AI boars provide precise genetic selection and enhanced disease control, improving overall herd quality and reproductive efficiency. Natural service boars offer natural mating behavior and ease of management but carry higher risks of disease transmission and less control over genetics. Choosing between AI and natural service depends on farm goals, biosecurity, and desired genetic improvements.
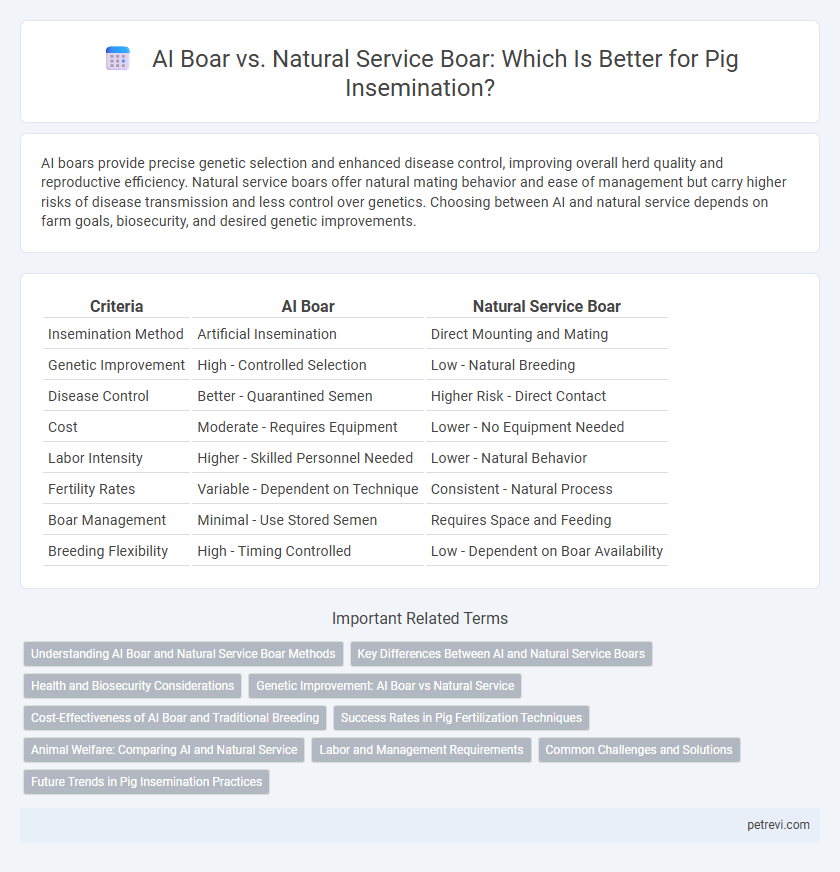
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | AI Boar | Natural Service Boar |
|---|---|---|
| Insemination Method | Artificial Insemination | Direct Mounting and Mating |
| Genetic Improvement | High - Controlled Selection | Low - Natural Breeding |
| Disease Control | Better - Quarantined Semen | Higher Risk - Direct Contact |
| Cost | Moderate - Requires Equipment | Lower - No Equipment Needed |
| Labor Intensity | Higher - Skilled Personnel Needed | Lower - Natural Behavior |
| Fertility Rates | Variable - Dependent on Technique | Consistent - Natural Process |
| Boar Management | Minimal - Use Stored Semen | Requires Space and Feeding |
| Breeding Flexibility | High - Timing Controlled | Low - Dependent on Boar Availability |
Understanding AI Boar and Natural Service Boar Methods
AI boar insemination involves using collected and processed semen from a selected boar to artificially inseminate sows, optimizing genetic traits and improving herd productivity. Natural service boar methods require direct mating between the boar and sow, allowing natural behavior and potentially lower technological costs but with less control over genetics. Both techniques impact reproductive efficiency, with AI offering precise timing and disease control while natural service maintains natural breeding dynamics.
Key Differences Between AI and Natural Service Boars
AI boars are selected based on superior genetic traits and health screening to enhance herd performance, while natural service boars rely on physical presence and natural breeding behavior. AI boars enable precise timing and controlled insemination, reducing disease transmission and increasing reproductive efficiency compared to natural service boars. Natural service boars provide continuous mating opportunity but often result in less genetic diversity control and higher management efforts.
Health and Biosecurity Considerations
AI boars significantly reduce health risks and biosecurity threats in pig insemination by minimizing direct contact and limiting disease transmission between animals, a critical factor in large-scale pig farming operations. Natural service boars, while effective for breeding, present higher risks of spreading pathogens such as porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) and swine influenza due to close physical interaction. Implementing AI with rigorous health monitoring and strict sanitation protocols enhances herd immunity and biosecurity management, promoting safer reproductive practices in swine production.
Genetic Improvement: AI Boar vs Natural Service
AI boars enable precise genetic improvement by allowing the selection of superior sires with desirable traits such as disease resistance, growth rate, and feed efficiency, thereby accelerating herd productivity. Natural service boars, while providing natural mating behavior, offer limited genetic diversity and slower progress in trait enhancement due to fewer controlled matings. Integration of AI in pig breeding maximizes genetic gain through optimized sire selection and broader dissemination of elite genetics across populations.
Cost-Effectiveness of AI Boar and Traditional Breeding
AI boars significantly reduce breeding costs by eliminating the need for maintaining multiple boars on-site, lowering feed, housing, and veterinary expenses compared to natural service boars. The use of AI technology enhances genetic selection, improving herd quality and productivity while minimizing the risk of disease transmission. Although initial setup for AI requires investment, the long-term cost-effectiveness and scalability make it a superior choice over traditional breeding methods in commercial pig production.
Success Rates in Pig Fertilization Techniques
AI boars demonstrate higher success rates in pig fertilization techniques due to precise semen quality control and optimized timing, enhancing sow conception efficiency. Natural service boars provide variable results influenced by individual boar fertility and mating conditions, often leading to less predictable pregnancy outcomes. Studies show that AI can achieve conception rates exceeding 85%, whereas natural service typically results in 70-80% success depending on management practices.
Animal Welfare: Comparing AI and Natural Service
Artificial insemination (AI) in pigs reduces the physical stress and injury risks associated with natural service by eliminating aggressive behavior and mounting conflicts between boars and sows. AI enables precise timing and controlled semen doses, improving reproductive efficiency while minimizing stress and promoting better overall welfare for both animals. Natural service may expose animals to higher injury rates and stress from social hierarchies and physical exertion.
Labor and Management Requirements
AI boar insemination significantly reduces labor intensity by eliminating the need for boar management, feeding, and housing, streamlining the breeding process through controlled scheduling. Natural service boars require constant care, supervision during mating, and regular health monitoring, increasing labor demands and complicating herd management. Employing AI boars enhances overall efficiency by minimizing human intervention and optimizing labor allocation in pig breeding operations.
Common Challenges and Solutions
AI boars in pig insemination face challenges such as sperm viability reduction during storage and precise timing for insemination to maximize conception rates. Natural service boars encounter difficulties including boar libido variability and the risk of physical injury during mating, which can affect reproductive efficiency. Solutions for AI involve optimized semen extenders and improved estrus detection technologies, while natural service management benefits from controlled boar rotation and health monitoring protocols.
Future Trends in Pig Insemination Practices
AI boars in pig insemination enable controlled genetic selection and increased biosecurity, driving efficiency in breeding programs compared to natural service boars. Emerging trends highlight integration of advanced data analytics and precision livestock farming technologies to optimize AI protocols and improve reproductive outcomes. The shift towards AI boars is expected to accelerate with development of automated semen collection and preservation technologies, enhancing scalability and genetic diversity in swine production.
AI boar vs Natural service boar for Pig insemination Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com