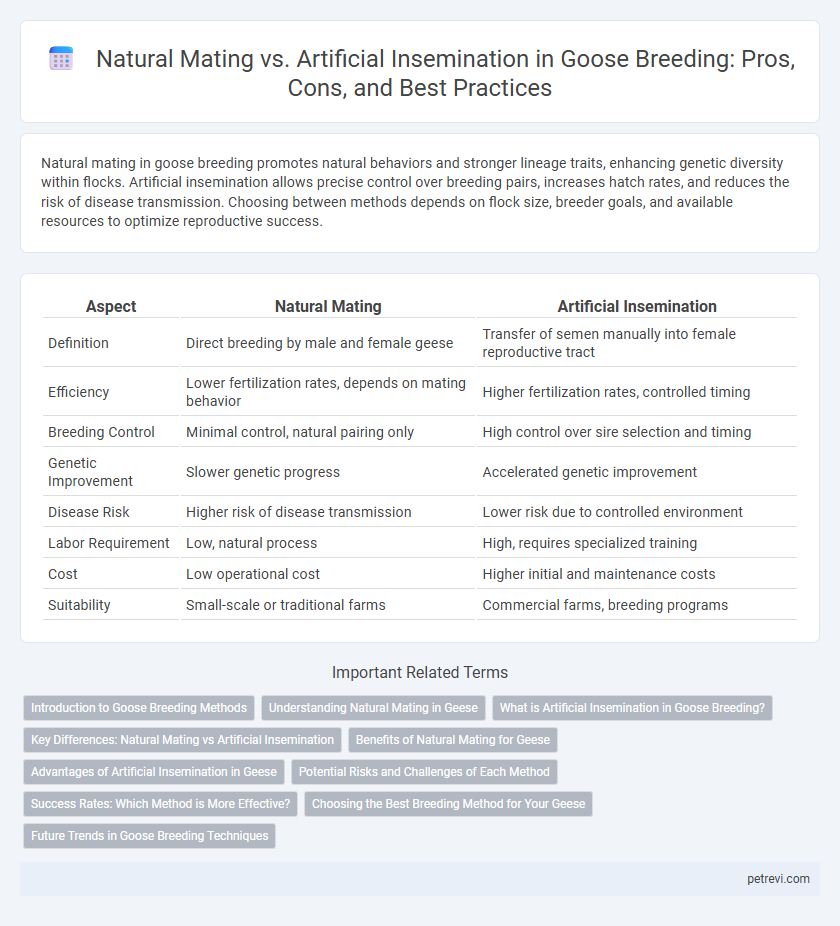
Natural mating in goose breeding promotes natural behaviors and stronger lineage traits, enhancing genetic diversity within flocks. Artificial insemination allows precise control over breeding pairs, increases hatch rates, and reduces the risk of disease transmission. Choosing between methods depends on flock size, breeder goals, and available resources to optimize reproductive success.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Natural Mating | Artificial Insemination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct breeding by male and female geese | Transfer of semen manually into female reproductive tract |
| Efficiency | Lower fertilization rates, depends on mating behavior | Higher fertilization rates, controlled timing |
| Breeding Control | Minimal control, natural pairing only | High control over sire selection and timing |
| Genetic Improvement | Slower genetic progress | Accelerated genetic improvement |
| Disease Risk | Higher risk of disease transmission | Lower risk due to controlled environment |
| Labor Requirement | Low, natural process | High, requires specialized training |
| Cost | Low operational cost | Higher initial and maintenance costs |
| Suitability | Small-scale or traditional farms | Commercial farms, breeding programs |
Introduction to Goose Breeding Methods
Goose breeding primarily involves two methods: natural mating and artificial insemination, each with unique advantages depending on flock size and breeding goals. Natural mating relies on direct pairing of male and female geese, promoting natural behavior and genetic diversity. Artificial insemination offers precise control over genetics and improved fertility rates, making it ideal for large-scale or selective breeding operations.
Understanding Natural Mating in Geese
Natural mating in geese involves direct interaction between male and female birds, ensuring natural selection and genetic diversity within the flock. This reproductive method allows geese to exhibit natural behaviors, which can improve fertility rates and offspring viability. Understanding the nuances of courtship rituals and mating season timing is crucial for optimizing breeding success in natural settings.
What is Artificial Insemination in Goose Breeding?
Artificial insemination in goose breeding involves collecting semen from a male goose and manually introducing it into the female's reproductive tract to enhance fertilization rates. This technique allows for controlled breeding schedules, genetic diversity, and improved hatchability by bypassing natural mating behaviors. It is particularly useful in managing valuable or genetically superior goose lines where natural mating may be inefficient or impractical.
Key Differences: Natural Mating vs Artificial Insemination
Natural mating in geese involves direct pairing and natural copulation, promoting natural behaviors and genetic diversity, but it may limit control over breeding seasons and sire selection. Artificial insemination allows precise timing, controlled genetic pairing, and increased hatchability rates, though it requires specialized skills and equipment. Understanding these key differences helps optimize breeding efficiency and improve flock quality in commercial and conservation programs.
Benefits of Natural Mating for Geese
Natural mating in geese ensures stronger genetic diversity and promotes natural behavioral patterns crucial for healthy offspring development. This traditional method supports better fertility rates and reduces the stress associated with handling during artificial insemination. Furthermore, natural mating fosters stronger pair bonds, enhancing the overall wellbeing and reproductive success of geese populations.
Advantages of Artificial Insemination in Geese
Artificial insemination in geese enables precise control over genetic selection, improving offspring quality and boosting productivity. It reduces disease transmission risks commonly associated with natural mating by minimizing physical contact between birds. This method also allows breeding during off-peak seasons, enhancing reproductive efficiency and flock management.
Potential Risks and Challenges of Each Method
Natural mating in goose breeding carries risks such as physical injury to birds, aggressive behavior leading to stress, and the potential for disease transmission through direct contact. Artificial insemination offers controlled breeding and reduces physical harm but presents challenges like the need for skilled technicians, potential fertility reduction due to improper semen handling, and higher operational costs. Both methods require careful management to minimize health risks and optimize reproductive success in goose populations.
Success Rates: Which Method is More Effective?
Natural mating in goose breeding often results in higher fertility rates, with success rates typically ranging from 70% to 85%, due to natural behavioral cues and timing. Artificial insemination, while offering precise control over genetic selection and timing, generally achieves success rates between 60% and 75%, influenced by semen quality and insemination technique. Studies indicate that natural mating maintains a slight edge in overall reproductive effectiveness, though artificial insemination remains valuable for managing breeding programs and enhancing genetic diversity.
Choosing the Best Breeding Method for Your Geese
Natural mating in geese ensures genetic diversity and instinctual pair bonding, promoting healthier offspring and natural behaviors. Artificial insemination allows precise control over genetics, improves breeding efficiency, and increases hatchability rates by bypassing physical mating challenges. Selecting the best breeding method depends on flock size, genetic goals, and resource availability to optimize reproductive success and maintain flock health.
Future Trends in Goose Breeding Techniques
Future trends in goose breeding techniques emphasize integrating genetic selection with precision farming technologies to enhance reproductive success. Advances in artificial insemination methods, including improved semen preservation and automated insemination devices, aim to increase fertilization rates while reducing reliance on natural mating. Biotechnology applications such as genomic editing and hormone therapies are expected to revolutionize breeding efficiency and disease resistance in goose populations.
Natural Mating vs Artificial Insemination for Goose Breeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com