Organic cow farming prioritizes natural feed, avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which promotes healthier soil and reduces chemical exposure for the animals. Conventional cow farming often relies on industrial feed and synthetic inputs to maximize production efficiency but may increase environmental and health risks due to chemical residues and antibiotics. Choosing organic methods enhances animal welfare and sustainability by minimizing pollution and supporting biodiversity in farm ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
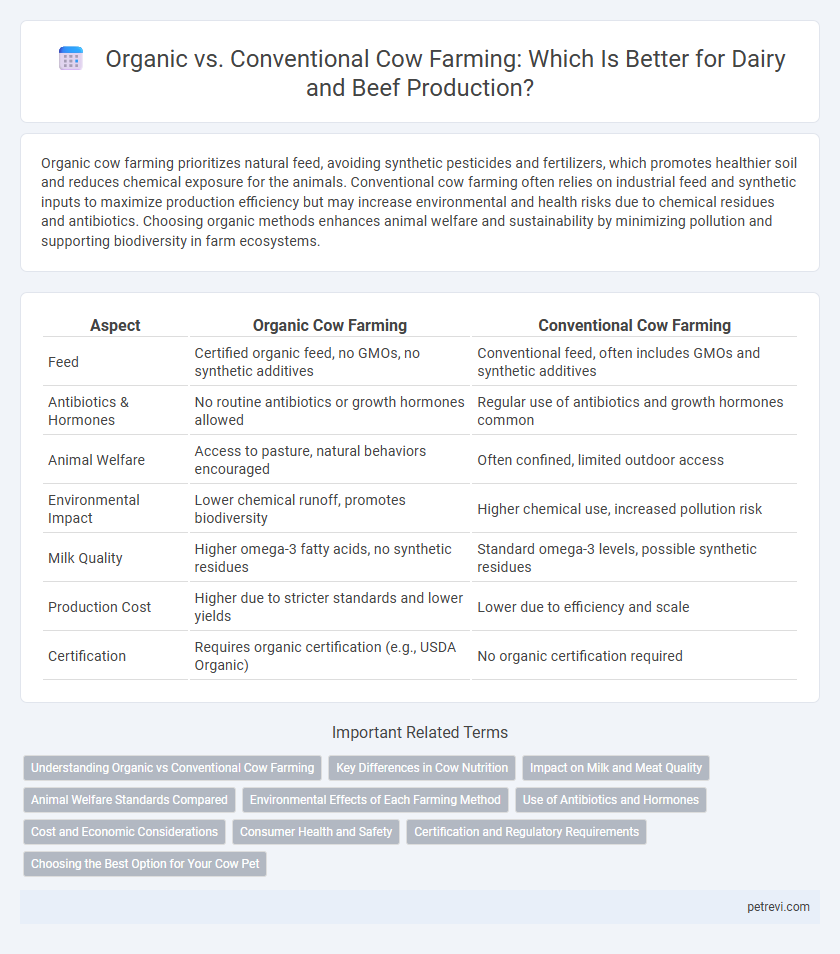
| Aspect | Organic Cow Farming | Conventional Cow Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Feed | Certified organic feed, no GMOs, no synthetic additives | Conventional feed, often includes GMOs and synthetic additives |
| Antibiotics & Hormones | No routine antibiotics or growth hormones allowed | Regular use of antibiotics and growth hormones common |
| Animal Welfare | Access to pasture, natural behaviors encouraged | Often confined, limited outdoor access |
| Environmental Impact | Lower chemical runoff, promotes biodiversity | Higher chemical use, increased pollution risk |
| Milk Quality | Higher omega-3 fatty acids, no synthetic residues | Standard omega-3 levels, possible synthetic residues |
| Production Cost | Higher due to stricter standards and lower yields | Lower due to efficiency and scale |
| Certification | Requires organic certification (e.g., USDA Organic) | No organic certification required |
Understanding Organic vs Conventional Cow Farming
Organic cow farming emphasizes natural feed, no synthetic hormones or antibiotics, and promotes animal welfare through pasture access and rotational grazing. Conventional cow farming often utilizes grain-based feed, growth hormones, and preventive antibiotics to increase productivity and control diseases. Understanding these differences helps consumers make informed choices about environmental impact, animal welfare, and product quality.
Key Differences in Cow Nutrition
Organic cow farming prioritizes pasture-based diets rich in diverse grasses and legumes, enhancing nutrient absorption and promoting natural digestive health. Conventional cow farming often relies on grain-heavy feed containing synthetic additives, which can impact metabolic efficiency and alter milk composition. These nutritional differences influence animal welfare, milk quality, and environmental sustainability in dairy production.
Impact on Milk and Meat Quality
Organic cow farming often results in milk and meat with higher omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants compared to conventional methods, due to access to organic feed and pasture grazing. Conventional farming typically relies on grain-based diets and antibiotics, which can affect the nutritional profile and raise concerns about antibiotic residues. Studies indicate organic milk contains more beneficial nutrients like conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), enhancing both milk and meat quality.
Animal Welfare Standards Compared
Organic cow farming adheres to stricter animal welfare standards, including access to outdoor pasture, natural diets, and prohibiting the use of synthetic hormones and antibiotics. Conventional cow farming often relies on confined feeding operations and routine antibiotic use, which can stress animal health and well-being. Studies indicate organic practices promote better behavioral expression and lower incidence of disease, reflecting higher welfare outcomes compared to conventional methods.
Environmental Effects of Each Farming Method
Organic cow farming minimizes environmental impact by avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which reduces soil and water contamination. Conventional farming often leads to higher greenhouse gas emissions due to intensive feed production and manure management practices. Organic methods promote biodiversity and improve soil health, fostering long-term ecosystem sustainability compared to conventional systems.
Use of Antibiotics and Hormones
Organic cow farming strictly prohibits the use of synthetic antibiotics and growth hormones, relying on natural remedies and preventive care to maintain herd health. Conventional cow farming often uses antibiotics to promote growth and prevent disease, which can contribute to antibiotic resistance and residue concerns in dairy and meat products. Hormone use in conventional systems aims to increase milk production and weight gain but raises consumer health and environmental impact debates.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Organic cow farming generally incurs higher costs due to expensive organic feed, stringent certification processes, and limited use of synthetic inputs, impacting overall profitability. Conventional cow farming benefits from lower feed costs, higher stocking densities, and more intensive production practices, leading to increased short-term economic efficiency. Market demand for organic dairy products, however, can command premium prices that may offset the elevated operational expenses in organic systems.
Consumer Health and Safety
Organic cow farming eliminates synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, and hormones, reducing consumers' exposure to potentially harmful residues and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Studies indicate organic milk and beef typically contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which contribute to improved nutritional quality and health benefits. Conventional farming often relies on chemical inputs that may affect food safety, whereas organic practices promote animal welfare and sustainability, enhancing overall consumer confidence in product safety.
Certification and Regulatory Requirements
Organic cow farming requires adherence to strict certification standards such as USDA Organic or EU Organic, ensuring cows are raised without synthetic hormones, antibiotics, or genetically modified feed. Conventional farming typically follows less stringent regulatory frameworks focused on maximizing productivity, allowing the use of synthetic chemicals and growth enhancers. Certification processes for organic farms involve regular inspections, detailed record-keeping, and compliance with animal welfare and environmental sustainability criteria.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Cow Pet
Organic cow farming prioritizes natural feed, hormone-free growth, and cruelty-free practices, promoting healthier cows and potentially higher-quality milk. Conventional farming may offer cost-effective solutions with controlled environments and faster growth but often relies on synthetic inputs and antibiotics. Choosing the best option involves assessing your cow's health needs, your budget, and long-term sustainability goals.
Organic vs Conventional for Cow Farming Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com