Wild-type geese possess genetic traits adapted for survival in natural environments, including strong flight muscles and seasonal migratory behaviors, while domestic geese have been selectively bred for traits such as increased body size, reduced flight capability, and docile temperament. These genetic differences result in variations in growth rates, feeding habits, and reproductive cycles, influencing their care and management. Understanding the genetic distinctions between wild-type and domestic geese supports effective breeding programs and conservation efforts.
Table of Comparison
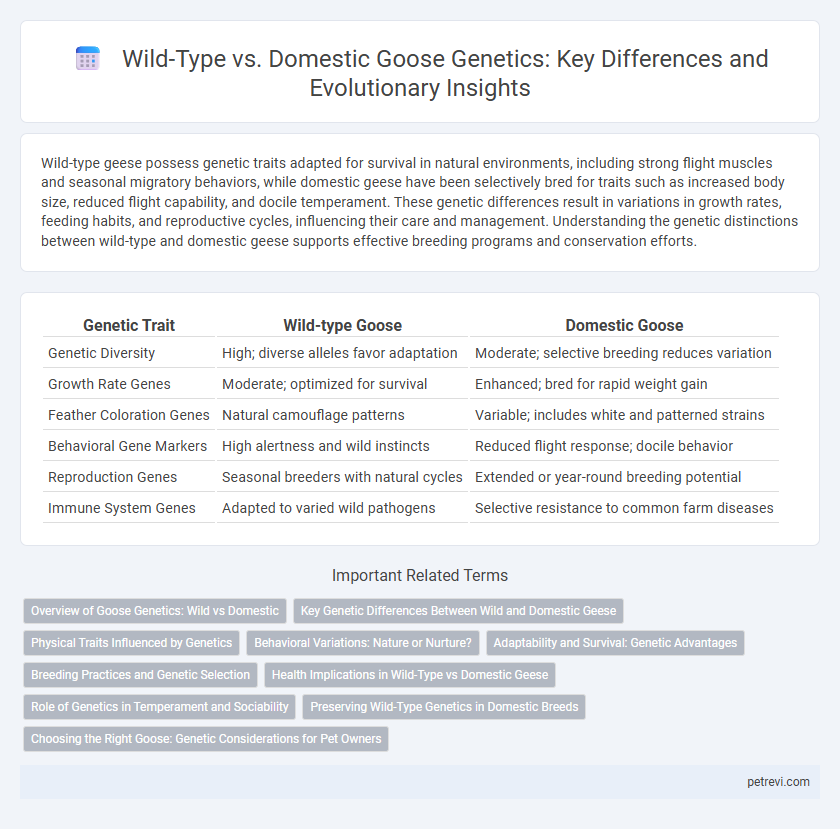
| Genetic Trait | Wild-type Goose | Domestic Goose |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | High; diverse alleles favor adaptation | Moderate; selective breeding reduces variation |
| Growth Rate Genes | Moderate; optimized for survival | Enhanced; bred for rapid weight gain |
| Feather Coloration Genes | Natural camouflage patterns | Variable; includes white and patterned strains |
| Behavioral Gene Markers | High alertness and wild instincts | Reduced flight response; docile behavior |
| Reproduction Genes | Seasonal breeders with natural cycles | Extended or year-round breeding potential |
| Immune System Genes | Adapted to varied wild pathogens | Selective resistance to common farm diseases |
Overview of Goose Genetics: Wild vs Domestic
Wild-type goose genetics exhibit greater genetic diversity with traits adapted for survival in natural habitats, including stronger flight muscles and enhanced foraging behaviors. Domestic geese have been selectively bred for size, growth rate, and docility, resulting in reduced genetic variability and traits favoring meat and egg production. Understanding these genetic differences aids in conservation efforts and improves selective breeding programs.
Key Genetic Differences Between Wild and Domestic Geese
Wild-type geese possess genetic traits that enhance flight capability, predator awareness, and seasonal migration patterns, while domestic geese exhibit genetic modifications favoring increased body mass, reduced flight ability, and tameness due to selective breeding. Key differences include variations in genes regulating muscle composition, growth rate, and behavior, with domestic geese showing altered expression of growth hormone and neural crest cell-related genes. These genetic adaptations reflect evolutionary pressures in the wild versus artificial selection within agricultural environments.
Physical Traits Influenced by Genetics
Wild-type geese exhibit physical traits such as darker plumage, longer necks, and more robust body structures, influenced by genetic adaptations for survival in natural habitats. Domestic geese have been selectively bred for traits like enlarged body mass, shorter wings, and paler feather coloration to enhance meat production and manageability. Genetic variations between wild-type and domestic geese directly impact physical characteristics, reflecting evolutionary pressures versus human-driven selection.
Behavioral Variations: Nature or Nurture?
Wild-type geese exhibit strong migratory instincts and heightened wariness of predators compared to domestic geese, whose behaviors are significantly shaped by selective breeding for docility and reduced flight response. Genetic analyses reveal that certain alleles linked to stress response and social interaction differ between wild and domestic populations, suggesting inherent behavioral predispositions. Environmental factors and human management further modulate these traits, highlighting the complex interplay between nature and nurture in goose behavior.
Adaptability and Survival: Genetic Advantages
Wild-type geese possess genetic traits that enhance adaptability and survival in natural environments, such as superior foraging skills and heightened predator awareness. Domestic geese, bred for traits like size and docility, often lack these survival advantages, making them less resilient in the wild. Understanding these genetic differences is crucial for breeding programs aimed at improving environmental adaptability and long-term survival rates.
Breeding Practices and Genetic Selection
Wild-type geese exhibit greater genetic diversity compared to domestic geese, which have undergone selective breeding to enhance traits such as size, egg production, and temperament. Breeding practices in domestic geese prioritize genetic selection for traits favoring agricultural productivity, including rapid growth rates and disease resistance. This selective breeding narrows the gene pool, often reducing adaptability present in wild-type populations but optimizing geese for commercial use.
Health Implications in Wild-Type vs Domestic Geese
Wild-type geese possess genetic diversity that enhances their resistance to common diseases compared to domestic geese, which often have reduced genetic variability due to selective breeding. Domestic geese may exhibit increased susceptibility to respiratory infections and metabolic disorders because of their confined environments and inbreeding. Understanding these genetic health implications is crucial for improving breeding practices and managing disease risks in domestic populations.
Role of Genetics in Temperament and Sociability
Wild-type geese exhibit genetic traits that promote heightened alertness and strong flock cohesion, essential for survival in natural habitats. Domestic geese have been selectively bred for reduced aggression and increased docility, resulting in genetic variations that influence calmer temperaments and enhanced sociability with humans. Understanding these genetic differences aids in breeding programs aimed at improving behavioral traits for both conservation and agricultural purposes.
Preserving Wild-Type Genetics in Domestic Breeds
Preserving wild-type genetics in domestic geese is crucial for maintaining genetic diversity and resilience against diseases and environmental changes. Wild-type geese possess unique alleles that contribute to traits like enhanced foraging ability and adaptability, which are often diminished in selectively bred domestic populations. Conserving these genetics through controlled breeding programs helps sustain the natural gene pool and supports long-term viability of both wild and domestic goose populations.
Choosing the Right Goose: Genetic Considerations for Pet Owners
Selecting the right goose involves understanding the genetic differences between wild-type and domestic breeds, as wild-type geese retain natural behaviors and stronger survival instincts, while domestic geese have been bred for docility and adaptability to human environments. Genetic considerations include assessing temperament, growth rate, and disease resistance, which vary significantly between wild and domestic strains. Pet owners should prioritize breeds with genetic traits matching their care abilities and environment to ensure a healthy and manageable companion.
Wild-type vs Domestic for Goose Genetics Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com