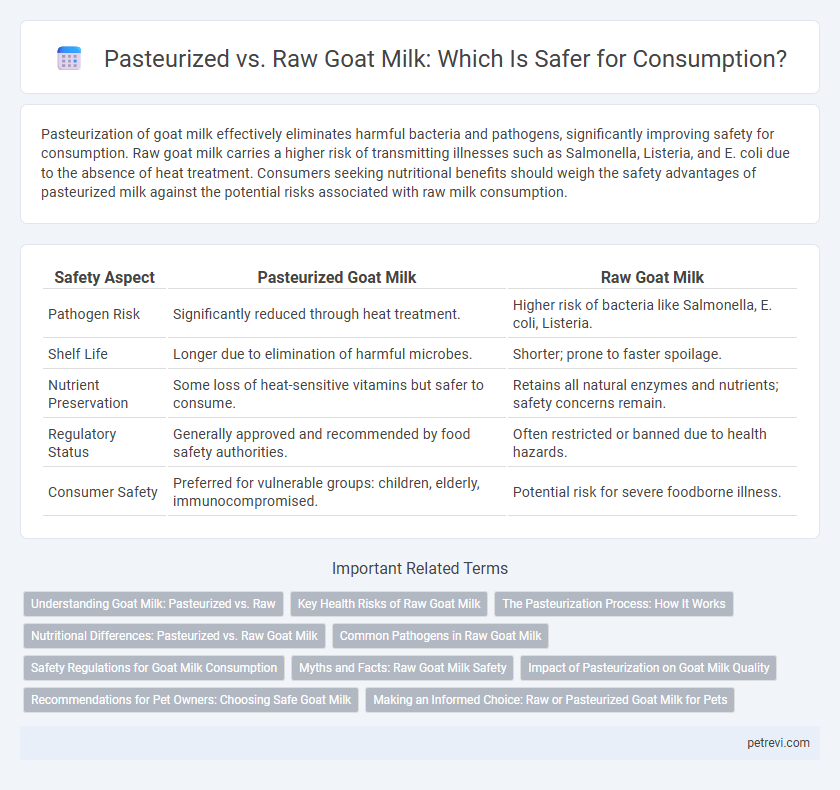
Pasteurization of goat milk effectively eliminates harmful bacteria and pathogens, significantly improving safety for consumption. Raw goat milk carries a higher risk of transmitting illnesses such as Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli due to the absence of heat treatment. Consumers seeking nutritional benefits should weigh the safety advantages of pasteurized milk against the potential risks associated with raw milk consumption.
Table of Comparison
| Safety Aspect | Pasteurized Goat Milk | Raw Goat Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogen Risk | Significantly reduced through heat treatment. | Higher risk of bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, Listeria. |
| Shelf Life | Longer due to elimination of harmful microbes. | Shorter; prone to faster spoilage. |
| Nutrient Preservation | Some loss of heat-sensitive vitamins but safer to consume. | Retains all natural enzymes and nutrients; safety concerns remain. |
| Regulatory Status | Generally approved and recommended by food safety authorities. | Often restricted or banned due to health hazards. |
| Consumer Safety | Preferred for vulnerable groups: children, elderly, immunocompromised. | Potential risk for severe foodborne illness. |
Understanding Goat Milk: Pasteurized vs. Raw
Goat milk safety hinges on the differences between pasteurized and raw varieties, with pasteurization effectively eliminating harmful pathogens while retaining essential nutrients. Raw goat milk, prized for its natural enzymes and probiotics, carries higher risks of bacterial contamination, necessitating stringent quality controls. Understanding these factors helps consumers make informed choices about health benefits and safety when choosing goat milk.
Key Health Risks of Raw Goat Milk
Raw goat milk carries significant health risks due to potential contamination with harmful pathogens such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, which can cause severe foodborne illnesses. Pasteurization effectively eliminates these bacteria by heating milk to a specific temperature, thereby reducing the risk of infections and ensuring safer consumption. Consumers seeking the nutritional benefits of goat milk are strongly advised to choose pasteurized products to avoid the dangers of raw milk consumption.
The Pasteurization Process: How It Works
Pasteurization involves heating goat milk to a specific temperature, typically 161degF (72degC) for at least 15 seconds, to eliminate harmful pathogens such as Listeria, Salmonella, and E. coli. This process effectively reduces microbial load while preserving essential nutrients and enzymes, enhancing the safety of goat milk for consumption. In contrast, raw goat milk bypasses this heating step, increasing the risk of bacterial contamination and potential foodborne illnesses.
Nutritional Differences: Pasteurized vs. Raw Goat Milk
Pasteurized goat milk undergoes heat treatment that kills harmful bacteria but can slightly reduce heat-sensitive nutrients such as vitamin C and certain enzymes. Raw goat milk retains all natural enzymes, beneficial probiotics, and higher levels of some vitamins like B12, offering enhanced nutritional benefits yet carries a higher risk of pathogens. Nutritional differences between pasteurized and raw goat milk hinge on balancing safety concerns with the preservation of delicate nutrients inherent in raw milk.
Common Pathogens in Raw Goat Milk
Raw goat milk often contains common pathogens such as Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and Campylobacter jejuni, which pose significant health risks. Pasteurization effectively eliminates these harmful microorganisms by heating the milk to a specific temperature for a set time, ensuring safer consumption. Consuming raw goat milk increases the risk of bacterial infections, especially in vulnerable populations like children, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals.
Safety Regulations for Goat Milk Consumption
Pasteurization of goat milk is mandated by many national safety regulations to eliminate harmful pathogens such as Listeria, Salmonella, and E. coli, significantly reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses. Raw goat milk, while rich in enzymes and beneficial bacteria, poses a higher safety risk due to the potential presence of undetected pathogens, leading to stricter regulatory controls and warning labels in numerous countries. Compliance with safety standards often requires pasteurized milk for commercial sale, ensuring consumer protection and adherence to public health policies.
Myths and Facts: Raw Goat Milk Safety
Raw goat milk is often mistaken as unsafe due to myths about bacterial contamination; however, studies show that properly sourced raw goat milk can harbor beneficial probiotics and enzymes that pasteurization destroys. Pasteurization, while effective at killing harmful pathogens like Listeria and Salmonella, also reduces the milk's nutritional quality and natural defenses. Ensuring raw goat milk safety relies on rigorous hygiene, animal health monitoring, and timely refrigeration rather than automatic pasteurization.
Impact of Pasteurization on Goat Milk Quality
Pasteurization of goat milk effectively eliminates harmful pathogens, ensuring safety for consumption, but it can slightly reduce some heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C and certain enzymes. Raw goat milk retains its full nutrient profile and beneficial enzymes, which may support digestion, but carries a higher risk of bacterial contamination. Careful sourcing and handling practices are critical when consuming raw goat milk to minimize foodborne illness risks.
Recommendations for Pet Owners: Choosing Safe Goat Milk
Pet owners should prioritize pasteurized goat milk to minimize the risk of harmful bacteria such as Listeria, Salmonella, and E. coli, which can be present in raw milk. Pasteurization heats the milk to a temperature that effectively eliminates pathogens while preserving essential nutrients like calcium and vitamins. For pets with specific dietary sensitivities, consulting a veterinarian ensures the safest choice of goat milk tailored to their health needs.
Making an Informed Choice: Raw or Pasteurized Goat Milk for Pets
Choosing between raw and pasteurized goat milk for pets involves understanding the safety and nutritional benefits of each option. Pasteurized goat milk is heated to eliminate harmful bacteria, reducing health risks while preserving most nutrients, making it a safer choice for pets with sensitive immune systems. Raw goat milk maintains more natural enzymes and probiotics, supporting digestion and immunity, but requires strict hygiene and sourcing from healthy herds to minimize potential pathogens.
Pasteurization vs Raw for Goat milk safety Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com