Estrus synchronization in cows allows for precise control over breeding schedules, improving reproductive efficiency and herd management compared to natural estrus cycles, which are unpredictable and vary across individual animals. Synchronization techniques utilize hormonal treatments to induce ovulation simultaneously within a group, facilitating planned artificial insemination or natural breeding. This method reduces the interval between calving and conception, enhancing overall productivity and genetic advancement in the herd.
Table of Comparison
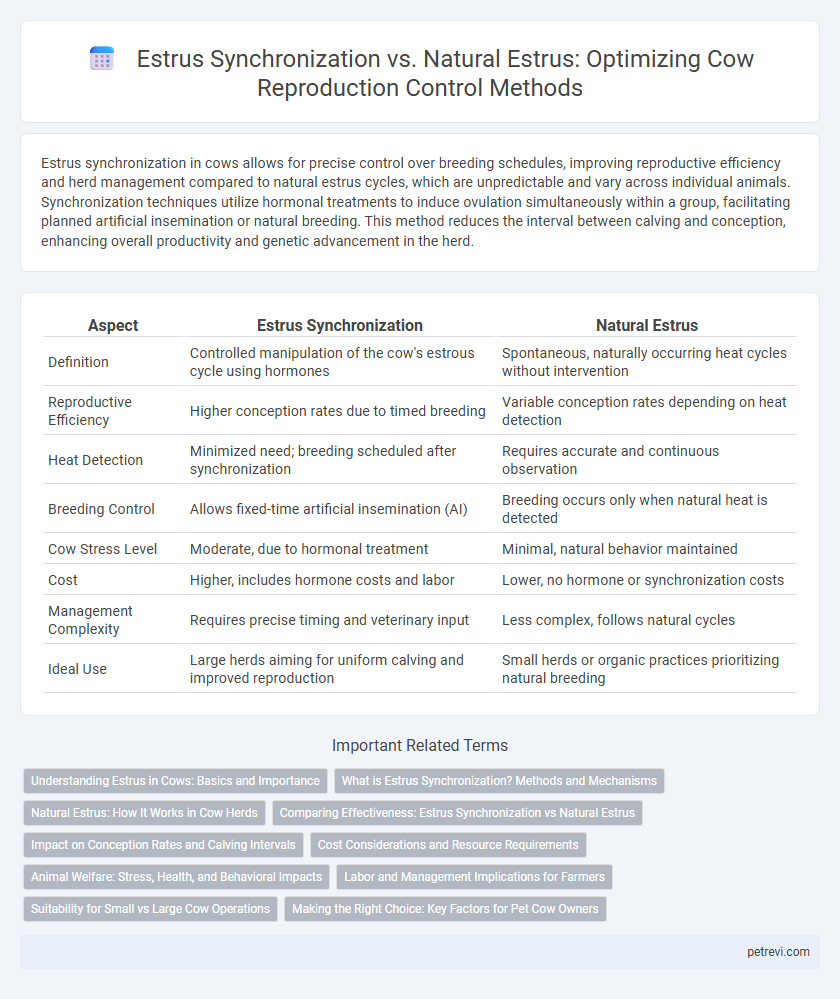
| Aspect | Estrus Synchronization | Natural Estrus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled manipulation of the cow's estrous cycle using hormones | Spontaneous, naturally occurring heat cycles without intervention |
| Reproductive Efficiency | Higher conception rates due to timed breeding | Variable conception rates depending on heat detection |
| Heat Detection | Minimized need; breeding scheduled after synchronization | Requires accurate and continuous observation |
| Breeding Control | Allows fixed-time artificial insemination (AI) | Breeding occurs only when natural heat is detected |
| Cow Stress Level | Moderate, due to hormonal treatment | Minimal, natural behavior maintained |
| Cost | Higher, includes hormone costs and labor | Lower, no hormone or synchronization costs |
| Management Complexity | Requires precise timing and veterinary input | Less complex, follows natural cycles |
| Ideal Use | Large herds aiming for uniform calving and improved reproduction | Small herds or organic practices prioritizing natural breeding |
Understanding Estrus in Cows: Basics and Importance
Estrus synchronization in cows allows precise control over reproductive cycles by aligning ovulation across a herd, improving breeding efficiency compared to natural estrus detection, which depends on observing behavioral signs that may be missed. Understanding the hormonal and physiological changes during estrus is crucial, as it influences timing for artificial insemination and increases conception rates. Effective estrus management enhances overall herd fertility, reduces calving intervals, and maximizes productivity in cattle operations.
What is Estrus Synchronization? Methods and Mechanisms
Estrus synchronization in cows involves manipulating hormonal cycles to induce simultaneous heat periods, enhancing reproductive management efficiency. Common methods include administering prostaglandins, progesterone-releasing devices, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) to regulate ovulation timing. These hormonal treatments optimize breeding schedules, improve artificial insemination success rates, and facilitate better herd fertility control compared to natural estrus detection.
Natural Estrus: How It Works in Cow Herds
Natural estrus in cow herds relies on the cow's inherent reproductive cycles, typically occurring every 21 days when the cow is in heat. Farmers observe behavioral signs such as mounting, restlessness, and vocalization to identify estrus and time breeding accurately. This method leverages the cow's biological rhythm without hormonal intervention, promoting natural fertility patterns and reducing management costs.
Comparing Effectiveness: Estrus Synchronization vs Natural Estrus
Estrus synchronization in cows enhances reproductive efficiency by allowing timed artificial insemination, increasing conception rates compared to natural estrus detection, which relies on variable heat signs and can delay breeding. Controlled synchronization protocols such as CIDR or Ovsynch optimize herd fertility management by reducing calving intervals and improving uniformity in offspring. Natural estrus, while cost-effective and less labor-intensive, often results in lower reproductive performance due to missed or irregular estrus detection.
Impact on Conception Rates and Calving Intervals
Estrus synchronization in cows significantly improves conception rates by enabling timed artificial insemination, reducing the variability of natural estrus cycles. This controlled breeding approach shortens calving intervals by ensuring more precise timing of insemination, leading to consistent reproductive performance. Natural estrus detection often results in missed or delayed breeding opportunities, extending calving intervals and lowering overall fertility efficiency.
Cost Considerations and Resource Requirements
Estrus synchronization in cows demands higher upfront costs due to hormone treatments and veterinary supervision, while natural estrus relies on lower expenses but requires extended observation periods and labor. Resource allocation for synchronization involves investments in synchronization protocols, skilled personnel, and controlled housing, contrasting with the minimal intervention and lower infrastructure needs in natural estrus detection. Overall, synchronization offers improved reproductive efficiency at a premium, whereas natural estrus remains cost-effective with increased time and labor commitments.
Animal Welfare: Stress, Health, and Behavioral Impacts
Estrus synchronization in cows allows for controlled breeding schedules but may increase stress due to hormonal interventions compared to natural estrus detection. Natural estrus supports cow autonomy and typical behaviors, promoting better health and reduced stress-related issues. Balancing reproduction control with animal welfare requires careful management of stress, behavioral changes, and overall health impacts linked to synchronization protocols.
Labor and Management Implications for Farmers
Estrus synchronization in cows streamlines breeding schedules, enabling farmers to plan labor more efficiently and reduce the time spent monitoring individual animals for natural heat cycles. This controlled reproductive management minimizes the variability of calving periods, facilitating better resource allocation and improved herd health monitoring. Natural estrus requires continuous observation, which can increase labor demand and unpredictability in herd management, impacting overall farm productivity.
Suitability for Small vs Large Cow Operations
Estrus synchronization offers precise control over breeding schedules, making it highly suitable for large cow operations aiming to optimize reproductive efficiency and reduce labor costs. Small cow operations may find natural estrus observation more practical due to lower expenses and simpler management requirements. Choosing the appropriate method depends on herd size, available resources, and desired reproductive outcomes.
Making the Right Choice: Key Factors for Pet Cow Owners
Estrus synchronization offers pet cow owners precise reproductive control, enabling planned breeding schedules and improved herd management compared to natural estrus cycles. Factors such as cost, labor intensity, and animal welfare significantly influence the decision, with synchronization requiring hormonal treatments while natural estrus depends on regular heat detection. Understanding behavioral signs, estrus duration, and reproductive goals ensures pet cow owners select the optimal method for efficient and humane reproduction control.
Estrus Synchronization vs Natural Estrus for Cow Reproduction Control Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com