Piglet fostering involves moving piglets to another sow within the same litter to balance litter sizes, enhancing individual piglet care and survival rates. Cross-fostering transfers piglets between different sows, often across multiple litters, to optimize sow productivity and ensure uniform piglet growth by matching piglet needs with sow milk capacity. Both techniques improve piglet management by reducing competition and promoting healthier development, but cross-fostering requires careful planning to prevent disease spread and maintain sow-piglet bonding.
Table of Comparison
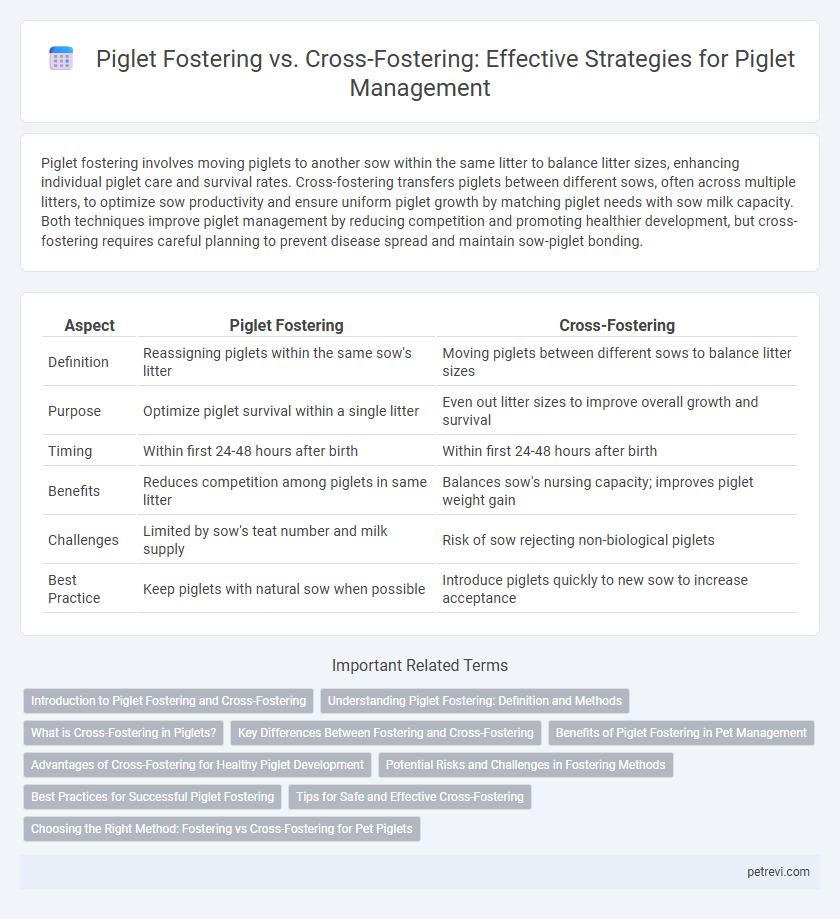
| Aspect | Piglet Fostering | Cross-Fostering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reassigning piglets within the same sow's litter | Moving piglets between different sows to balance litter sizes |
| Purpose | Optimize piglet survival within a single litter | Even out litter sizes to improve overall growth and survival |
| Timing | Within first 24-48 hours after birth | Within first 24-48 hours after birth |
| Benefits | Reduces competition among piglets in same litter | Balances sow's nursing capacity; improves piglet weight gain |
| Challenges | Limited by sow's teat number and milk supply | Risk of sow rejecting non-biological piglets |
| Best Practice | Keep piglets with natural sow when possible | Introduce piglets quickly to new sow to increase acceptance |
Introduction to Piglet Fostering and Cross-Fostering
Piglet fostering involves transferring a piglet to another sow within the same litter group to balance litter sizes and improve survival rates, while cross-fostering refers to moving piglets between different sows or litters shortly after birth to optimize sow milk availability and piglet growth. Both techniques aim to reduce competition among piglets, enhance uniformity in weight gain, and lower pre-weaning mortality in commercial pig production. Effective piglet management through fostering practices requires timely intervention, understanding sow maternal behavior, and ensuring piglet health status to maximize reproductive efficiency.
Understanding Piglet Fostering: Definition and Methods
Piglet fostering involves transferring piglets from their biological mother to another sow to ensure better care and survival, commonly applied when litter sizes exceed the sow's nursing capacity. Cross-fostering is a specific type of fostering where piglets are redistributed among sows shortly after birth to balance litter sizes and improve uniformity, reducing competition and mortality risks. Effective fostering methods require careful timing, usually within the first 24 to 48 hours postpartum, and consideration of piglet weight, health status, and sow maternal abilities.
What is Cross-Fostering in Piglets?
Cross-fostering in piglets involves transferring newborns from one sow to another to balance litter size and improve piglet survival and growth. This practice helps ensure that piglets receive adequate nutrition and care when their biological mother has insufficient milk or an excessively large litter. Effective cross-fostering reduces mortality rates and promotes uniform piglet development within the herd.
Key Differences Between Fostering and Cross-Fostering
Piglet fostering involves transferring piglets within the same litter or sow to balance litter size and improve nursing efficiency, while cross-fostering moves piglets between different sows to optimize growth and survival rates. Key differences include the timing of transfer, with fostering usually occurring shortly after birth and cross-fostering often done within 24 to 48 hours, as well as the purpose, where fostering mainly addresses uneven teat access and cross-fostering addresses severe litter size disparities or health issues. Both methods require careful consideration of sow temperament and piglet health to ensure successful adaptation and minimize stress.
Benefits of Piglet Fostering in Pet Management
Piglet fostering enhances piglet survival rates by ensuring consistent access to maternal care and nutrition, which is crucial for their growth and development. Unlike cross-fostering, piglet fostering minimizes stress by keeping piglets within the same litter environment, improving overall health outcomes. This method also supports maternal bonding and reduces the risk of disease transmission, promoting better welfare in pet pig management.
Advantages of Cross-Fostering for Healthy Piglet Development
Cross-fostering improves piglet survival by balancing litter sizes, ensuring uniform access to teats and adequate nutrition, which promotes consistent growth rates. It reduces competition among piglets and minimizes stress, enhancing immune system development and overall health. This practice also allows for better utilization of sow milk production, leading to healthier, more vigorous piglets during the critical early life stages.
Potential Risks and Challenges in Fostering Methods
Piglet fostering poses risks such as increased stress and disease transmission due to interrupted maternal bonding, while cross-fostering may lead to uneven competition among piglets vying for teats. Both methods challenge piglet immunity and growth rates, with cross-fostering sometimes causing aggression or rejection by the sow. Effective management requires monitoring piglet health closely and ensuring compatible litter sizes to mitigate these fostering challenges.
Best Practices for Successful Piglet Fostering
Successful piglet fostering relies on matching litter sizes closely and ensuring uniform piglet weight to minimize competition and stress. Maintaining strict hygiene and providing a calm environment during transfer reduces the risk of mortality and promotes acceptance by the foster sow. Cross-fostering demands early intervention within 24 to 48 hours post-farrowing to optimize colostrum intake and enhance piglet survival rates.
Tips for Safe and Effective Cross-Fostering
Safe and effective cross-fostering in piglet management requires thorough hygiene and minimizing stress by transferring piglets within 24 to 48 hours after birth. Ensure matching piglet size and weight to the foster sow's existing litter to promote acceptance and reduce competition. Frequent monitoring post-transfer helps identify rejection signs early, allowing timely intervention and improving piglet survival rates.
Choosing the Right Method: Fostering vs Cross-Fostering for Pet Piglets
Choosing between piglet fostering and cross-fostering involves assessing the piglets' health, sow lactation capacity, and litter size. Fostering places piglets with the same mother to optimize familiar bonding, while cross-fostering transfers piglets to different sows to balance litter sizes and improve survival rates. Effective management of either method requires monitoring piglets' weight gain, sow acceptance, and minimizing stress to ensure optimal growth for pet piglets.
Piglet fostering vs Cross-fostering for Piglet management Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com