Rambouillet sheep offer superior wool quality with finer fibers compared to Merino, making them ideal for premium textile production. They are hardier and better adapted to diverse climates, enhancing their versatility for various farming environments. Merino sheep, while known for their exceptional wool softness and density, tend to require more specialized care in colder, wetter conditions.
Table of Comparison
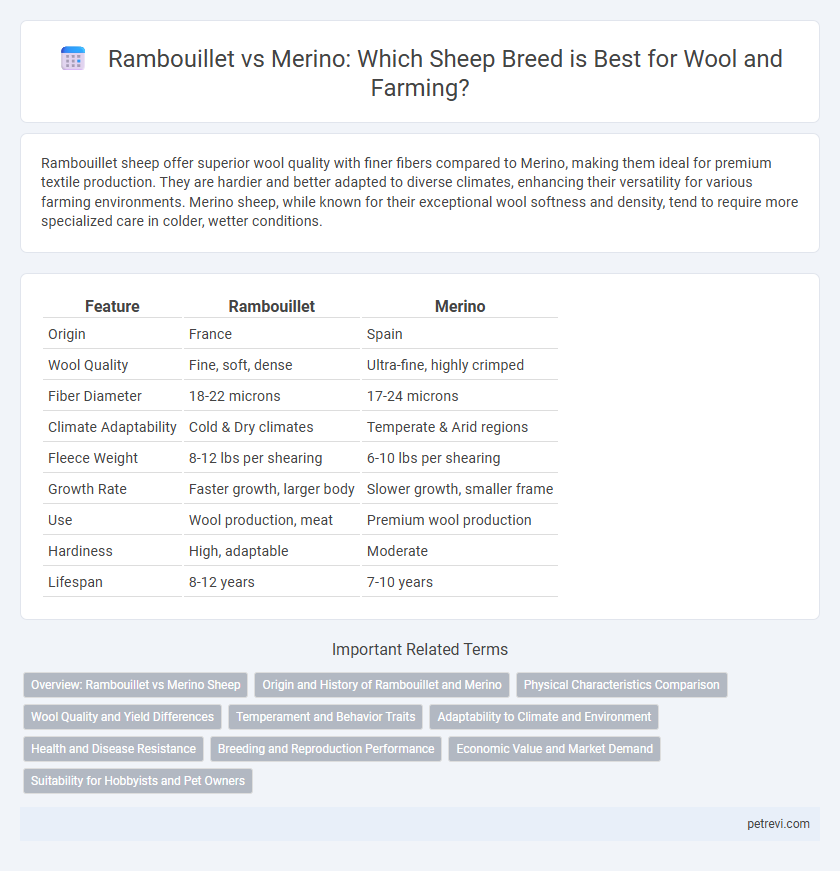
| Feature | Rambouillet | Merino |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | France | Spain |
| Wool Quality | Fine, soft, dense | Ultra-fine, highly crimped |
| Fiber Diameter | 18-22 microns | 17-24 microns |
| Climate Adaptability | Cold & Dry climates | Temperate & Arid regions |
| Fleece Weight | 8-12 lbs per shearing | 6-10 lbs per shearing |
| Growth Rate | Faster growth, larger body | Slower growth, smaller frame |
| Use | Wool production, meat | Premium wool production |
| Hardiness | High, adaptable | Moderate |
| Lifespan | 8-12 years | 7-10 years |
Overview: Rambouillet vs Merino Sheep
Rambouillet sheep, derived from the Spanish Merino, are known for their larger size and adaptability to various climates compared to the traditional Merino breed. Rambouillet wool is finer and longer, making it highly valued in the textile industry for softness and strength. Both breeds excel in wool quality, but Rambouillet sheep offer improved hardiness and meat production.
Origin and History of Rambouillet and Merino
Rambouillet sheep trace their origin to France, developed in the 18th century from Spanish Merino stock at the royal flock in Rambouillet, enhancing wool quality and adaptability. Merino sheep, originating from Spain during the Middle Ages, became prized for their fine wool, significantly influencing global sheep breeding practices. Both breeds share a strong genetic lineage, with Rambouillet representing an improved French adaptation of the original Spanish Merino.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Rambouillet sheep exhibit a fine, dense wool with a creamy white face and a robust body, characterized by a well-muscled frame and curved horns present in rams. Merino sheep are renowned for their exceptionally fine and soft wool, featuring a white face with minimal wool coverage and a more compact, less muscular physique, often without horns. The Rambouillet's heavier fleece weight and larger body size contrast with the Merino's finer fiber diameter and adaptability to diverse climates.
Wool Quality and Yield Differences
Rambouillet sheep produce fine wool with a fiber diameter averaging 18-22 microns, known for its softness and elasticity, making it highly sought after for luxury garments. Merino wool, typically finer with fiber diameters ranging from 17-24 microns depending on the strain, offers exceptional softness and superior crimp, which enhances its insulation properties. Rambouillet sheep generally yield more wool per shearing, approximately 8-10 pounds, compared to Merino's 6-8 pounds, balancing quality with higher fleece weight.
Temperament and Behavior Traits
Rambouillet sheep exhibit a calm and docile temperament, making them easier to handle in comparison to Merino sheep, which can be more flighty and skittish. Rambouillet are known for their adaptability and social behavior, often forming strong flock bonds that reduce stress during shearing and handling. Merino sheep, while highly valued for fine wool, tend to have higher sensitivity and require more experienced handling to manage their reactive behavior effectively.
Adaptability to Climate and Environment
Rambouillet sheep exhibit exceptional adaptability to diverse climates, thriving in both hot, arid regions and colder environments due to their fine wool and strong resilience. Merino sheep, while renowned for their superior wool quality, prefer temperate climates and can face challenges in extreme heat or humidity. Farmers often select Rambouillet for fluctuating environmental conditions, whereas Merino breeds are favored in stable, mild climates for optimal wool production.
Health and Disease Resistance
Rambouillet sheep exhibit strong resilience to common sheep diseases such as foot rot and parasitic infections, owing to their robust immune system and adaptability to varied climates. Merino sheep, while renowned for fine wool quality, often require more intensive management to prevent health issues like flystrike and internal parasites. Selecting Rambouillet breeds can enhance flock health and reduce veterinary costs due to their superior disease resistance in diverse environmental conditions.
Breeding and Reproduction Performance
Rambouillet sheep exhibit superior reproductive efficiency with higher lambing rates and better maternal instincts compared to Merino sheep, enhancing flock productivity. Their adaptability to diverse environments supports consistent breeding cycles and improved lamb survival. Merino sheep offer exceptional wool quality but generally show lower fertility and slower breeding intervals than Rambouillet breeds.
Economic Value and Market Demand
Rambouillet sheep command higher market value due to their superior wool quality, characterized by fine, soft fibers sought after in luxury textile markets, enhancing their economic appeal. Merino sheep, while also prized for high-quality wool, often have broader global demand, driving steady market prices and diverse commercial opportunities. Economically, Rambouillet's dual-purpose traits--meat and wool--offer increased profitability compared to Merino's primary wool focus, influencing breed selection based on regional market priorities.
Suitability for Hobbyists and Pet Owners
Rambouillet sheep offer a hardy, adaptable breed known for fine wool and gentle temperament, making them ideal for hobbyists and pet owners seeking manageable livestock. Merino sheep provide exceptional fine wool but require more attentive care and environment control, suited for those dedicated to wool production. Both breeds serve distinct purposes, with Rambouillet favored for ease of handling and Merino prized for premium fleece quality.
Rambouillet vs Merino for Sheep Breed Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com