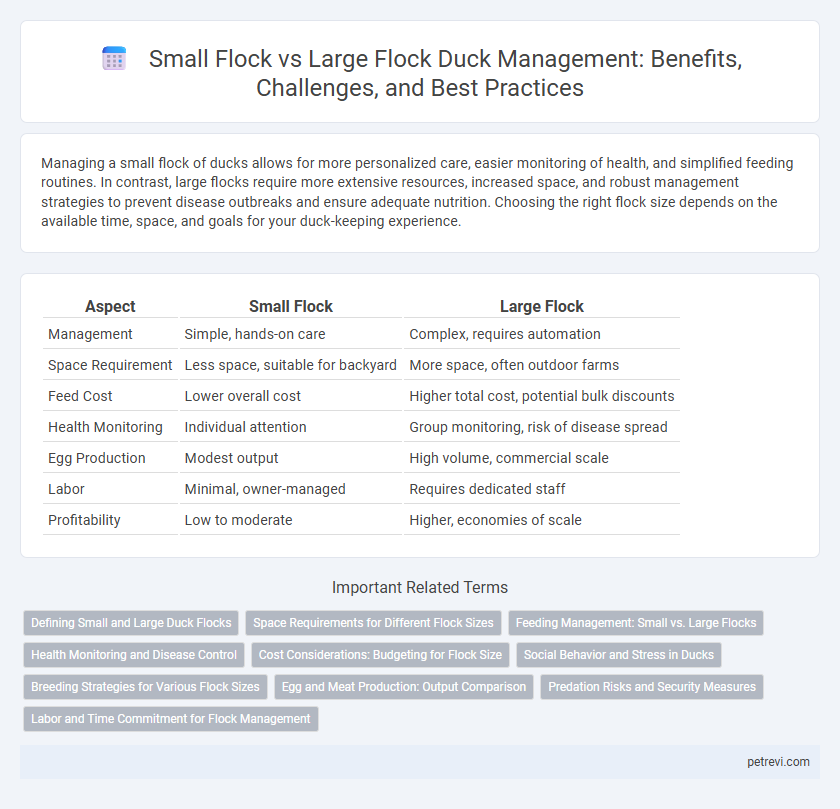
Managing a small flock of ducks allows for more personalized care, easier monitoring of health, and simplified feeding routines. In contrast, large flocks require more extensive resources, increased space, and robust management strategies to prevent disease outbreaks and ensure adequate nutrition. Choosing the right flock size depends on the available time, space, and goals for your duck-keeping experience.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Small Flock | Large Flock |
|---|---|---|
| Management | Simple, hands-on care | Complex, requires automation |
| Space Requirement | Less space, suitable for backyard | More space, often outdoor farms |
| Feed Cost | Lower overall cost | Higher total cost, potential bulk discounts |
| Health Monitoring | Individual attention | Group monitoring, risk of disease spread |
| Egg Production | Modest output | High volume, commercial scale |
| Labor | Minimal, owner-managed | Requires dedicated staff |
| Profitability | Low to moderate | Higher, economies of scale |
Defining Small and Large Duck Flocks
Small duck flocks typically consist of fewer than 20 birds, allowing for easier individual monitoring and management of health, feeding, and behavior. Large duck flocks exceed 50 birds, requiring more comprehensive infrastructure, automated feeding systems, and disease control protocols to maintain flock welfare. Properly defining small and large flocks helps optimize resource allocation and biosecurity practices in duck farming.
Space Requirements for Different Flock Sizes
Small flocks of ducks require significantly less space, typically around 4 square feet per bird, facilitating easier management and efficient use of limited areas. Large flocks demand extensive space, often exceeding 2,000 square feet for 500 ducks, to prevent overcrowding, reduce stress, and maintain proper hygiene. Adequate space allocation in both flock sizes directly impacts duck health, productivity, and overall flock welfare.
Feeding Management: Small vs. Large Flocks
Feeding management in small duck flocks allows precise control over individual nutritional needs, minimizing feed waste and ensuring uniform growth. Large flocks require automated feeding systems and strategic feed distribution to prevent competition and uneven intake. Optimizing feed type and delivery frequency according to flock size enhances overall health and productivity in duck populations.
Health Monitoring and Disease Control
Managing small flocks allows for more precise health monitoring due to easier observation of individual ducks, facilitating early detection of illness and targeted treatment. Large flocks pose challenges for disease control, as close proximity increases the risk of rapid pathogen spread, necessitating stringent biosecurity measures and regular health screenings. Implementing systematic health protocols is critical in both scenarios to prevent outbreaks and ensure overall flock vitality.
Cost Considerations: Budgeting for Flock Size
Managing a small flock of ducks generally incurs lower initial costs for housing, feed, and healthcare compared to a large flock, making it more budget-friendly for beginners or hobbyists. Large flocks require significant investment in infrastructure, bulk feed purchases, and labor, but benefit from economies of scale that reduce the per-duck cost over time. Effective budgeting for flock size must account for these cost differences to balance financial resources with production goals.
Social Behavior and Stress in Ducks
Ducks in small flocks exhibit stronger social bonds and reduced aggression compared to large flock groups, which often lead to increased stress due to overcrowding and competition for resources. Stress indicators like elevated corticosterone levels are more prevalent in large flocks, negatively impacting immune function and growth rates. Effective duck management balances optimal flock size to encourage natural social behaviors while minimizing stress-related health issues.
Breeding Strategies for Various Flock Sizes
Small flocks allow for controlled breeding with precise selection, minimizing inbreeding and enhancing genetic traits, ideal for maintaining high-quality stock. Large flocks facilitate genetic diversity through broader mate selection, supporting robustness and adaptability but require meticulous record-keeping to prevent genetic drift. Tailoring breeding strategies to flock size optimizes reproductive efficiency and improves overall flock health in duck management.
Egg and Meat Production: Output Comparison
Small flock management for ducks typically yields higher-quality eggs and meat due to better individual care and reduced stress, enhancing production efficiency. Large flocks offer greater total output but may face challenges like increased disease risk and inconsistent product quality, impacting overall performance. Optimizing flock size balances maximizing egg and meat yield with maintaining animal health and product standards.
Predation Risks and Security Measures
Small flocks of ducks experience higher predation risks due to limited vigilance and fewer birds to deter predators, necessitating enhanced security measures such as secure housing and regular monitoring. Large flocks benefit from collective vigilance, where multiple ducks alert to danger, reducing individual vulnerability; however, they require robust perimeter fencing and predator-proof netting to manage the increased attraction to predators. Implementing motion-activated lighting and predator deterrent devices is critical regardless of flock size to minimize losses and maintain duck welfare.
Labor and Time Commitment for Flock Management
Managing a small flock of ducks typically requires less labor and time, allowing for more individualized care, easier monitoring of health, and simpler feeding routines. Large flocks demand significant time investment for daily maintenance tasks such as feeding, cleaning, and health inspections, often necessitating specialized equipment or additional labor to maintain efficiency. Efficient large flock management relies on structured protocols and automation to handle the increased labor and time commitments effectively.
Small Flock vs Large Flock for Duck management Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com