Hoof trimming and hoof paring are essential techniques in sheep foot care that prevent lameness and infections like foot rot. Hoof trimming involves clipping overgrown hooves to maintain proper shape and length, promoting healthy weight distribution and mobility. Hoof paring goes deeper by removing diseased or damaged hoof material, targeting infection control and encouraging tissue regeneration for optimal hoof health.
Table of Comparison
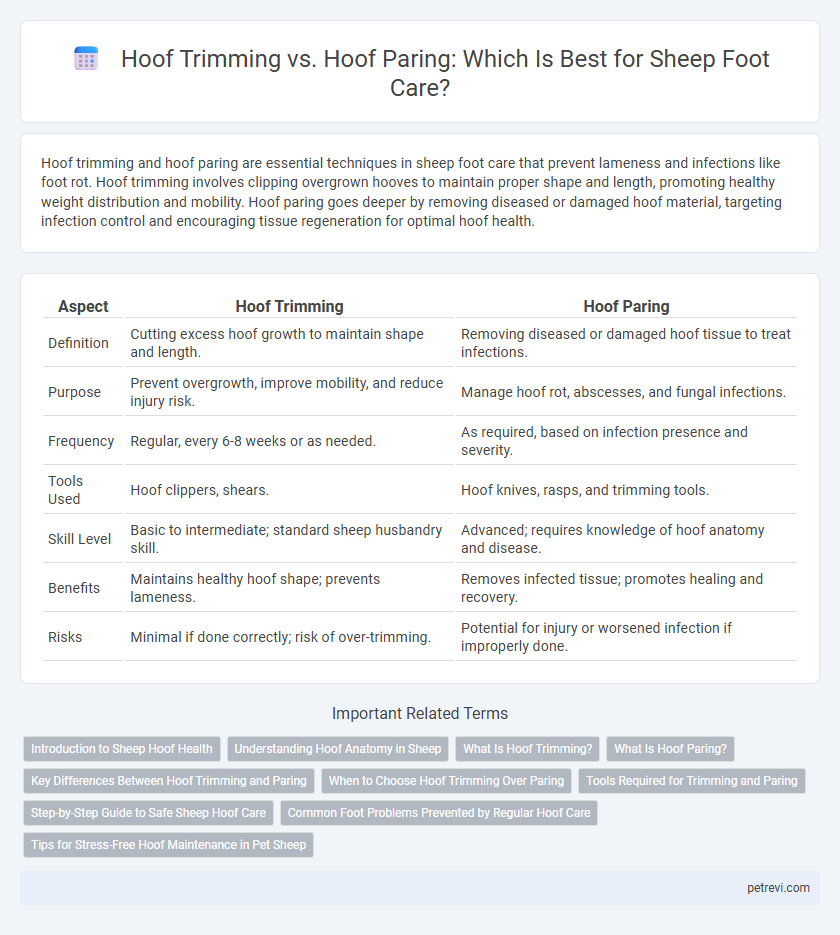
| Aspect | Hoof Trimming | Hoof Paring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cutting excess hoof growth to maintain shape and length. | Removing diseased or damaged hoof tissue to treat infections. |
| Purpose | Prevent overgrowth, improve mobility, and reduce injury risk. | Manage hoof rot, abscesses, and fungal infections. |
| Frequency | Regular, every 6-8 weeks or as needed. | As required, based on infection presence and severity. |
| Tools Used | Hoof clippers, shears. | Hoof knives, rasps, and trimming tools. |
| Skill Level | Basic to intermediate; standard sheep husbandry skill. | Advanced; requires knowledge of hoof anatomy and disease. |
| Benefits | Maintains healthy hoof shape; prevents lameness. | Removes infected tissue; promotes healing and recovery. |
| Risks | Minimal if done correctly; risk of over-trimming. | Potential for injury or worsened infection if improperly done. |
Introduction to Sheep Hoof Health
Sheep hoof health is essential for preventing lameness and infections such as foot rot, which can significantly impact flock productivity. Regular hoof trimming removes overgrown horn tissue, maintaining proper shape and reducing the risk of debris accumulation, while hoof paring involves more precise removal of diseased or damaged sole and horn. Proper hoof care balances trimming and paring techniques to promote healthy growth, prevent infection, and ensure sheep mobility and welfare.
Understanding Hoof Anatomy in Sheep
Sheep hooves consist of two main claws with a hard outer hoof wall and softer sole, requiring precise care to prevent infections and lameness. Hoof trimming involves removing overgrown hoof material to maintain natural shape, while hoof paring targets diseased or damaged areas to promote healing. Understanding the intricate anatomy of sheep hooves ensures effective foot care practices that support animal health and mobility.
What Is Hoof Trimming?
Hoof trimming in sheep involves the regular cutting and shaping of the hoof to maintain proper foot health and prevent overgrowth, which can lead to lameness and infections such as foot rot. This practice focuses on balancing the hoof wall, sole, and heel to promote natural wear and support optimal weight distribution. Proper hoof trimming is essential for sheep management, enhancing mobility and overall welfare.
What Is Hoof Paring?
Hoof paring in sheep foot care involves carefully removing diseased, overgrown, or damaged hoof material to restore healthy hoof shape and prevent infections like foot rot. This precise technique targets damaged areas while preserving healthy tissue, promoting better mobility and overall hoof health. Regular hoof paring supports early detection of foot problems and reduces the risk of lameness in sheep flocks.
Key Differences Between Hoof Trimming and Paring
Hoof trimming for sheep involves removing excess hoof wall and sole to maintain proper shape and prevent overgrowth, while hoof paring specifically targets diseased or damaged areas, such as infected or softened tissue. Trimming is a routine maintenance practice essential for healthy gait and weight distribution, whereas paring is a therapeutic procedure aimed at treating infections like foot rot or abscesses. Understanding the distinction between these techniques is crucial for effective sheep foot care and preventing lameness.
When to Choose Hoof Trimming Over Paring
Hoof trimming is preferred over hoof paring when maintaining regular foot health in sheep, especially to prevent overgrowth and reduce the risk of lameness. Trimming is sufficient for routine care and early signs of minor hoof issues, avoiding the deeper tissue exposure that paring entails. Hoof paring is generally reserved for severe hoof problems like advanced foot rot or abscesses requiring removal of diseased tissue.
Tools Required for Trimming and Paring
Hoof trimming for sheep requires specialized hoof trimmers or shears designed to cleanly cut overgrown hoof material, ensuring proper shape and preventing lameness. Hoof paring involves more precise tools like hoof knives and rasps to carefully remove diseased or damaged tissue and smooth the hoof surface. Both processes demand sharp, durable instruments to maintain sheep foot health and prevent infections such as foot rot.
Step-by-Step Guide to Safe Sheep Hoof Care
Sheep hoof care involves regular trimming and paring to prevent infections and lameness, with hoof trimming focusing on maintaining proper hoof length and shape, while hoof paring targets removal of diseased or overgrown tissue. Start by securely restraining the sheep, clean the hooves thoroughly using a hoof pick, then trim the outer edges with sharp hoof trimmers, and if needed, carefully pare away damaged areas using a hoof knife without cutting too deeply. Consistent inspection and proper technique ensure sheep maintain healthy hooves, reducing risks of foot rot and enhancing overall mobility.
Common Foot Problems Prevented by Regular Hoof Care
Regular hoof trimming prevents common foot problems in sheep such as foot rot, foot scald, and overgrowth-related lameness by maintaining proper hoof shape and length. Hoof paring targets specific diseased areas, effectively removing infected or necrotic tissue to halt the progression of bacterial infections like foot rot. Both practices are essential in sheep foot care to reduce the incidence of infections, improve mobility, and enhance overall flock health.
Tips for Stress-Free Hoof Maintenance in Pet Sheep
Regular hoof trimming removes overgrown hoof walls and prevents cracks, while hoof paring involves carefully shaping the sole to treat infections like foot rot in pet sheep. Stress-free hoof maintenance requires gentle handling, using proper tools such as sharp hoof knives, and performing care in a calm environment to keep sheep relaxed. Scheduling routine checks every 6-8 weeks ensures healthy hooves and reduces the risk of discomfort or lameness in pet sheep.
Hoof Trimming vs Hoof Paring for Sheep Foot Care Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com