Heritage breed chickens possess genetics that promote slower growth, natural mating, and better adaptability to varied environments, making them ideal for sustainable farming. Hybrid chickens are selectively bred for rapid growth, high egg production, and uniformity, often requiring controlled conditions to maintain health and productivity. Choosing between heritage and hybrid genetics impacts flock resilience, flavor quality, and long-term farming practices.
Table of Comparison
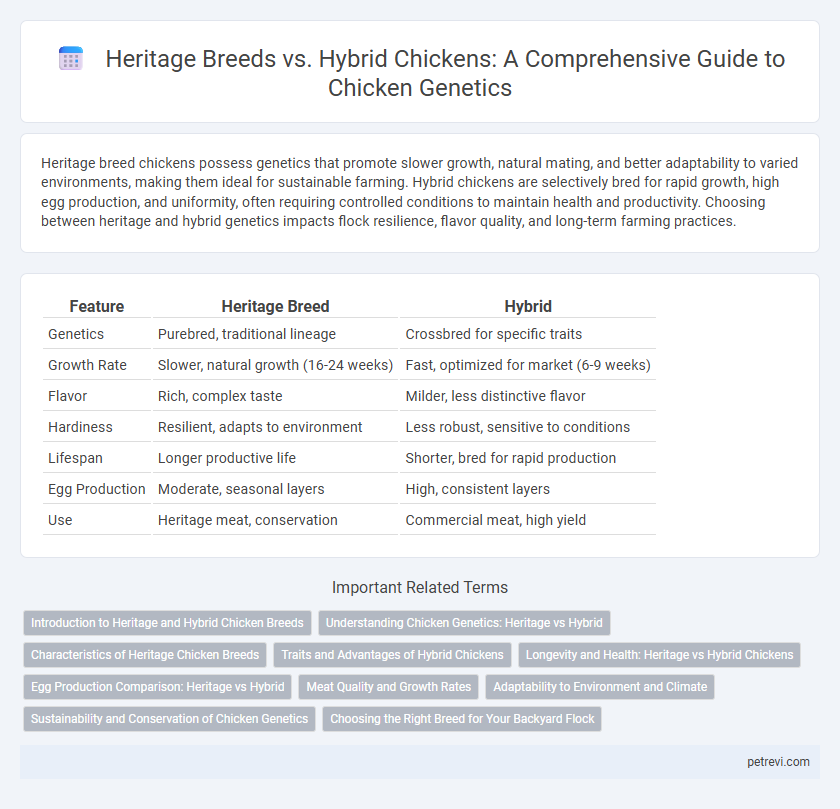
| Feature | Heritage Breed | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | Purebred, traditional lineage | Crossbred for specific traits |
| Growth Rate | Slower, natural growth (16-24 weeks) | Fast, optimized for market (6-9 weeks) |
| Flavor | Rich, complex taste | Milder, less distinctive flavor |
| Hardiness | Resilient, adapts to environment | Less robust, sensitive to conditions |
| Lifespan | Longer productive life | Shorter, bred for rapid production |
| Egg Production | Moderate, seasonal layers | High, consistent layers |
| Use | Heritage meat, conservation | Commercial meat, high yield |
Introduction to Heritage and Hybrid Chicken Breeds
Heritage chicken breeds are traditional poultry varieties known for their genetic diversity, robust health, and ability to thrive in natural environments without intensive human intervention. Hybrid chickens result from selective breeding aimed at maximizing specific traits such as rapid growth, high egg production, and feed efficiency, often compromising genetic diversity and long-term sustainability. Understanding the genetic distinction between heritage and hybrid chickens is essential for poultry farmers seeking a balance between sustainability, productivity, and breeding goals.
Understanding Chicken Genetics: Heritage vs Hybrid
Heritage breed chickens possess stable genetics passed down through generations, maintaining traits like longevity, natural foraging, and adaptability to local environments, which contribute to biodiversity and sustainability in poultry farming. Hybrid chickens result from crossbreeding different purebreds to enhance production traits such as rapid growth, higher egg yield, and feed efficiency, but their genetic uniformity can reduce resilience and breeding potential. Understanding the genetic distinctions between heritage and hybrid chickens is crucial for selecting breeds that align with specific farming goals, whether for sustainability, meat quality, or commercial production.
Characteristics of Heritage Chicken Breeds
Heritage chicken breeds exhibit slow growth rates, strong foraging abilities, and robust immune systems, which contribute to their adaptability and longevity. These breeds maintain genetic diversity with purebred lineage, preserving traits such as natural brooding behavior and resilience to local climates. Unlike hybrids, heritage chickens provide superior flavor and texture in meat and eggs due to their traditional breeding and natural rearing conditions.
Traits and Advantages of Hybrid Chickens
Hybrid chickens exhibit enhanced traits such as rapid growth, higher feed efficiency, and increased egg production compared to heritage breeds. These genetics result from crossbreeding selected for specific advantages like disease resistance and uniformity in size and behavior. Hybrid chickens provide commercial producers with consistent performance and cost-effective meat and egg yields.
Longevity and Health: Heritage vs Hybrid Chickens
Heritage breed chickens possess superior longevity and robust health traits due to their natural genetic diversity and slower growth rates compared to hybrid chickens, which are selectively bred for rapid growth and high productivity. Heritage breeds often exhibit stronger immune systems and resilience to diseases, leading to a longer productive lifespan, whereas hybrids tend to have shorter lifespans and greater susceptibility to health issues. Choosing heritage breeds supports genetic preservation and sustainable poultry farming with enhanced animal welfare outcomes.
Egg Production Comparison: Heritage vs Hybrid
Heritage breed chickens typically produce 150-200 eggs per year, reflecting their slower growth and natural reproductive cycles, whereas hybrid chickens are selectively bred to lay 250-300 eggs annually, maximizing commercial egg production. The egg quality from heritage breeds often features richer yolks and stronger shells, preferred in niche markets for flavor and nutritional value. Hybrid chickens dominate large-scale egg production due to their high yield and feed efficiency, but their genetic diversity is limited compared to the robust genetics of heritage breeds.
Meat Quality and Growth Rates
Heritage breed chickens, known for their slow growth rates and genetic diversity, offer superior meat quality with richer flavor and firmer texture compared to hybrid chickens. Hybrid chickens are selectively bred for rapid growth and high feed efficiency, often reaching market weight in half the time of heritage breeds but may have less flavorful and less textured meat. The genetic makeup of heritage breeds supports sustainability and resilience, while hybrids prioritize production efficiency at the cost of traditional meat characteristics.
Adaptability to Environment and Climate
Heritage breed chickens exhibit superior adaptability to diverse environmental conditions and climates due to their long-term natural selection and genetic diversity, making them resilient to temperature fluctuations and local diseases. Hybrid chickens, developed for rapid growth and high productivity, often lack this environmental adaptability, requiring controlled conditions to thrive and facing higher susceptibility to stress and illness. Choosing heritage breeds supports sustainable farming by enhancing genetic robustness and climate resilience in poultry populations.
Sustainability and Conservation of Chicken Genetics
Heritage breed chickens possess genetic diversity crucial for sustainability and conservation efforts, offering traits like disease resistance and adaptability that enhance long-term flock resilience. In contrast, hybrid chickens are selectively bred for rapid growth and production efficiency, often narrowing genetic variation and increasing vulnerability to environmental changes. Preserving heritage breeds supports biodiversity, safeguards unique genetic traits, and maintains ecosystems' balance critical for sustainable poultry farming.
Choosing the Right Breed for Your Backyard Flock
Heritage breed chickens possess stable genetics, offering traits like natural hardiness, superior foraging ability, and strong maternal instincts, making them ideal for sustainable backyard flocks. Hybrid chickens are bred for rapid growth, high egg production, and uniformity, providing efficiency and convenience for those prioritizing maximum yield. Selecting the right breed depends on balancing genetic traits such as longevity, productivity, and adaptability to your environment and flock management style.
Heritage Breed vs Hybrid for Chicken Genetics Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com