Sheep require a diet that supports their unique digestive system, where cud plays a crucial role by allowing them to regurgitate and re-chew fibrous feed for improved nutrient absorption. While feed provides essential nutrients and energy, the process of rumination with cud enhances digestion efficiency by breaking down tough plant materials. Balancing high-quality feed with sufficient forage promotes optimal rumen function and overall sheep health.
Table of Comparison
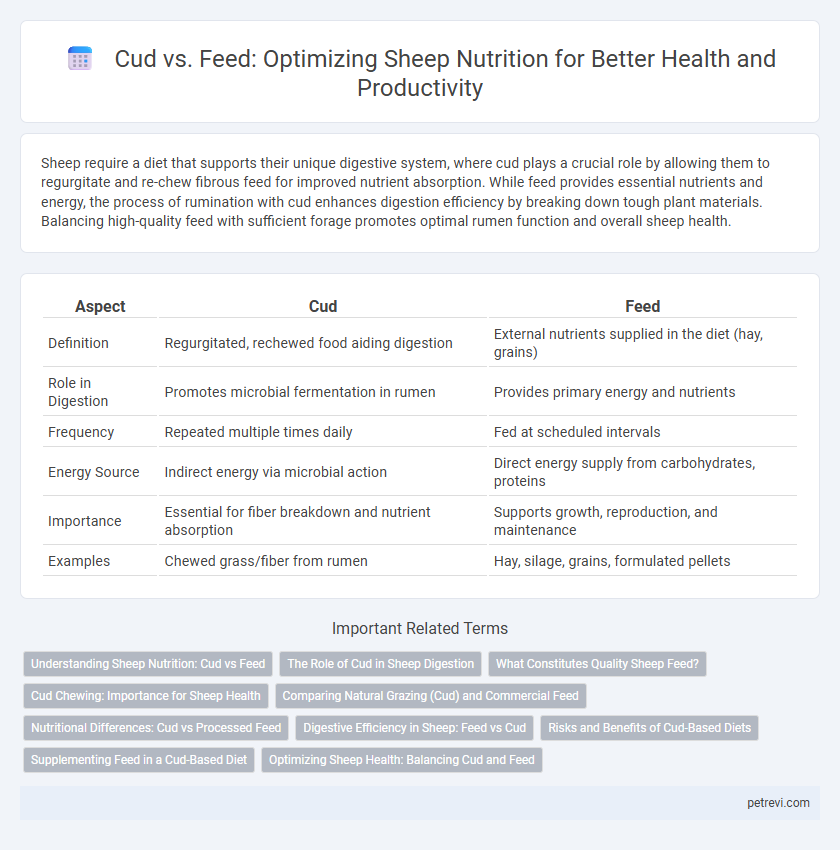
| Aspect | Cud | Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regurgitated, rechewed food aiding digestion | External nutrients supplied in the diet (hay, grains) |
| Role in Digestion | Promotes microbial fermentation in rumen | Provides primary energy and nutrients |
| Frequency | Repeated multiple times daily | Fed at scheduled intervals |
| Energy Source | Indirect energy via microbial action | Direct energy supply from carbohydrates, proteins |
| Importance | Essential for fiber breakdown and nutrient absorption | Supports growth, reproduction, and maintenance |
| Examples | Chewed grass/fiber from rumen | Hay, silage, grains, formulated pellets |
Understanding Sheep Nutrition: Cud vs Feed
Sheep nutrition relies heavily on the process of cud chewing, where partially digested feed is regurgitated and rechewed to enhance nutrient absorption and fiber breakdown. The feed, typically comprising grasses, hay, or specialized pellets, provides essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals necessary for sheep growth and maintenance. Understanding the interaction between cud chewing and feed quality is crucial for optimizing digestive efficiency and overall health in sheep management.
The Role of Cud in Sheep Digestion
Sheep rely on cud chewing to optimize nutrient absorption by breaking down fibrous plant material in their rumen. The regurgitated cud allows microbes to further digest cellulose, enhancing volatile fatty acid production essential for energy. This process improves feed efficiency and maintains rumen health, crucial for overall sheep nutrition and growth.
What Constitutes Quality Sheep Feed?
Quality sheep feed consists of nutrient-dense forage and grains that support rumen health and promote efficient cud chewing. High fiber content with balanced protein, vitamins, and minerals ensures optimal digestion and energy supply for sheep. Proper feed quality enhances microbial fermentation in the rumen, leading to better nutrient absorption and overall flock productivity.
Cud Chewing: Importance for Sheep Health
Cud chewing in sheep plays a critical role in optimizing digestion by allowing thorough breakdown of fibrous plant material, enhancing nutrient absorption and supporting overall health. This repetitive rumination process stimulates saliva production, which helps maintain rumen pH balance and prevents acidosis, a common digestive disorder. Effective cud chewing directly influences feed efficiency and promotes sustained energy levels essential for growth, wool production, and reproduction in sheep.
Comparing Natural Grazing (Cud) and Commercial Feed
Sheep derive essential nutrients from cud, which consists of partially digested forage that enhances fiber breakdown and promotes efficient nutrient absorption during natural grazing. Commercial feed provides a concentrated source of balanced vitamins, minerals, and proteins designed to supplement or replace natural forage, supporting faster growth and higher productivity in managed systems. Comparing these, natural cud-based nutrition fosters rumen health and sustainable digestion, while commercial feed offers precise nutrient control tailored to specific production goals.
Nutritional Differences: Cud vs Processed Feed
Cud, composed of partially digested fibrous plant material, provides sheep with essential volatile fatty acids, stabilizing rumen pH and supporting microbial protein synthesis critical for growth and wool production. Processed feed, often rich in concentrated carbohydrates and proteins, delivers rapidly available energy and specific nutrients like vitamins and minerals, enhancing productivity but requiring careful balance to avoid rumen acidosis. Understanding the nutritional differences between cud and processed feed helps optimize sheep health and performance through tailored feeding strategies that leverage natural rumen fermentation alongside supplement-based nutrition.
Digestive Efficiency in Sheep: Feed vs Cud
Sheep rely on rumination, where cud regurgitated and re-chewed, enhancing digestive efficiency by breaking down fibrous plant material more thoroughly than feed alone. The microbial fermentation in the rumen converts complex carbohydrates into volatile fatty acids, the primary energy source for sheep, making cud chewing essential for maximizing nutrient absorption. Efficient cud processing supports optimal feed utilization, promoting better growth rates and overall health in sheep.
Risks and Benefits of Cud-Based Diets
Cud-based diets in sheep nutrition enhance digestion by promoting rumination, which improves nutrient absorption and fiber breakdown, leading to better overall health and productivity. However, reliance on cud alone may increase the risk of bloat and acidosis if the balance of feed components is not properly managed. Integrating diverse feed with cud stimulation optimizes rumen function, reducing metabolic disorders and supporting sustainable sheep growth.
Supplementing Feed in a Cud-Based Diet
Supplementing feed in a cud-based diet enhances sheep nutrition by providing essential nutrients that rumination alone may not supply, such as concentrated energy, vitamins, and minerals. Effective supplementation supports optimal growth, milk production, and overall health by balancing the roughage from cud with high-quality feed ingredients like grains or protein-rich pellets. Precise feed management ensures microbial efficiency in the rumen while preventing nutrient deficiencies and promoting efficient feed conversion.
Optimizing Sheep Health: Balancing Cud and Feed
Effective sheep nutrition relies on balancing cud chewing and feed intake to optimize rumen function and nutrient absorption. Proper fiber from cud stimulates saliva production, which maintains rumen pH, while high-quality feed provides essential proteins and energy for growth and reproduction. Monitoring the ratio of forage to concentrate ensures sheep maintain optimal health, digestion efficiency, and overall productivity.
Cud vs Feed for Sheep Nutrition Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com