Split suckling and cross-fostering are essential management practices to enhance piglet survival during the critical early days after birth. Split suckling ensures smaller or weaker piglets receive adequate access to the sow's teats by temporarily separating stronger siblings, optimizing milk intake and reducing mortality. Cross-fostering balances litter sizes by redistributing piglets among sows, preventing competition and improving overall growth and survival rates.
Table of Comparison
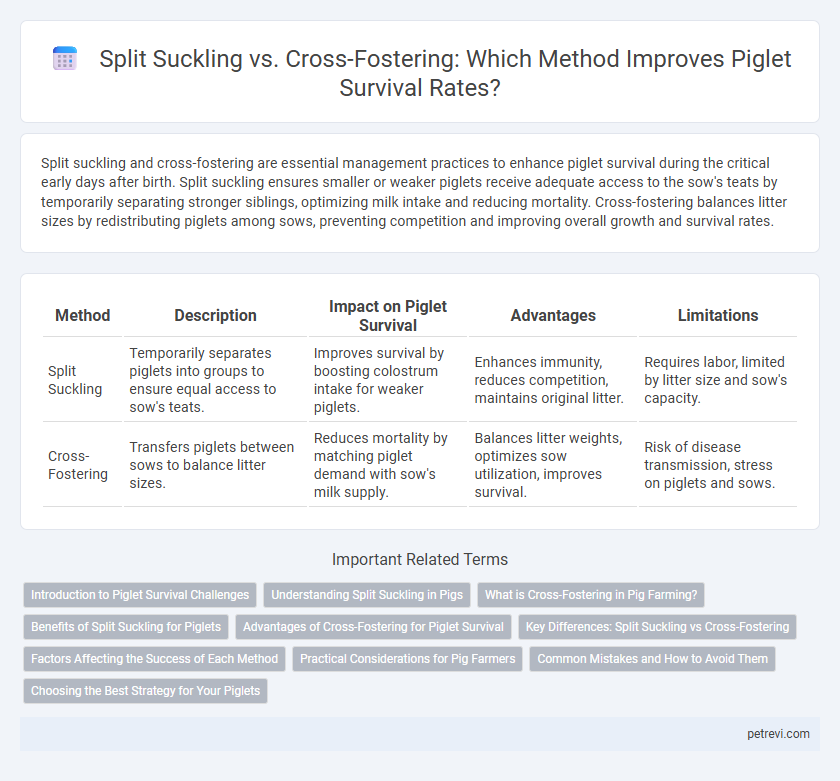
| Method | Description | Impact on Piglet Survival | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Split Suckling | Temporarily separates piglets into groups to ensure equal access to sow's teats. | Improves survival by boosting colostrum intake for weaker piglets. | Enhances immunity, reduces competition, maintains original litter. | Requires labor, limited by litter size and sow's capacity. |
| Cross-Fostering | Transfers piglets between sows to balance litter sizes. | Reduces mortality by matching piglet demand with sow's milk supply. | Balances litter weights, optimizes sow utilization, improves survival. | Risk of disease transmission, stress on piglets and sows. |
Introduction to Piglet Survival Challenges
Piglet survival faces significant challenges due to factors such as low birth weight, competition for teats, and limited colostrum intake immediately after birth. Split suckling and cross-fostering are management techniques used to improve access to nutrition and reduce mortality by ensuring equitable distribution of maternal resources among piglets. Effective implementation of these methods mitigates risks of starvation, hypothermia, and crushing, thereby increasing overall litter survival rates.
Understanding Split Suckling in Pigs
Split suckling in pigs is a management technique where larger, stronger piglets are temporarily separated during nursing to allow smaller, weaker piglets improved access to the sow's teats. This method enhances piglet survival by reducing competition and ensuring adequate colostrum intake, which is critical in the first few hours after birth. Split suckling supports uniform growth and reduces mortality rates compared to unmanaged nursing, making it essential for optimizing litter performance.
What is Cross-Fostering in Pig Farming?
Cross-fostering in pig farming involves transferring piglets from large litters to sows with fewer piglets to balance nursing demand and improve survival rates. This method reduces competition among piglets for teats, ensuring adequate colostrum intake for all. Cross-fostering enhances overall piglet growth, minimizes mortality, and supports uniform litter development.
Benefits of Split Suckling for Piglets
Split suckling improves piglet survival by ensuring smaller or weaker piglets receive adequate colostrum intake during the early postpartum period. This technique reduces competition among piglets at the sow's teat, promoting uniform growth and enhancing immune protection through sufficient antibody uptake. Effective split suckling leads to higher piglet vigor and reduces pre-weaning mortality compared to conventional nursing practices.
Advantages of Cross-Fostering for Piglet Survival
Cross-fostering enhances piglet survival by allowing even distribution of litter size across sows, reducing competition for teats and improving access to colostrum. This practice helps balance piglet birth weights within litters, decreasing mortality rates associated with low birth weight and weak piglets. Effective cross-fostering supports optimal growth rates and strengthens immune development by ensuring all piglets receive adequate nutrition during critical early life stages.
Key Differences: Split Suckling vs Cross-Fostering
Split suckling involves temporarily separating piglets by size or birth order to ensure smaller or weaker piglets access to the sow's teats, enhancing their survival chances through improved nutrition. Cross-fostering transfers piglets between sows to balance litter sizes and reduce competition, promoting uniform growth and higher overall piglet survival rates. The key difference lies in split suckling managing access within the same litter, while cross-fostering redistributes piglets across different sows to optimize nursing capacity.
Factors Affecting the Success of Each Method
Piglet survival rates are influenced by factors such as litter size, sow milk production, and piglet vitality when comparing split suckling and cross-fostering techniques. Split suckling depends on precise timing and careful monitoring of nursing intervals to ensure even colostrum intake, particularly beneficial in large litters to reduce competition. Cross-fostering success hinges on sow acceptance and minimizing stress during piglet transfer, with effective management improving uniformity in piglet growth and reducing mortality.
Practical Considerations for Pig Farmers
Split suckling enhances piglet survival by ensuring equal access to colostrum, reducing competition among large litters and improving immunity. Cross-fostering balances litter sizes by moving piglets to sows with fewer offspring, optimizing udder capacity and boosting growth rates. Practical implementation requires careful timing within the first 24 hours and monitoring sow behavior to prevent rejection and maximize survival outcomes.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in split suckling include uneven piglet grouping leading to weak piglets being overshadowed, while cross-fostering errors often involve transferring piglets too late or mismatched litter sizes causing increased stress. Avoid these issues by implementing split suckling within the first 24 hours postpartum and ensuring cross-fostering occurs within the initial 48 hours with careful consideration of sow capacity and piglet size. Proper timing and piglet monitoring significantly enhance piglet survival rates and overall litter performance.
Choosing the Best Strategy for Your Piglets
Split suckling enhances piglet survival by ensuring smaller or weaker piglets receive adequate colostrum during the critical first hours after birth, boosting immunity and vitality. Cross-fostering balances litter size by redistributing piglets among sows with similar farrowing times, reducing competition and improving overall growth rates. Selecting the best strategy depends on litter size, sow milk production, and timing, with a combination approach often yielding optimal piglet survival and health outcomes.
Split suckling vs Cross-fostering for Piglet survival Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com