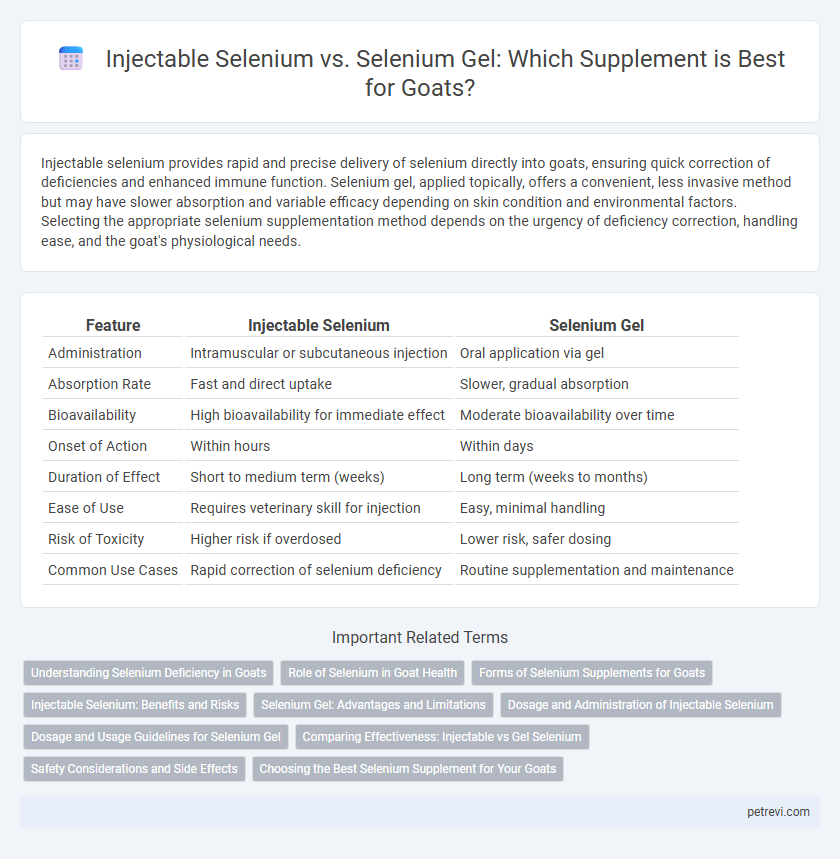
Injectable selenium provides rapid and precise delivery of selenium directly into goats, ensuring quick correction of deficiencies and enhanced immune function. Selenium gel, applied topically, offers a convenient, less invasive method but may have slower absorption and variable efficacy depending on skin condition and environmental factors. Selecting the appropriate selenium supplementation method depends on the urgency of deficiency correction, handling ease, and the goat's physiological needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Injectable Selenium | Selenium Gel |
|---|---|---|
| Administration | Intramuscular or subcutaneous injection | Oral application via gel |
| Absorption Rate | Fast and direct uptake | Slower, gradual absorption |
| Bioavailability | High bioavailability for immediate effect | Moderate bioavailability over time |
| Onset of Action | Within hours | Within days |
| Duration of Effect | Short to medium term (weeks) | Long term (weeks to months) |
| Ease of Use | Requires veterinary skill for injection | Easy, minimal handling |
| Risk of Toxicity | Higher risk if overdosed | Lower risk, safer dosing |
| Common Use Cases | Rapid correction of selenium deficiency | Routine supplementation and maintenance |
Understanding Selenium Deficiency in Goats
Selenium deficiency in goats leads to symptoms such as white muscle disease, reduced immunity, and poor growth, making adequate supplementation essential for herd health. Injectable selenium offers rapid correction of deficiency by directly increasing blood selenium levels, whereas selenium gel provides a slower, sustained release suitable for long-term maintenance. Choosing the appropriate supplementation method depends on the severity of deficiency, with injectable forms preferred for immediate correction and gels for ongoing nutritional support.
Role of Selenium in Goat Health
Selenium plays a critical role in goat health by supporting immune function, antioxidant defense, and reproductive performance. Injectable selenium provides rapid absorption and immediate bioavailability, which is essential during periods of high physiological demand or deficiency, while selenium gel offers a sustained release that maintains adequate selenium levels over time. Choosing the appropriate supplementation method depends on the goat's health status, environmental selenium availability, and the need for quick versus prolonged selenium supply.
Forms of Selenium Supplements for Goats
Injectable selenium provides rapid absorption and immediate bioavailability crucial for treating acute selenium deficiencies in goats, while selenium gels offer a slow-release mechanism suitable for maintaining adequate selenium levels over time. Injectable forms typically contain sodium selenite or sodium selenate in sterile solutions, ensuring precise dosing and bypassing gastrointestinal absorption variability. Selenium gels, often administered orally, combine selenium with a gel matrix that prolongs selenium retention and enhances intestinal uptake for long-term supplementation.
Injectable Selenium: Benefits and Risks
Injectable selenium provides rapid correction of selenium deficiency in goats, ensuring immediate bioavailability and preventing white muscle disease effectively. It offers precise dosage control, reducing the risk of under- or over-supplementation compared to oral gels. However, risks include potential injection site reactions, toxicity from overdose, and the need for veterinary administration to avoid complications.
Selenium Gel: Advantages and Limitations
Selenium gel for goat supplementation offers a convenient, stress-free application method that ensures consistent dosing and reduces the risk of injection site reactions commonly associated with injectable selenium. Its ease of use supports better compliance during large herd management but may result in slower absorption rates compared to injectable forms, potentially delaying the onset of selenium bioavailability. Limited data on long-term efficacy and variability in gel formulation absorption efficiency highlight the need for careful consideration when selecting selenium supplementation routes in goats.
Dosage and Administration of Injectable Selenium
Injectable selenium for goats typically requires a precise dosage of 0.1 mg/kg body weight, administered as a single intramuscular injection to quickly correct selenium deficiency. Unlike selenium gel, injectable forms ensure rapid absorption and bioavailability, providing immediate elevation of selenium levels critical in preventing white muscle disease. Proper administration techniques minimize tissue irritation and maximize efficacy, especially in pregnant or lactating does.
Dosage and Usage Guidelines for Selenium Gel
Selenium gel for goat supplementation typically offers a concentrated dose, with recommended topical application amounts varying between 0.1 to 0.3 mg/kg body weight, applied along the midline of the back. Unlike injectable selenium, which is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously, the gel form reduces handling stress and risk of injection site reactions. Careful adherence to manufacturer dosage instructions is crucial to prevent selenium toxicity while ensuring optimal antioxidant and immune support in goats.
Comparing Effectiveness: Injectable vs Gel Selenium
Injectable selenium offers rapid absorption and immediate increase in blood selenium levels, making it highly effective for preventing acute selenium deficiency in goats. Selenium gel provides a slower, sustained release that supports long-term selenium supplementation but may delay the onset of therapeutic effects. Choosing between injectable and gel selenium depends on the urgency of supplementation and absorption requirements for optimal goat health.
Safety Considerations and Side Effects
Injectable selenium provides rapid correction of selenium deficiency in goats but carries a higher risk of toxicity and tissue irritation if overdosed, requiring precise dosing and professional administration. Selenium gel offers a safer alternative with a slower absorption rate, minimizing the risk of acute toxicity and making it suitable for long-term supplementation. Monitoring for signs of selenium overdose, such as hoof deformities or neurological symptoms, is essential regardless of the delivery method to ensure goat health and safety.
Choosing the Best Selenium Supplement for Your Goats
Injectable selenium offers rapid absorption and precise dosing, making it ideal for immediate correction of deficiencies in goats, whereas selenium gel provides a slower, sustained release beneficial for long-term supplementation. The choice between injectable selenium and selenium gel depends on the goat's health status, deficiency severity, and ease of administration. For optimal goat health and performance, consider factors such as bioavailability, frequency of dosing, and safety profiles when selecting the best selenium supplement.
Injectable Selenium vs Selenium Gel for Goat Supplementation Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com