Method for Your Ducks
Natural mating in duck breeding allows for genetic diversity and natural behavior expression, promoting healthier offspring, but it requires space and time for the ducks to pair and mate effectively. Artificial insemination offers precise control over genetics and timing, improving breeding efficiency and reducing disease transmission risks, though it demands technical skill and equipment. Selecting the right method depends on factors like flock size, breeding goals, resources, and the desired control over genetic traits for optimal duck production.
Future Trends in Duck Breeding Techniques
Future trends in duck breeding techniques emphasize the integration of advanced artificial insemination (AI) methods to enhance genetic diversity and improve hatchability rates. Precision breeding tools, including genetic marker-assisted selection, are increasingly combined with AI for more efficient and targeted outcomes compared to traditional natural mating. Emerging technologies such as automated semen collection and cryopreservation promise to revolutionize duck reproduction by enabling large-scale, year-round breeding programs.
Natural Mating vs Artificial Insemination for Duck Breeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com